Hardware2 - My university, Adelphi University
advertisement

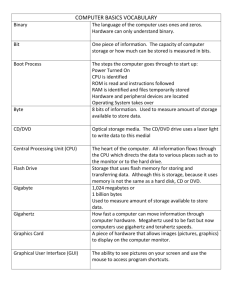
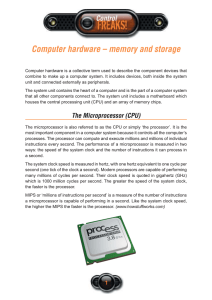
Hardware Basics Professor Pepper Major Objectives Microprocessor RAM ROM BIOS Motherboard Storage (CD, DVD, Hard Drive, Floppy, Zip, Jump, Tape) Expansion slots and ports Monitor Computer Desktop Shopping Dell website Comp USA Buy.com Microprocessor theory Clock time (x mhz, x ghz) Word size (x bit) Cache (l1 in chip; l2 close; l3 less close) Instruction set (categories:CISC, RISC; architectures: IA64,IA-32) Hyper-threading Many processors inside one processor Many separate processors on one board Manufacturer See moodle’s useful sites – hardware for updates Microprocessors on the market Intel i-3, i-5, i-7 Intel Core2 Duo; Extreme; Quad Pentium dual-core; Pentium 1- 4; Pentium M: laptop Celeron : budget AMD Athlon II X4 Phenom; Turion; Opteron : current Athlon X64 ; old premier Duron, Sempron : old budget Transmeta Crusoe – tablet Motorola Power PC – MAC no longer used in mac since OS 10.7 Microprocessor high needs 3-D animated computer games Desktop publishing Video editing Upgrading later is usually not cost-effective RAM Random Access Memory Lose it when computer off Like your head’s short term memory Main measurement is size (Gb, Mb) More than cache, much less than hard drive Speed (Mhz) Has a type: RDRAM; SDRAM; DDRRAM Expandable limits ROM BIOS & CMOS ROM BIOS Read only memory to start up your system No relation to CD-ROM CMOS Basic hardware path settings Programmable Very low battery needed Neither usually effect your purchase Motherboard Traffic cop Everything connects to it Hard disk to RAM to CPU via bus Motherboard chipset moves data faster 800 MHZ bus last year to Storage Introduction CD, DVD, Hard Drive, Floppy, Zip, Tape, flash drive Media – holds the data Device - writes and reads the data • Need drive bays • Need expansion slots Measures • • • • Versatility of drive Durability Speed Capacity Devices Device Size Comments Floppy 1.4 MB Easily damaged; Zip CD DVD Blu-Ray 750 MB 680 MB 8.5 GB 50GB Special drives HD-DVD 30GB Hard disk 80 GB++ Tape 4.7 single layer 100GB in prototype 45 GB prototype Not very portable; quick access; possible crash 200 GB++ Slow to read; quick to write; sequential Hard disk - Magnetic Notebook – Space Controller Serial ATA Ultra ATA – 2 x EIDE (UDMA data transfer) EIDE - old SCSI – fast, but expensive Memory Sudden Death – backup Speed (RPM) vs Access Time (MS) GOOD MOVIE or Hard Disk to RAM CD / DVD - Optical Access speed – 2x, 24x or kb/sec CD-ROM (read only) – just read CD-R(ecordable) – write once ;read by all CD-RW (read /write) – write a lot; read by few Same for DVD, but it has +/- formats DVD-RAM : video editing Blu-Ray (Sony, Samsung, Sharp, Thomson, Hitachi, Matsushita, Pioneer and Philips, Mistubishi and LG Electronics ; supported by Warner Bros.)* HD-DVD (AOD) (Toshiba and NEC; supported by Paramount and Universal ) * * Blue Violet Rays insteadof Red LINK TO INFO ON HD-DVD Solid State Storage USB Flash Card Key chain 32 – 512 mb Compact Flash Card Camera 8 mb – 1 gb Multi-media cards Digital camera 32-256 mb Secure Digital card Mp3 player 32-16 mb Smart Media (no controller needed, but not durable) 32-128 mb Pointing Devices Track pad Track ball Mouse Pointing stick (the red knob on a laptop) Expansion Slots ISA – old / modems PCI –graphics, sound, video, modem, NIC ACP – graphics PCMCIA – laptop Type I – memory Type II – modem, sound, nic Type III – hard drive or two of the other Expansion Ports Device plug Often on expansion card (in expansion slot) Types Serial – mouse or modem Parallel – printer; external drive USB – lots SCSI – disk drive; cd rom; scanner; tape backup IEEE (firewire) – video camera; DVD player VGA - monitor Monitors Graphics card to give a boost CRT (large, all angles, smaller screen, cheaper) / LCD (small, full screen) / Plasma (expensive) Resolution – dp (dot pitch –smaller is better) Viewable image size Color depth or bit depth (true color is 24) Graphics card Terminology www.webopedia.com www.hyperdictionary.com Many others Diagram Computer Desktop Shopping Dell website Comp USA Buy.com PC purchase exercise Textbook purchase exercise