Experience Maintenance
advertisement

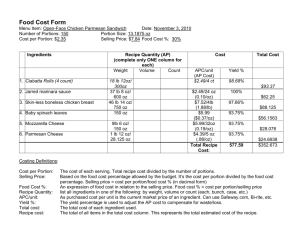
Experience Maintenance Why Experience Maintenance? Consider the cases - when a highly skilled employee leaves, he “takes his experience” with him - when new employees are inducted, they have to be trained manually - when the current project at hand is very similar to one that has been done before – do we need to do it all over again? Solution : Experience Maintenance! What is Experience Maintenance Formally, it is defined as …‘the acquisition, sharing and use of knowledge within organizations, including learning processes and management information systems’ What is Experience Maintenance In other words It is an information system that aids knowledge workers to create, integrate and reuse knowledge in an organization. What is the role of knowledge in IS, and IS development? Requirements Analysis Systems Design System Implementation Customer Forms Order Spec ERD Product Customer Order Scheduled Delivery Product Scheduled Delivery Salesperson Salesperson Architecture Update Marketing Authorize Credit Tables Order Entry Bill Customer VB Code Schedule Delivery Inventory Knowledge about world Refer Experience Base Reuse applicable experience Update Experience Base VC++ Code Types of Experience Explicit You can communicate Easy to formalize Savable on different media disembodied Implicit hard to communicate Hard to formalize Saved in brain embodied Experience Maintenance System converts implicit knowledge into explicit Data to Knowledge Very Valuable! Experience Maintenance Cycle Collect Identify Classify Create Organize/ Store Use/Exploit Access Share/ Disseminate Why Experience Maintenance? Product lifecycle becomes shorter Streamline operations and reduce costs by eliminating redundant or unnecessary processes Reduce training time Foster innovation by encouraging the free flow of ideas Improve customer service by streamlining response time Boost revenues by getting products and services to market faster Enhance employee retention rates by recognizing the value of employees' knowledge and rewarding them for it Main Areas of Experience Maintenance Capturing knowledge Storing knowledge Creating knowledge Distributing knowledge Sharing knowledge Using knowledge Transfer knowledge from the individual to the collective realm What does an Experience Management System Share Skills Experiences Reflections Lessons Memoirs Technical advice Experts intuition Case studies Best practices Methodologies INRECA INRECA supports the development of experience management applications by an experience management approach itself. Targeted at industrial experience management applications development Based on software engineering techniques and using these techniques to build/maintain experience management applications Applies Case-Based Reasoning to experience management application development INRECA INRECA Company 1 Company 2 Company 3 Company 4 … Company N … EMA 1 EMA 2 EMA 3 EMA 4 EMA N INRECA Product 1 Product 2 Company 1 EMA 1 Product 3 . . . Product N INRECA Methodology The INRECA Methodology (contd.) - Has an experience base containing specific experience on how to build experience management applications - This experience base is represented in the form of linked HTML documents. - The structure of these documents and the linking structure is derived from software process modeling Using this form (textual based) of representation results in: Increased flexibility Decreased accuracy INRECA Process Model The INRECA Process Model has 3 main components: 1. Process – Describes what should be done 2. Method – Describes how to do it 3. Product – Describes what is output of the process Input Product Complex Method Output Product Process Simple Method INRECA Experience Base INRECA Experience Base is organized on 3 levels of abstraction: 1. Common Generic Level The processes, products and methods in this level are common across a wide spectrum of different experience management applications. 2. Cookbook Level The processes, products and methods in this level are tailored for a particular class of applications (e.g. help desk, technical maintenance, product catalog). 3. Specific Project Level This level describes experience in the context of a single, particular project that has been carried out. INRECA Experience Base Common Generic Level Cookbook level Specific Project Level Building blocks & general purpose approach Recipe 1 Recipe 2 … Recipe N … App. 1 App. 2 App. 3 App. N INRECA Processes The INRECA methodology adapts techniques used in software engineering. As a result of this, the INRECA process modeling is very much similar to software process modeling. Like in software process modeling, the processes in INRECA are divided into 3 types: Technical processes Organizational processes Managerial processes INRECA Processes Technical processes These describe the development of the system and the required documentation. e.g. requirement analysis, testing, system design. Organizational processes These address those parts of the organization’s business process in which the newly developed system will be embedded. e.g. in building a help-desk system, organizational processes could be training help-desk personnel, updating help-desk system INRECA Processes Managerial processes The primary goal of these is to provide services for enacting the technical and the organizational processes. e.g. project planning, quality assurance and monitoring INRECA Descriptions The INRECA methodology contains descriptions of each of the processes, methods and products. There are 2 kinds of descriptions Generic Descriptions These describe the products, methods and processes in a way that is independent of a specific development project e.g. for a GUI development project, generic description would specify the general information the GUI should contain Specific Descriptions These elaborate processes, methods and products for a particular development project. e.g. for a GUI development project, specific description would be the GUI tool used, client GUI specification etc. INRECA Descriptions These descriptions are stored as HTML documents and the documents are linked hierarchically. There are totally 8 kinds of documents in the INRECA experience base 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Generic Generic Generic Generic Process Description Sheet Product Description Sheet Simple Method Description Sheet Complex Method Description Sheet Specific Specific Specific Specific Process Description Sheet Product Description Sheet Simple Method Description Sheet Complex Method Description Sheet INRECA Process Description Sheet INRECA Reuse The INRECA Reuse Procedure 1. Characterize New Project 2. Recipe Available? 3a.Analyze Process From Recipe 3b. Select Similar Specific Project 3c.Develop Project Plan by Reuse 4a. Analyze Process From Common Generic Level 4b. Develop Project Plan by Combining Processes 5. Enact Project & Record Project Trace INRECA Reuse 1. Identify the application area of the experience management project. 2. Identify if an appropriate recipe is available. 3. a) An appropriate recipe is available. The process model contained in this recipe must be analyzed. b) Analyze project descriptions on specific project level. If a match is found, the reusability is analyzed. c) Develop a project plan for the new project based on the process model from the selected recipe. INRECA Reuse 4. a) The set of processes described at the generic level are analyzed in the light of the new project to identify those processes that are important. b) Based on the selected processes, a new project plan must be assembled. 5. Execute the project by enacting the project plan. Document the experience during the enactment of the project. Maintaining INRECA The INRECA Maintenance Procedure 6. Analyze project trace 7. Add specific project 8. Create or update Recipe 9. Update Generic Level Maintaining INRECA 6. Analyze all the information collected about the project and identify the actually enacted processes. 7. Document the project by creating a specific project description and add to the specific project level of INRECA experience base. 8. If the project falls under an existing recipe, update the recipe if deviations from the original plan have been noticed. Else, create a new recipe. 9. Any new generic processes, methods or products identified in the above steps that are of generic interest are added to the common generic level. Open issues in experience maintenance Expressiveness of modelling concepts • Knowledge conversion, learning • Authority, ownership, location • Viewpoints, scenarios, time, dynamics Analysis and design techniques Qualitative and quantitative reasoning Tools, visualization Reusable design knowledge, patterns Usage methodologies Some Companies Using Experience Maintenance Systems Benetton General Electric National Bicycle Netscape Ritz Carlton Agro Corp Frito-Lay Dow Chemical Outokumppu Skandia Switzerland Steelcase 3M Analog Devices Boeing Buckman Labs Chaparral Steel Ford Motor Co Hewlett-Packard Oticon WM-data McKinsey Bain & Co Chevron British Petroleum PLS-Consult Skandia AFS Telia Celemi Skandia WM-data Buckman Labs IBM Pfizer WM-data Affaersvaerlden Hewlett-Packard Honda PLS-Consult Xerox Matsushita Summary What we’ve seen about experience maintenance… What is it? Why do wee need it? What does it do? How does an organization benefit from it? The working of INRECA – an experience maintenance/development system