CHAPTER 2 Sampling and Sampling Plan
advertisement
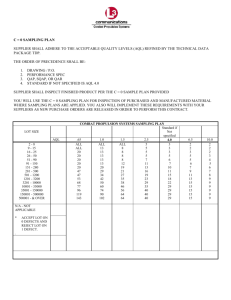
Laws of probability must be considered Producer’s risk rejecting a good batch Consumer’s risk accepting a bad batch determines the size and frequency of sample basis for accepting or rejecting a product requires 3 numbers N - number of items from where the sample is drawn n - a random sample drawn from a lot or batch C – acceptance number ; specified by AQL (acceptable quality level) determines the size and frequency of sample basis for accepting or rejecting a product requires 3 numbers N - number of items from where the sample is drawn n - a random sample drawn from a Example Lot or Batch sample defects N-50 lot or batch random C – acceptance Reject ornumber Accept Square root system formula: 𝑛= 𝑥= Example 𝑁+1 2𝑎 N-50 𝑛 = 50 + 1 𝑥= 2𝑎 = Military Government Standards Sampling (MILSTD-D Plan 105D) Adopted by the US Department of Defense Bell Telephone Engineers Laboratories - 1942 MASTER TABLE - Sample size, acceptance and rejection numbers NEED TO KNOW 1. AQL 2. SAMPLE CODE LETTER 3. TYPES OF SAMPLING Simple Double Multiple 4. INSPECTION SCHEMES Normal Tightened Reduced