Identifying Minerals
advertisement

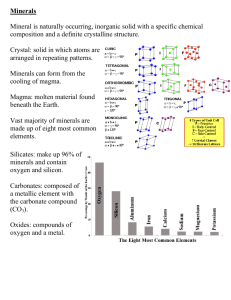
…the same type of mineral! They are examples of quartz!! There are over 3000 types of minerals in the Earth’s crust As you could see with the quartz, often times even the same kind of minerals can look very different Therefore, geologists (scientists who study minerals and rocks) often use several different tests to determine type of a mineral they have found! Color is obviously one of the most noticeable characteristics of a mineral, but it also the least reliable of all the characteristics The color of a mineral is often caused by tiny amounts of other elements or compounds inside For example, what people call amethyst is actually just quartz with iron in it! The way that a mineral reflects light from its surface is its luster The two types of luster are: - metallic - nonmetallic Metallic Luster Texture describes how a mineral feels to the touch. Minerals can range anywhere between glassy feeling, rough feeling, greasy feeling, and even soapy feeling! Talc has a soapy texture. Fluorite has a glassy texture. When a mineral is rubbed against a tile, it will leave behind a colored powdered streak on the tile Sometimes a mineral’s streak does not match the mineral’s external color For example, one way to tell the difference between pyrite (Fool’s gold) and real gold is by streak. Pyrite leaves a greenish-black streak while real gold leaves a yellow streak. Hardness Hardness is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched Geologists use Mohs scale to give minerals their hardness ratings Mineral Associations and Uses 1 Talc Talcum powder. 2 Gypsum Plaster of paris. Gypsum is formed when seawater evaporates from the Earth’s surface. 3 Calcite Limestone and most shells contain calcite. 4 Fluorite Fluorine in fluorite prevents tooth decay. 5 Apatite When you are hungry you have a big "appetite". 6 Orthoclase Orthoclase is a feldspar, and in German, "feld" means "field". 7 Quartz 8 Topaz The November birthstone. Emerald and aquamarine are varieties of beryl with a hardness of 8. 9 Corundum Sapphire and ruby are varieties of corundum. Twice as hard as topaz. 10 Diamond Used in jewelry and cutting tools. Four times as hard as corundum. The pattern of atoms will determine how a mineral will break A mineral that breaks relatively easily and evenly at angles is said to have cleavage Minerals that break with rough or jagged edges are said to have fracture Some minerals have unique properties For example, Iceland spar can create double images Some minerals react with hydrochloric acid and releases carbon dioxide (bubbles)