5 V dc power supply
advertisement

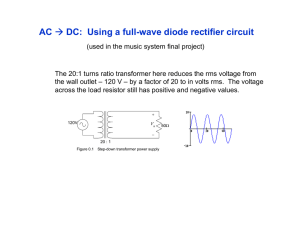
5V DC POWER SUPPLY A PROJECT REPORT ON Submitted by MRINAL KESHRI In fulfilment for the award of the degree Of BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING in ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION BABARIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY , VADODARA GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD DECEMBER, 2015 BABARIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY , VADODARA ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION 2015 CERTIFICATE Date: This is to certify that the dissertation entitled “5V DC POWER SUPPLY” has been carried out by Mrinal Keshri under my guidance in fulfilment of the degree of Bachelor of Engineering in ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION [ 1ST Semester] of Gujarat Technological University, Ahmedabad during the academic year 2014-15. Guides: Head of the department ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I would like to express my special thanks of gratitude to my teachers who gave me the golden opportunity to do this wonderful project on the topic which also helped me in doing a lot of Research and I came to know about so many new things. I am really thankful to them. Secondly, I would also like to thank my parents and friends who helped us a lot in finishing this project within the limited time. I have also used internet and some standard reference books [H.C. VERMA and NCERT] for the better understanding of my subject. ABSTRACT With today’s technological advancement, new miniaturized electrical and electronic products continue to emerge and these products require either a very low AC source or DC source for their operation. Many of the existing power supply devices with various levels of complexities and sophistication can only give a single DC output which cannot serve the same purpose when a very low AC power output is greatly desired. Hence, the need for designing and developing a multi-output power supply that can serve a dual purpose of providing DC and AC outputs of different values for use in miniaturized electrical and electronic appliances as well as for various domestic and laboratory experimental purposes. In this work, a simple, cost effective and reliable power supply that produces AC outputs of5V, 10V, 15V, 20V and 25V, variable DC outputs of 0-20V, regulated DC output of 5V and regulated dual DC outputs of ±15V was developed. A centre tapped transformer 220/30V (15V-0-15V) was constructed to produce the desired AC voltage range 0-30V at interval of 5V, For the DC section, 25V, 20V and 15V from the output of the transformer were rectified, smoothened and regulated using appropriate discrete components. The major components used include transistors, comparator LM393 and regulators LM317, LM7915 and LM7815. Short circuit test, open circuit test and earthing test were carried out on the developed power supply unit. The output measurements showed that the power supply was functional and the measured values gave minima variation from the nominal designed values. The developed multi output power supply is much useful in measurements, laboratory works and general applications requiring power supply. Keywords: miniature, AC source, DC source, multi-output power supply, accuracy. TABLE OF CONTENTS Acknowledgement Abstract Introduction to Project Principle Working / Implementation of the Project work Result Analysis Conclusion INTRODUCTION 1. Place the leads of four diodes through contact points in an unpopulated circuit board. Arrange the diodes in a square so that the leads can be connected together. Also, two of the diodes should have their anodes adjacent to each other, and the other two diodes should have their cathodes facing each other. The cathode ends of diodes have bars or stripes as identifying marks. 2. Use needle-nose pliers to twist together each pair of leads. There should be four connections. As you go around your square arrangement of diodes, the twisted leads should consist of cathode-cathode, anodecathode, anode-anode and cathode-anode. 3. Turn on the soldering iron, allow the tip to heat up and use lead-free solder at the twisted lead pairs. Use diagonal cutters to snip off excess leads. 4. Prepare four wires to add to your circuit. The length of the wires will depend on your planned use for your bridge rectifier. Cut the wires to your desired length, and strip a short amount of insulation from the ends. Expose enough wire at the ends to make electrical connections. 5. Solder the input wires to your bridge rectifier. Label them as you proceed. Connect one AC input wire to the anode-cathode twisted leads. Connect the other AC input to the cathode-anode twisted leads. 6. Solder the output wires to your circuit. The positive DC output connects to the positive AC wire input to the cathode-cathode twisted leads. The negative DC output connects to the anode-anode twisted leads. 7. Add insulating pads to the bottom of your circuit board so it doesn't create a short circuit. Turn off the soldering iron. The bridge rectifier is ready to convert AC input to a DC output. PRINCIPLE Bridge rectifier is an electronics component that is used in a circuit to turn alternating current (AC) electricity into direct current (DC) electricity. Although there are single components that can perform this function, you can make your own bridge rectifier by creating a bridge rectifier circuit with four diodes. A diode is a radial component with a metal lead protruding from each end. The diode allows electrical current to pass in one direction, from the cathode, or positive end, to the anode, or negative end. By electrically connecting the four diodes, you can make your own bridge rectifier. Working / Implementation of the Project work Component List : 1. Step down transformer 2. Voltage regulator 3. Capacitors 4. Diodes Let’s get into detail of rating of the devices: Voltage regulator As we require a 5V we need LM7805 Voltage Regulator IC. 7805 IC Rating: Input voltage range 7V- 35V Current rating Ic = 1A Output voltage range VMax=5.2V ,VMin=4.8V Transformer Selecting a suitable transformer is of great importance. The current rating and the secondary voltage of the transformer is a crucial factor. The current rating of the transformer depends upon the current required for the load to be driven .The input voltage to the 7805 IC should be at least 2V greater than the required 2V output, therefore it requires an input voltage at least close to 7V. So I chose a 9-0-9 transformer with current rating 500mA The best is using a full wave rectifier Its advantage is DC saturation is less as in both cycle diodes conduct. Higher Transformer Utilization Factor (TUF). 1N4007 diodes are used as its is capable of withstanding a higher reverse voltage of 1000v whereas 1N4001 is 50V Capacitor It only allows alternating current. RESULT ANALYSIS We observed that we are getting constant DC output. There may be some error i.e. output would be about 5V CRO also shows the same thing. CONCLUSION Due to the need for most domestic and laboratory equipment of small ratings to be powered by electricity in one form or the other coupled with the problem of insufficiency of number of specially designed power supply for the needed domestic application or laboratory experiment as well as electrical project design, a multi-output power supply unit was developed. The developed multi-output power supply consists of four segmental outputs; AC output, variable DC output, regulated dual rectified DC output and regulated single DC output. The AC outputs produced 5V, 10V, 15V, 20V and 25V. The variable DC output produced values ranging from 0-20V while the regulated and regulated dual outputs produced 5V and ±15V respectively. Tripping circuit was incorporated with transistors TIP41C and TIP42C and comparator LM393 and was provided to guard against overloading and short circuit for the DC circuits while fuses were used to protect the AC circuit. Short circuit test and earthing test were carried out on the developed power supply unit. The output measurements showed that the developed power supply was effective and the measured values gave minima variation from the nominal designed values. The developed system is cheap, robust and very useful for domestic application and laboratory experimental purposes.