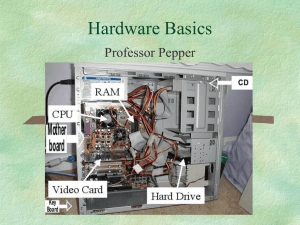
Hardware Vocabulary
advertisement
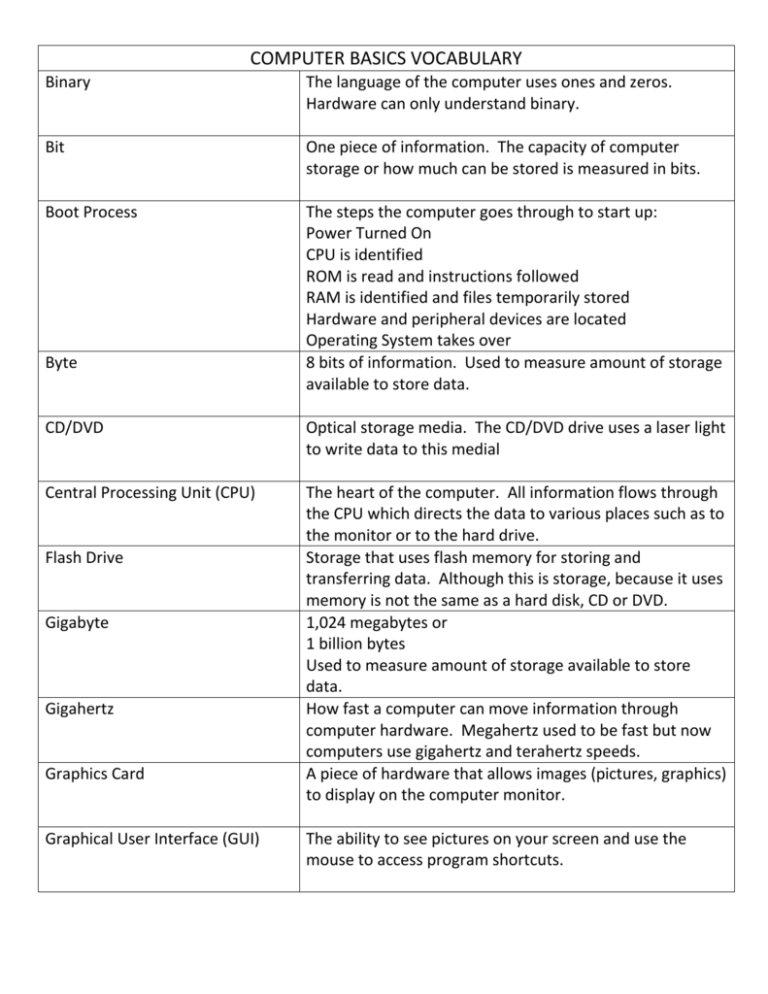
COMPUTER BASICS VOCABULARY Binary The language of the computer uses ones and zeros. Hardware can only understand binary. Bit One piece of information. The capacity of computer storage or how much can be stored is measured in bits. Boot Process The steps the computer goes through to start up: Power Turned On CPU is identified ROM is read and instructions followed RAM is identified and files temporarily stored Hardware and peripheral devices are located Operating System takes over 8 bits of information. Used to measure amount of storage available to store data. Byte CD/DVD Optical storage media. The CD/DVD drive uses a laser light to write data to this medial Central Processing Unit (CPU) The heart of the computer. All information flows through the CPU which directs the data to various places such as to the monitor or to the hard drive. Storage that uses flash memory for storing and transferring data. Although this is storage, because it uses memory is not the same as a hard disk, CD or DVD. 1,024 megabytes or 1 billion bytes Used to measure amount of storage available to store data. How fast a computer can move information through computer hardware. Megahertz used to be fast but now computers use gigahertz and terahertz speeds. A piece of hardware that allows images (pictures, graphics) to display on the computer monitor. Flash Drive Gigabyte Gigahertz Graphics Card Graphical User Interface (GUI) The ability to see pictures on your screen and use the mouse to access program shortcuts. Hard Disk Drive Hardware used to write information to disk. Hardware The physical components of the computer or the computer parts that you can touch with your hand. Icons A picture that allows access to a program. Input Devices Hardware that allows information to be put into the computer. Such as: keyboard, mouse, microphone, camera, etc. 1,024 bytes of information. Used to measure amount of storage available to store data. A hard disk drive uses magnets to store data so the hard disk drive is sometimes called “magnetic storage.” Old movies were recorded on VHS tapes. A popular computer data backup storage system is similar to VHS or video tapes which uses magnets to write the data to the tape. Used to store large amounts of data such as school records, income and property tax records, health records and more. Storage for files and program. The platter inside a hard drive, CDs, and DVDs are considered storage media. Kilobyte Magnetic Storage Mainframe Media Megabyte Megahertz Microprocessor Modem 1,048,576 bytes or 1,024 kilobytes Used to measure amount of storage available to store data. How fast a computer can move information through computer hardware. Megahertz used to be fast but now computers use gigahertz and terahertz speeds. As information is flowing through the CPU it is converted to binary. Sometimes the CPU is called the “processor” or “microprocessor.” Hardware that allows the computer to connect over telephone lines and cable to other computers. Motherboard Mouse The main piece inside the computer that holds all the other part together. The mother board also provides the wire that data flows along from one point to another. A device used to point to objects and text on a computer screen. Network Interface Card (NIC) A piece of hardware that allows computers to access a network. Optical Storage Optical storage devices use a laser light to write information to a CD or DVD. Output Devices Hardware that allows information to be taken out of the computer. Such as: printers, speakers, headphones, etc. Peripheral Any hardware that is plugged into the outside of the computer such as monitor, keyboard, mouse, speakers, headphones, camera, printer, etc. Small computers, least expensive, and used for individual work and play. Personal Computer Processor Random Access Memory (RAM) Read Only Memory (ROM) Sound Card Storage Devices Supercomputer As information is flowing through the CPU it is converted to binary. Sometimes the CPU is called the “processor” or “microprocessor.” Temporary memory. Used for storage of programs and files while the program or file is being used. Whatever is stored in RAM is lost when the power is turned off. Permanent memory that stores start up information. Information in ROM is still there even if the computer is turned off. A piece of hardware that allows the computer to play audio (sound). Hardware that stores programs and files onto media. Hardware such as the hard disk drive and the CD/DVD drive. This is different from “media.” Larger, faster, and more expensive computers. Used by governments, military, and for scientific research and calculations. System Unit The box that contains all the hardware that runs the computer such as the motherboard, RAM, and ROM, etc. Terabyte 1,024 gigabytes or 1 trillion bytes Used to measure amount of storage available to store data. How fast a computer can move information through computer hardware. Megahertz used to be fast but now computers use gigahertz and terahertz speeds. Used to store data (information) into memory. This type of storage is different from other storage because the data is stored electronically. Older storage systems physically write or change the storage media. Terahertz USB/Flash