Forms of Business Ownership
advertisement

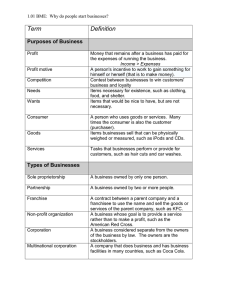
Ch. 5 Forms of Business Ownership Forms of Business Ownership 1. Sole Proprietorship owned by one person 2. Partnership Usually owned by two or more partners 3. Cooperative Owned by its workers or by members who buy from the business 4. Franchise One business licenses (allows) another to use its name, operating procedure, etc. Can have any form of ownership 5. Corporation Business is an artificial “person” created by law and owned by shareholders Sole Proprietorship Simplest form of business ownership One owner of a business Sole Proprietorship A business owned by one person – Small firms - Less than 50 people employed – Can easily be managed by owner – Few legal requirements – Sole control – Owner receives all profits & debts! More than 2/3 (66%) of U.S. businesses are operated as sole proprietorships – Most common form Requirements for Starting Knowledge of industry area – What type of small business is going to be successful and profitable? – What goods/services do consumers need? Equipment – For physical facility – For creating goods Business name? Permit or license? Little capital needed Sole Proprietorship Must account for income and expenses Pay taxes on profits – Tax advantage All income is taxed as a part of your personal income Business expenses can be used to reduce the income (tax write-offs) Sole Proprietorship Advantages Keep all the profits Make all the decisions You are your own boss (i.e Financial information can be kept secret. from competitors), but not the government Disadvantages Unlimited Liability Facing personal and financial risks and challenges on your own Borrowing money may be more difficult Huge time commitment Sole Proprietors Examples may include individuals who are: Artists Authors Carpenters Computer specialists Digital designers Ecotourism guides Farmers Industrial designers Photographers Web designers Chefs or Bakers Hair stylists Partnership More complex and needs a written agreement Owned by 2 or more people Partners must discuss and agree on issues such as: how much time and money each partner will put into the business How the profits will be shared Who will make decisions about different aspects of the business Who will manage the employees How the partnership might be ended Partnership Agreement All partners must sign the partnership agreement which includes: the name and location of the business Its purpose The amount of partner’s investment The way that the profits and losses are to be divided The duties and responsibilities of each partner The procedures for ending the partnership Partnerships Advantages Inexpensive to set up and organize ($1000) Two people to invest and it is easier to borrow from a bank More brains filled with different knowledge, experience, skills Shared responsibility eases stress and workload Share debt and can more easily take a vacation Disadvantages Unlimited liability Your personal assets (home, care etc may need to be used to pay off business debts) Conflicts between partners that can not be worked out Typical Partnerships Small independent service or retail businesses. bakeries, hair salons, flower shop, convenience store, landscaping or décor store, consignment shop, restaurants, retail stores,plumbers, electricians, mechanics, carpenters Professional Designations or Apprenticeships accountants, lawyers, doctors, veterinarians, mechanics, plumbers, electricians, carpenters Co-operatives Also called Co-ops Business owned and operated by a group of people with a strong common interest Start-up costs are shared among members Members own and control and make all the business decisions Examples of Coops Farmers Belong to producer co-ops Members bring crops to a central location to sell them Coop monitors the supply of the crop and controls its sale and price Farmers do not compete against each other or undercut other’s prices Farmers can combine to buy equipment and reduce costs and share expertise Example: Saskatchewan Wheat Pool sells products all over the world. Consumer Co-ops Join together to operate a business that provides them with goods and services Profits are divided among the members in proportion to the amount of business that each member does Examples: Omish Community Furniture Co-ops Credit Unions/ Caisses Populaires Financial co-ops Like banks but profits are distributed annually to their members Co-operatives Advantages Shared skills and experiences Less risk than for sole proprietor and partnership Liability is limited to the amount of your share in the capital of the coop Each member gets one vote – equal decision making and influence If you have more shares, you still get one vote, but more share of the profits Coops get discounts due to volume purchasing by many people Control sale and price of goods Disadvantages Individual members hesitant to invest more – only one vote Decision-making can be difficult because of multiple members Commitment of members may vary because some have more money at stake and some may take things more seriously than others Corporations A business owned by a number of people and operated under written permission from the sate in which it is located – Articles/Certificate of Incorporation Corporation’s Name Corporation’s Purpose Location Amount of stock to be issued Names of the Board of Directors Invisible, intangible and existing only in the eyes of the law (an individual) – Few compared to sole proprietorships Only 15%-20% of businesses are corporations Over 80% of all business is done by corporations Corporation Legal entity that exists independently of its owners who are the shareholders. Has the same rights and obligations under U.S. law as a natural person It can be found guilty of committing a crime Corporations Ability to: – Borrow or loan money – Buy and sell goods – Make contracts – Sue or be sued Ownership in a corporation: – Individuals (stockholders) can share in profits by buying shares of stock Represent ownership in the corporation Stockholders risk only the amount they invest Shareholders receive dividends (part of the profit earned by the corporation) Advantages of Corporations Limited liability – Only responsible for your personal investment in the company (your personal assets are not at stake) Unlimited life – The corporation will still survive with changing personnel (owners) Easy to transfer ownership – Through selling stock - ownership Skilled personnel – Highly trained and prepared Financial power Owners/Shareholders (Elect Board of Directors) Board of Directors (hire officers) STRUCTURE OF A CORPORATION Officers i.e. CEO (Chief Executive Officer) (set corporate objectives and hire managers) Managers (Supervise Employees) Employees Disadvantages of Corporations Difficult to form and operate Separate owners and managers – Varied opinions and strategies = +, - More complex requirements (govt.) Taxation – The corporation is taxed twice At the individual’s level with owning shares At the corporate level for the business entity The Franchise One of the fastest growing forms of business ownership The franchisor sells to another person (the franchisee) the rights to use the business name and to sell a product or service in a given territory. Available in many different sectors (fast food, wine, funeral homes) Franchise can be any form of business ownership (i.e. sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation) Franchise Agreement Written contract between the franchise seller and buyer Permit the franchisee to use the franchisor’s name, products, packaging Franchisor will specify how the franchise is to be operated, what products can be sold, the advertising, etc. Provide more than 1 million jobs directly, many more indirectly Annual sales of $100 billion Franchises Advantages Proven track record and nationally or internationally recognized name Personal ownership like a sole proprietorship Less stress in initial set up as most issues like process, products and location, equipment, décor are spelled out by the franchisor Disadvantages Expensive to buy Must pay royalties for your sales Little say in many of the business decisions If the franchisor fails, so does the franchisee Now it’s time to………. Go to kahoot.it