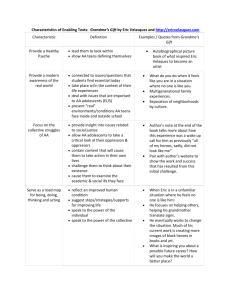
A Strategic Dependency Model
advertisement

Agenda Session 1 – Introduction December 13, 14:30-16:30 • Motivations • Basic concepts – The Strategic Dependency Model – The Strategic Rationale Model • More Examples – Software process modelling – Software architecture – Business redesign • Homework 1 © Eric Yu 2001 2 © Eric Yu 2001 The intentional structure of a software process • What goals does an actor want others to achieve? • What tasks does an actor want others to perform? • What resources does an actor want others to furnish? • The intentional structure of a software process ismodelled as a network of intentional dependencies among actors – the 3 actor dependency model. © Eric Yu 2001 Understanding a software process • The “whys” can be traced to motivations, goals, and interests of different participants/ stakeholders in the software process. © Eric Yu 2001 4 Modelling the intentional structure of a (simple) software process 5 © Eric Yu 2001 Roles, Agents, and Positions 6 © Eric Yu 2001 Software process example from IWSP 6/7 7 © Eric Yu 2001 Analyzing opportunities • Matching Wants and Abilities 8 © Eric Yu 2001 Analyzing vulnerabilities • Example of enforcement mechanism – Reciprocal dependency • Loop analysis 9 © Eric Yu 2001 Analyzing vulnerabilities • Example of assurance mechanism – Goal synergy or conflict • Node analysis 10 © Eric Yu 2001 Agenda Session 1 – Introduction December 13, 14:30-16:30 • Motivations • Basic concepts – The Strategic Dependency Model – The Strategic Rationale Model • More Examples – Software process modelling – Software architecture – Business redesign • Homework 11 © Eric Yu 2001 Modelling software architecture with i* Daniel Gross & Eric Yu. Evolving System Architecture to Meet Changing Business Goals: an Agent and Goal-Oriented Approach. ICSE-2001 Workshop: From Software Requirements to Architectures (STRAW 2001) May 2001. pp. 13-21. Daniel Gross & Eric Yu. From Non-Functional Requirements to Design through Patterns. Requirement Engineering. (2001) 6:18-36. 12 Agents at Design Level 13 © Eric Yu 2001 Design Reasoning 14 Goals: Daniel Gross & Eric Yu. Evolving System Architecture to Meet Changing Business Yu 2001 an Agent and Goal-oriented Approach.© Eric STRAW01 at ICSE 2001. Goals in Design Patterns The reasoning structure behind the Observer pattern Daniel Gross & Eric Yu. From Non-Functional Requirements to Design © Eric Yu 2001 through Patterns. Requirement Engineering. (2001) 6:18-36. 15 Agenda Session 1 – Introduction December 13, 14:30-16:30 • Motivations • Basic concepts – The Strategic Dependency Model – The Strategic Rationale Model • More Examples – Software process modelling – Software architecture – Business redesign • Homework 16 © Eric Yu 2001 Strategic Modelling for Enterprise Integration Eric Yu University of Toronto 14th World Congress International Federation of Automatic Control July 5-9, 1999 Beijing China 17 Consider one very successful enterprise... • important organizational and social aspects are missing in conventional models © Eric Yu 2001 18 A Strategic Dependency Model LEGEND actor © Eric Yu 2001 goal dependency task dependency resource dependency 19 softgoal dependency Wants and Abilities I can provide ... I want ... 20 © Eric Yu 2001 Some strategic dependencies between IKEA and its customers 21 © Eric Yu 2001 A Strategic Rationale Model 22 © Eric Yu 2001 Roles, Positions, Agents LEGEND agent position role • A Strategic Dependency model showing reward structure for improving performance, based on an example in [Majchrzak96] 23 © Eric Yu 2001 Agenda Session 1 – Introduction December 13, 14:30-16:30 • Motivations • Basic concepts – The Strategic Dependency Model – The Strategic Rationale Model • More Examples – Software process modelling – Software architecture – Business redesign • Homework 24 © Eric Yu 2001 Homework exercise: Work out a small i* modelling example from your own experience • At least 2 SD models (before vs. after, or as-is vs. to-be) and an SR model showing the reasoning behind the change. • Pick an area that you know well, or have thought about recently. • Characteristics to look for: – 2 or more actors (possibly with multiple roles) – Different strategic interests, possibly conflicting – Some freedom of action in operational processes 25 © Eric Yu 2001 Example areas (just to get your imagination going…) • E-business models – clicks vs. bricks, B2C, B2B • Educational systems, organizational structures – online vs. classroom learning • Healthcare – payment methods, prevention vs. treatment • Government/administrative processes – multi-step approval processes, can they be concurrent? • Financial services – linking to purchase patterns? • Food production, preparation, delivery, consumption – cultural preferences, differences. Eg. Pizza online? • Entertainment – personalized video programming? • Transportation – parking & traffic congestion • Publishing – e-books, e-journals… 26 © Eric Yu 2001 Once you have a basic model… (an as-is SD, and an initial SR) Consider whether these are applicable: – Producer/consumer relationships • What do they want from each other? – – – – Regulators, evaluators, … - why are they needed? Intermediaries, eg. Brokers Markets vs. hierarchies Roles vs. holders of roles For ideas about alternative SD’s, consider: – Eliminating or adding actors (eg. Intermediaries) – Shifting responsibilities between 2 actors (move up/down along means-ends chain) – Changing the dependency type (eg. Softgoal to hardgoal) – Reassigning roles to different agents/positions 27 © Eric Yu 2001 Further ideas about sources of disturbances prompting change • New technologies – Internet, mobile phone, GIS, web services, digital imaging, …. • New knowhow, techniques – preventive healthcare… • Migration of people, with knowhow, attitudes, resources – gain/loss • Changes in attitudes – eg. Notions of quality, safety… • Changes in supply/demand of important resources – eg. Oil, time – abrupt change or critical limits • Changes in legislation, policies, authorities, standards, dominant players, … 28 © Eric Yu 2001