Project Management:
A Managerial Approach 4/e
By Jack R. Meredith and Samuel J. Mantel, Jr.
Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Presentation prepared by RTBM WebGroup
Project Management
A Managerial Approach
Chapter 4
Project Organization
Growth of Project Oriented
Organizations
There are many reasons for the rapid
growth, but most of them can be grouped
in four general areas:
Speed and market responsiveness have
become absolute requirements for successful
competition
The development of new products, processes,
or services regularly requires input from diverse
areas of specialized knowledge
Chapter 4-1
Growth of Project Oriented
Organizations
Four reasons for growth (cont.)
Rapid expansion of technological possibilities in
almost every area of enterprise tends to
destabilize the structure of organizations
A majority of senior managers rarely feel much
confidence in their understanding and control
of the activities in their areas
Chapter 4-2
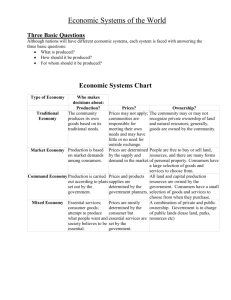
Types of Project Organizations
There are two fundamentally different ways
of organizing projects within the parent
organization
The project as part of the Functional
Organization
The project as a free-standing part of the parent
organization
A third type, called a Matrix Organization is a
hybrid of the two main types
Each has advantages and disadvantages
Chapter 4-3
The Project as Part of the
Functional Organization
Advantages of using the functional elements of the
parent organization as the administrative home for a
project include:
Maximum flexibility in the use of staff
Individual experts can be utilized by many different projects
Specialists in the division can be grouped to share
knowledge and experience
The functional division also serves as a base of technological
continuity when individuals choose to leave the project
The functional division contains the normal path of
advancement for individuals whose expertise is in the
functional area
Chapter 4-4
The Project as Part of the
Functional Organization
There are also disadvantages to housing the project
in a functional area:
The client is not the focus of activity and concern
The functional division tends to be oriented toward the
activities particular to its function
Occasionally, no individual is given full responsibility for
the project
There are often several layers of management between
the project and the client
There is a tendency to suboptimize the project
Chapter 4-5
Pure Project Organization
Advantages of a pure project organization:
The project manager has full line authority over the
project
All members of the project work force are directly
responsible to the project manager
When the project is removed from the functional division,
the lines of communication are shortened
When there are several successive projects of a similar
kind, the pure project organization can maintain a
permanent cadre of experts who develop skills in specific
technologies
Chapter 4-6
Pure Project Organization
Advantages of a pure project organization (cont.)
A project team that has a strong and separate identity and
develops a high level of commitment from its members
Because the authority is centralized, the ability to make a
swift decision is enhanced
Unity of command exists
Pure project organizations are structurally simple and
flexible, which makes them relatively easy to understand
and implement
The organizational structure tends to support a holistic
approach to the project
Chapter 4-7
Pure Project Organization
Disadvantages of a pure project organization:
Each project tends to be fully staffed which can lead to a
duplication of effort in every area from clerical staff to
technological support
There is a need to ensure access to technological
knowledge and skills that results in an attempt by project
managers to stockpile equipment and technical assistance
The functional division is a repository of technical lore, but
it is not readily accessible to team members of the pure
project team
Chapter 4-8
Pure Project Organization
Disadvantages of a pure project organization
(cont.)
Pure project groups seem to foster inconsistency in the
way in which policies and procedures are carried out
In a pure project organization, the project takes on a life
of its own
There tends to be concern among team members about
“life after the project ends”
Chapter 4-9
The Matrix Organization
The matrix organization is a combination of
functional and pure project
A matrix organization can take on a wide variety
of specific forms
“Project” or “strong” matrix organization most
resembles the pure project organization
The “coordination” or “functional” or “weak” matrix
most resembles the functional form
The “balanced” matrix lies in between the others
Chapter 4-10
The Matrix Organization
Rather than being a stand alone organization,
like the pure project, the matrix project is not
separated from the parent organization:
Chapter 4-11
The Matrix Organization
As with other organizational forms, the
matrix organization has its own unique
advantages:
The project is the point of emphasis
Because the project is overlaid on the functional
divisions, the project has reasonable access to
the reservoir of technology in all areas
There is less anxiety about what happens when
the project is completed
Chapter 4-12
The Matrix Organization
Advantages of a Matrix (cont.)
Response to client’s needs is as rapid as in the pure
project organization
Matrix management gives the project access to
representatives from the administrative units of the
parent firm
The matrix organization allows a better companywide balance of resources to achieve goals
There is a great deal of flexibility in precisely how
the project is organized within the matrix
Chapter 4-13
The Matrix Organization
There are also disadvantages to using the
matrix organization; most involve conflict
between the functional and project managers:
The balance of power between the project and
functional areas is very delicate
The movement of resources from project to
project may foster political infighting
Problems associated with shutting down projects
can be as severe as in a pure project organization
Chapter 4-14
The Matrix Organization
Disadvantages of a Matrix (cont.)
The division of authority and responsibility in a
matrix organization is complex, and uncomfortable
for the project manager.
Matrix management violates the management
principle of unity of command. Project workers
have at least two bosses, their functional heads
and the project manager.
Chapter 4-15
Mixed Organizational Systems
Divisionalization is a means of dividing a large
organization into smaller more flexible units
This enables the parent organization to
capture some of the advantages of small,
specialized organizational units while retaining
some of the advantages that come with larger
size units
Chapter 4-16
Mixed Organizational Systems
Pure functional and pure project organizations
may coexist in a firm
Chapter 4-17
Mixed Organizational Systems
Advantages of a mixed organization:
The hybridization of the mixed form leads to flexibility
The firm is able to meet special problems by appropriate
adaptation of its organizational structure
Disadvantages include:
Dissimilar groupings within the same accountability center
tend to encourage overlap, duplication, and friction
because of incompatibility of interests
Conditions still exist that result in conflict between
functional and project managers
Chapter 4-18
Choosing an
Organizational Form
Selecting the organizational interface between the
project and the firm is a difficult task
The choice is determined by the situation, but is also partly
intuitive
Must consider the nature of the potential project, the
characteristics of the various organization options, the
advantages and disadvantages of each, the cultural
preferences of the parent organization, and then make the
best compromise that can be made
Chapter 4-19
Choosing an
Organizational Form
Criteria for the selection of a project organization:
1. Define the project with a statement of the objective(s)
that identifies the major outcomes desired
2. Determine the key tasks associated with each objective
and locate the units in the parent organization that serve
as functional “homes” for these types of tasks
3. Arrange the key tasks by sequence and decompose them
into work packages
Chapter 4-20
Choosing an
Organizational Form
Criteria for the selection of a project organization
(cont.):
4. Determine which organizational units are required to
carry out the work packages and which units will work
particularly closely with which others
5. List any special characteristics or assumptions
associated with the project
6. In light of items 1-5, and with full cognizance of the
pros and cons associated with each structural form,
choose a structure
Chapter 4-21
The Project Team
To staff a project, the project manager works from
a forecast of personnel needs over the life cycle of
the project
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is prepared to
determine the exact nature of the tasks required to
complete the project
Skills requirements for these tasks are assessed and like
skills are aggregated to determine work force needs
From this base, the functional departments are contacted
to locate individuals who can meet these needs
Certain tasks may be subcontracted
Chapter 4-22
The Project Team
There are some people who are more critical to
the project’s success than others and should
report directly to the project manager or the
project manager’s deputy:
Senior project team members who will be having a
long-term relationship with the project
Those with whom the project manager requires
continuous or close communication
Those with rare skills necessary to project success
Chapter 4-23
Human Factors and the
Project Team
Meeting schedule and cost goals, without
compromising performance is a technical
problem, with a human dimension
Project professionals tend to be perfectionists
Pride in workmanship leads the team member to
improve (and thus change) the product
These changes cause delays in the project
Chapter 4-24
Human Factors and the
Project Team
Motivating Project Team Members:
The project manager often has little control over the
economic rewards and promotions of project team
members, but this does not mean he/she cannot
motivate members of the team
How are technical employees motivated?
Recognition
Achievement
The work itself
Responsibility
Advancement
Chapter 4-25
The chance to learn new skills
Human Factors and the
Project Team
Empowerment of project teams is also a
motivational factor:
1. It harnesses the ability of the team members to
manipulate tasks so that project objectives are met.
The team is encouraged to find better ways of doing
things
2. Professionals do not like being micromanaged.
Participative management does not tell them how to
work but given a goal, allows them to design their
own methods
3. The team members know they are responsible and
accountable for achieving the project deliverables
Chapter 4-26
Human Factors and the
Project Team
Advantages of Empowerment (cont.):
4. There is a good chance that synergistic solutions
will result from team interaction
5. Team members get timely feedback on their
performance
6. The project manager is provided a tool for
evaluating the team’s performance
Chapter 4-27
Interpersonal Conflict
The focus of conflict can often be related to the
stage in the project’s life cycle
When the project is first organized, priorities, procedures
and schedules all have roughly equal potential to cause
conflict
During the buildup phase, priorities become significantly
more important than any other conflict factor
In the main program phase schedules are the most
important cause of conflict followed by technical
disagreements
At the project finish, meeting the schedule is the critical
issue
Chapter 4-28
Interpersonal Conflict
Conflict and the Project Manager
Most of the conflict on project teams is the result of
individuals focusing on the project through the eyes of
their individual discipline or department
Conflict avoiders do not make successful project
managers
On occasion, compromise appears to be helpful, but
most often, gently confronting and resolving the conflict
is the method of choice, for a win-win situation
Chapter 4-29
Summary
There are various organizational structures
that can be used for projects including:
Projects within functional organizations, pure
project, matrix, and mixed organizational
structures
Selecting the appropriate project
organizational form is critical to the success
of the project
Chapter 4-30
Summary
A useful procedure for selecting an
organizational form is:
Identify the specific outcomes desired
Determine the key tasks to attain these outcomes
Sequence the key tasks
Determine which project subsystems will be assigned
which steps and which subsystems must closely
cooperate
Identify any firm or project characteristics
Consider all pros and cons, then make a decision
Chapter 4-31
Summary
Perfectionism, motivation, and conflict are often
the major behavioral problems facing the
project manager
Sources of project conflict are often priorities
and policies at first, schedule and technical
problems during the main phase, and schedule
and personal issues near termination
Chapter 4-32
Project Organization
Questions?
Chapter 4-33
Project Organization
Picture Files
Project Organization
Figure 4-1
Project Organization
Figure 4-2
Project Organization
Figure 4-3
Project Organization
Figure 4-4
Project Organization
Figure 4-5
Project Organization
Figure 4-7
Project Organization
Figure 4-8
Copyright © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights
reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work
beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United
States Copyright Act without the express written
permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request
for further information should be addressed to the
Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The
purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use
only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher
assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or
damages, caused by the use of these programs or from
the use of the information contained herein.
Project Organization
Table Files
Project Organization
Project Organization