Biome Gallery Walk - Mr. Obiechefu's Life Science
advertisement
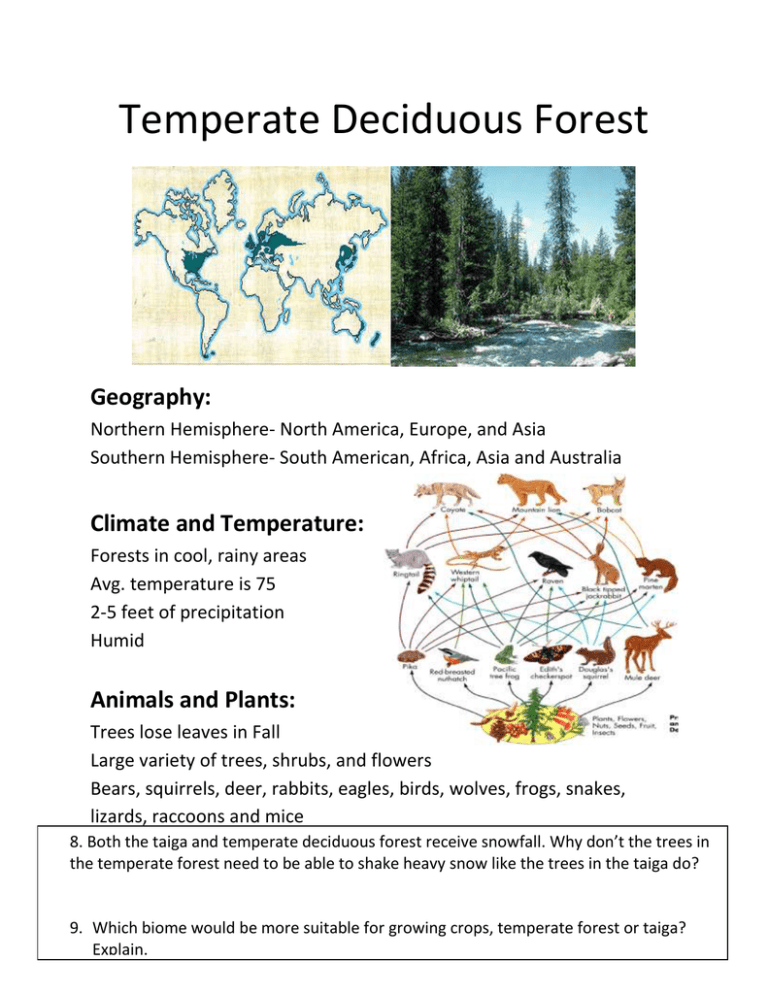
Temperate Deciduous Forest Geography: Northern Hemisphere- North America, Europe, and Asia Southern Hemisphere- South American, Africa, Asia and Australia Climate and Temperature: Forests in cool, rainy areas Avg. temperature is 75 2-5 feet of precipitation Humid Animals and Plants: Trees lose leaves in Fall Large variety of trees, shrubs, and flowers Bears, squirrels, deer, rabbits, eagles, birds, wolves, frogs, snakes, lizards, raccoons and mice 8. Both the taiga and temperate deciduous forest receive snowfall. Why don’t the trees in the temperate forest need to be able to shake heavy snow like the trees in the taiga do? 9. Which biome would be more suitable for growing crops, temperate forest or taiga? Explain. Desert Geography: One fifths of earth’s land Usually flat and sandy, but also in Antarctica Climate and Temperature: Less than 10 in of rain a year- very dry Extreme heat during day and cold during night Animals and Plants: Plants with small leaves- cacti and grasses Many nocturnal animals Coyotes, snakes, spiders etc. 10. What types of plants are able to grow in the desert? How can they live in such dry climates? 11. Evaluate whether an animal from a hot desert, such as a camel, could survive in a cold desert. What adaptations does the camel already have? What adaptations does it need? 12. What adaptations might humans need to make to survive in the desert? Tropical Rainforest Geography: Found in mountains, valleys and flat lands Usually near equator Climate and Temperature: Year around warmth Avg. of 50-260 in of rain High heat and humidity Animals and Plants: Most animal and plant diversity Monkeys, panthers, birds, frogs, iguanas, many insects Plants with large leaves 13. The tropical rainforest receives more precipitation than any other biome, yet has some of the poorest soil. How does this happen? 14. Both the rainforest and temperate deciduous forest have many trees and wild animals. How are they different? Taiga (Boreal Forest) Geography: Northern parts of North American, Europe and Asia South of tundra’s Larges biome on Earth Climate and Temperature: Cold harsh climate Low precipitation Animals and Plants: Deer, moose, wolves , rabbits, bears Plants are mostly pine trees- always green and never lose leaves 1. How are the adaptations between animals in the taiga and tundra similar? How are they different? 2. Would it be beneficial for organisms in the taiga to hibernate like organisms in the tundra? Why or why not? 3. Would it be beneficial for organisms in the taiga to be nocturnal like organisms in the desert? Why or why not? 4. A leopard has a thin, short coat of fur and primarily eats monkeys and other rainforest mammals. What adaptations might a leopard need to make in order to survive in the taiga? Tundra Geography: Always found near the North Pole Climate and Temperature: Cold, treeless area Little precipitation Coldest biome Animals and Plants: Arctic foxes, polar bears, wolves, owls Few plants due to frozen ground 5. What does it mean for an organism to have blubber? Why is this helpful for an animal living in the tundra? 6. Describe the fur an animal would need to survive in the tundra. 7. What is permafrost? What affect does permafrost have on the type of plants that can live in the tundra? Tropical Grasslands (Savanna) Geography: Flat or slightly hilly areas Located in mostly the southern hemisphere in South America, Europe, Australia and Africa Climate and Temperature: Windy, mostly dry area Animals and Plants: Many insects and large mammals such as wild cats, elephants, antelope Most all plants are tall deep rooted grasses 15. Both the savanna and tropical rain forest have similar temperatures, yet the plant and animal life found in each biome is very different. Why is this? 16. What adaptations might the plants and animals in the savanna have to make in order to survive the dry season? Temperate Grasslands Geography: Flat or slightly hilly areas Located in mostly the southern hemisphere in Central North America, South America, Europe, Australia and Africa Climate and Temperature: Winters are cold; summers are typically hot Animals and Plants: Large grazers such as bison and wild horses. There are many burrowing mammals as well such as prairie dogs in North America Most all plants are tall deep rooted grasses and forbs 17. The soil of temperate grasslands is nutrient rich. What factors in the environment are contributing to this nutrient rich soil base? 18. What type of industries benefit the most from biotic and abiotic factors that characterize the temperate grassland biome? Why? 19 a 19 b 19 c 19 d 19 e 19ff 19 #19 a – f Identify: 1. The name of each biome pictured in the graph 2. The Annual mean temperature range in degrees Celsius (⁰C). 3. The Annual mean precipitation range in centimeters (cm) Questions #21-35 Matching: Match each term with its correct definition. Answer Word Definition(s) 21. adaptation A. a large environmental area characterized by similar vegetation, temperature, or other environmental characteristics 22. biome B. the ability of an organism to change in response to its environmental surroundings in order to survive 23. canopy ______ C. the struggle between the organisms of an ecosystem to obtain the resources needed for survival 24. competition ______ D. the line that divides the earth into two equal parts, the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere, and over the course of a year receives the most amount of heat from the sun causing seasonal changes in weather to be less dramatic and almost non-exist 25. desert ______ E. the largest body of water on earth covering more than 70% of the surface with a salt content of 3% or greater 26. drought ______ F. one of the most biologically diverse biomes, characterized by standing water such as marshes, bogs, and swamps; high precipitation; and usually humid conditions 27. equator G. a biome characterized by extremely dry conditions, usually sandy with little to no vegetation 28. grassland H. the most widespread land-based biome on earth that contains mostly grass like vegetation with few to no trees, experiences seasonal changes in weather, and receives average amounts of rainfall 29. ocean I. a term used to describe land or soil that is permanently frozen thus unable to support vegetation growth 30. permafrost J. the term used to refer to moisture that falls to the earth's surface in the form of rain, snow, or sleet 31. precipitation K. a long period of time with little to no rainfall 32. rainforest ______ L. one of the sub-categories of the grassland biome characterized by a wet and dry season with moderate to significant tree growth but where the trees are too sparse to form a canopy 33. savanna ______ M. a biome characterized by dense tree growth with a thick, multilayered canopy, high amounts of precipitation, and an average temperature of 77 degrees Fahrenheit that doesn't vary more than about 5 degrees all year 34. tundra N. the natural, continuous cover provided by the branches and leaves of trees blocking out sunshine to ground level plants 35. wetlands O. the coldest biome on earth, characterized by no trees, a layer of permafrost under the top layer of soil, and low precipitation ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______