Electrical notes
advertisement

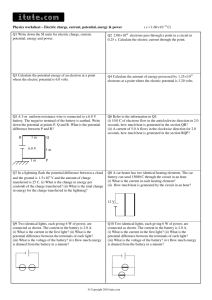
Automotive Electrical Notes PHS Auto 2 Basic notes for auto shop class study and refer back to your text book Electron theory the electrical phenomenon is produced by a flow of electrons from one area to another. Flow of electrons The flow of electrons is caused by having an excess number in one area, shortage in another surplus negative short supply positive Matter Anything that takes up space and has mass: solid, liquid or gas Molecule Smallest portion of matter and retain all original properties of the original matter, it is made up of atoms Atoms 100 + different types One molecule of water, is made up of one atom of oxygen, two atoms of hydrogen H20 Atom make up PROTON - positive charge + ELECTRON - negative charge NEUTRON - no charge (neutral) If there are more protons in the atom then electrons, it is a positive charged atom. proton and neutron in center; electrons orbit Size of atom ? Bound electrons Are in the inner orbits, Bound electrons are very difficult to remove from their orbit. Free electrons Outer orbits only, one, two or three electrons, are easily knocked out of their orbit Conductors Have 1-3 electrons in outer orbit, (Free electrons)easily knocked out of orbit. Materials such as silver, copper, aluminum, gold make good conductors. Semi-Conductors 4 electrons in outer orbit Not a good conductor Not a good insulator Non conductors Insulators, 5 or more electrons in outer orbit, glass, ceramics, plastics, rubber, fiber, porcelain, paper and wood are common Insulators. Hard to knock the electrons out of orbit if they have a strong magnetic pull to the protons in the nucleus of the atom. Current Movement of free electrons through a conductor current flow is measured in amperes(Amps). Must have shortage of electrons at one end, surplus at other one electron does not go the whole distance moves and bumps others. Voltage (electromotive force, EMF) Pressure differential causes current to flow, this pressure is known as voltage Voltage is a measure in volts with voltmeter. Resistance Caused by electrons bumping into other atoms, a poor conductor has greater resistance than a good conductor. Poor conductors will heat up (like a heater). Larger conductors (wire size) offers less resistance then a smaller one, Resistance is measured in ohms Current will flow in the one path with least resistance. Current will flow from negative to positive, negative has surplus of electrons, positive has short supply. Which way does it flow ? Ask the experts Circuits Must have a power source. A load (something to operate such as a light bulb or motor) Wiring for path of electron flow (Conductor) Switch Circuit protection Thanks Kevin http://www.autoshop101.com/ Series circuit, only one path for current to flow Series Circuit Parallel circuit, more than one path for current to flow, current flows through all units at once. Parallel Circuit Series parallel, combination of both circuits. Series Parallel Circuit Problems Open circuit, Wire is broken Short to ground, Wire is touching ground Short to voltage, wire is touching a hot wire. Load device is on even though switch is off. High resistance, current is being slowed by corrosion or a poor connection Car frame Acts as a ground wire, some cars like a corvette have to run ground wires because of fiberglass body Ground symbol: Ohms law Amperes = I - Intensity Volts = E - Electromotive force Ohms = R - Resistance to find E = IxR I = E/ R R = E/ I E IXR Ohms laws For Auto Techs Some Auto Techs will use the following Amperes = A - Amps Volts = V - Volts Ohms = R - Resistance to find V = AxR A = V/ R R = V/ A V AXR M, m, K, μ Prefix Symbol Factor Numerically Name giga G 109 1 000 000 000 billion Mega M 106 1 000 000 million kilo k 103 1 000 thousand centi c 10-2 0.01 hundredth milli m 10-3 0.001 thousandth micro μ 10-6 0.000 001 millionth nano n 10-9 0.000 000 001 billionth Magnetism Materials that have this are called Magnets Some are Natural Some are made Magnetic Domains These small sections of a magnet must all line up to be a strong magnet. If not, they will cancel each other out and the piece of metal will be unmagnetized Lines of Force Leave north pole, enter south Unlike poles attract Like poles repel Left hand rule, know which way current flows, fingers point in direction magnetic field is moving Magnetic fields surround any conductor carrying an electrical current Lines of Force magnetic effects of parallel conductors, magnetic effects of conductors with current flowing in opposite direction, spark plug wires magnetic field in coils compared to single wire left hand rule for coils thumb points north soft iron core in coils, lines of force increase several hundred times Solenoid can be used to push or pull iron core if off set will be drawn into the middle Battery Electro Chemical Device 4 functions 1. provides electrical energy to start car. 2. provides electrical energy to ignition system 3. provides electrical energy to accessories when demands exceed alternators output 4. voltage stabilizer absorbs abnormal voltages created by electrical components Top post Side post side and top post A side and top post is becoming very common today because it will fit so many cars. Batteries a little history Up to 1955 most batteries were 6 volt General Motors started the move to 12 volts, Volkswagen was the last in 1966 to switch over. By 2010 some cars may have a 42V/14V System. Several problems lie in wait such as cost of the components. Life of batteries & arcing between components. Battery Construction Elements consist of two groups of plates one more negative than positive plates with insulated separators in between usually 9, 11, or 13 plates. 54, 66, or 78 total. case is made of hard rubber (rough service) or plastic (light service) one element in each cell, connected to the adjoining element, connected in series, each cell produces about 2.1 volts case is divided into 6 cells (12.6 volts) case is divided into 3 cells (6.3 volts) Electrolyte 64% water 36% Sulfuric acid H20-water 64% specific gravity 1.00 H2S04-sulfuric acid 36% specific gravity 1.835 - caution electrolyte 100% specific gravity 1.270 Charged positive plate negative plate electrolyte H2S04 pb02 pb lead peroxide lead Discharge oxygen and hydrogen form water, lead and sulfate form lead sulfate pbso4 H20 pbSo4 Charging send electrons through opposite way reversing the cycle Sulfated plates refer to plates harden with lead sulfate Slow long charge to correct sulfated plates sometimes can't Little brown particles floating around can short out battery (flakes off of the sulfated plates ) Batteries can freeze if discharged H2O is water Charging battery emits oxygen and hydrogen gas - can explode To replace add distilled water Battery types WET CHARGE shipped with electrolyte must charged during storage DRY CHARGE shipped empty manufacture gives forming charge dries the cell elements and seals it. If you keep moisture out it will remain fully charged for long time. When needed just add electrolyte Group size Batteries come in many different group sizes. A battery's group size simply determines it's length, width, height, and terminal configuration Will have a number like group 75,78 or 24 or 24F, 26, 34 Battery capacity 1) Plate size, the case same size, plates are different size Larger plates more amps 2) Number of plates 3) Amount of acid in electrolyte and battery additives increase the sulfuric acid content of battery Battery capacity rating Cold Cranking Amperes CCA most common “Number of amperes load of battery will maintain at 0 degrees Fahrenheit for 30 seconds without battery voltage falling below 7.2 volts” (1.2 volts per cell) Size of engine should be smaller than cold cranking ampere Do not be misled by CA that’s just cranking amps. It will give you a higher reading but it misleads you because it is tested at a higher temperature. Cranking amps are the numbers of amperes a lead-acid battery at 32 degrees F (0 degrees C) can deliver for 30 seconds and maintain at least 1.2 volts per cell (7.2 volts for a 12 volt battery). Recommended Minimum battery size 4-cylinder 400 CCA 6-cylinder 500 CCA 8-cylinder 575 CCA Battery checking visual Inspection Battery checking visual Inspection Cracked or leaking case liquid level, add water use distilled water preferred (No minerals) or ice melted out of a freezer Voltage can discharge across top from post to post Clean battery top and post and cables, battery hold downs visual Inspection Cleaning The Battery Mix baking soda and water to clean batteries Clean post and cable with a terminal brush or post cutter Coat all connections with grease or use a spray like NOCO NCP-2 Battery corrosion spray Battery leakage test Voltmeter – lead at negative post Voltmeter + lead drag across battery No voltage should be present anywhere if it is clean the battery. Battery Open Circuit Voltage Test Measure what the voltage is with the key off Find out it’s state of charge. It is a good starting point, should be at least 12.66 volts 12.66 = fully charged 12.4 = 3/4 charged 12.2 = 1/2 charged 12.0 = 1/4 charged Battery Terminals & Bolts Post or top terminal Side terminal L terminal used on import Marine Terminal Test This is the first step. Take a voltmeter DVOM (Digital volt ohm meter) Turn to DC Volts Hook up like picture on next page. Terminal Test This is just a voltage drop test done on the battery terminals. You must disable the ignition and crank over the engine. Should be under .2 volts. Make sure you do both terminals Positive & Negative Battery Drain test Battery Drain Key off Hook up a ammeter in series reading should not exceed the following 77 older cars .01 amps, 10 ma (milliamps) 78-85 .02 amps-.025 amps, 20-25 ma 1986 & newer .05 amps, 50 ma Testing specific gravity Hydrometer check before adding water fully charged battery should read 1.270 should not vary more than 50 points between cells if it does recharge and check again Maintenance free batteries are sealed, cannot get into some. No way to add water or check specific gravity. Charging batteries Clean up first Unhook cables - check liquid level Don't charge over 16 volts if plates are sulfated or if battery has been discharged for some time Slow charge for a long period 24 hours don't allow temperature to exceed 100 Never fast charge batteries Most batteries in cars are 12 volt with negative ground. 6 volt older cars and 18 wheelers may have positive ground SAFETY: do not allow battery acid to contact eyes skin or fabrics if you do flush with lots of water, and get teacher or medical help flush eyes for 15 minutes Jump starting cars positive to positive negative to negative Hook up negative cable last on car with dead battery on a good ground. Not on the battery. If sparks occur no Hydrogen to blow up battery date tags Did You Know Batteries Lose Power While Sitting on the Shelf? A battery can permanently lose some of its capacity when it's stored in a partly or fully discharged state. Periodic charging during storage can minimize the deterioration, but not all battery distributors and dealers do the necessary charging. That's why you may want to know how to read the date codes, which show when the product was manufactured, on a new product, to help you make sure you're really buying a fresh battery. So, how do you read a date code? Most Brands of Batteries JOHNSON CONTROLS, INC. - INTERSTATE BATTERIES, Motorcraft, East penn - Deka, GNB -Champion, Stowaway: The letters and numbers are on a sticker affixed to the battery or hot-stamped into the case cover along the top edges of the battery. The ship date codes begin with a letter: A stands for January, B for February and so on (some shipping codes skip the letter I, so it cannot be confused with the number 1. In those cases, J would represent September, K - October, L - November and M - December). The next digit is a number which represents the year the battery was shipped. Therefore, an A6 would mean the battery was shipped in January of 1996. Exceptions DELCO - Freedom, Voyager, and some Sears brands: The code dates are stamped on the cover, usually near the posts. The first character represents the year (0-9) and the second shows the month (A-M, skipping I). For example, 4CN1 would stand for 1994, March. EXIDE - Napa Legend, Edge, Power-Tron and Titan: The fourth or fifth character may be a letter code for the month and the following character a number code for the year (i.e. RO8F3B stands for June 1993) Last 3 pages © 2000 Interstate Battery System of America, Inc. Removing Batteries Always Disconnect the ground cable first. (Negative Cable on cars) Always hook up the ground cable last If you disconnect the positive first and touch ground you will have sparks. Hooking batteries in series Voltage goes up Hooking batteries in parallel Voltage stays the same amperage goes up Generator Electromagnetic device, produces electricity to run accessories and charge battery If wire is passed through magnetic field voltage is generated If passed in the opposite direction current flow reversed To increase volts and amps 1. increase strength of magnetic field 2. increase the speed wire moves through the magnetic field Basic AC operation current flows positive, negative Basic DC operation Current flows one way, accomplished by split ring Charging Indicators ammeter indicator light Voltage Monitor Alternator Alternators More efficient at lower speeds Lighter - aluminum construction Requires only 2 or 3 amps passing through slip rings compared to high amperage in D.C. generator Governs its own maximum current output Alternator Generators - moving conductor through stationary field to induce voltage Alternator - a permanent magnet is rotated inside a stationary conductor maximum voltage occurs when conductor cuts heaviest lines of force Parts of a Alternator The End Pictures from Sals Illustrations from Chrysler Scanned images from Modern Automotive Technology and John Deere