Introduction-to-Nurition
advertisement

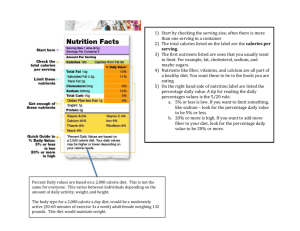
Week Nutritional Factors in Health and Performance 14 An Introduction to Nutritional Requirements. BTEC Level 3 National Certificate / Diploma in Uniformed Public Services. Unit 7 – Physical Preparation and Fitness for the Uniformed Services. Staff Litherland Session Aims • To explore the effects of lifestyle factors on health and fitness (Assignment 3) Descriptor P2 M2 D1. • To introduce the basics of nutrition and the daily energy requirements for individuals. Learning Outcomes • • • • Upon completion of the session; All students will be able to list the 7 nutrient groups and identify 2-3 examples of foods within each group. All students will be able to calculate their daily requirements. Most students will be able to explain basal metabolic rate (BMR). Some students will be able to calculate the percentages of nutrients required on a daily basis. Lifestyle Factors The following lifestyle choices impact upon our health and fitness: • • • • • • • Personal Hygiene Lifestyle Exercise (Physical Activity) Alcohol / Drug use / Smoking Stress Environment Diet Lifestyle Factors • • • • • • • Personal Hygiene Lifestyle Exercise (Physical Activity) Alcohol / Drug use / Smoking Stress Environment Diet Activity 1:Define Diet / Nutrition End 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 10 11 987654321 www.A6training.co.uk Health – Health is physical, mental and social wellbeing, its not just about avoiding disease its about adopting a healthy lifestyle to live healthier, longer lives, and being a positive role model for our children. » (World Health Organisation, 1999) Define Diet / Nutrition • Healthy eating is about maintaining a balanced diet. This means eating foods from all the different food groups in the right amounts. » NHS, 2009 Nutrition – Nutrition is the study of how the body uses foods and nutrients vital to health, promoting growth, maintenance and reproduction of cells. – In essence it is how what we eat and drink affects our health. – We have a physiological need to eat food. – Food is our fuel to function, like petrol in a car. Activity 2: Unscramble the anagrams on your worksheet to reveal the reasons why we need a balanced diet. Unscramble the anagrams in 2 minutes. 1:12 1:13 1:14 1:15 1:16 1:17 1:18 1:19 1:20 1:21 1:22 1:23 1:24 1:25 1:26 1:27 1:28 1:29 1:30 1:31 1:32 1:33 1:34 1:35 1:36 1:37 1:38 1:39 1:40 1:41 1:42 1:43 1:44 1:45 1:46 1:47 1:48 1:49 1:50 1:51 1:52 1:53 1:54 1:55 1:56 1:57 1:58 1:59 2:00 1:00 1:01 1:02 1:03 1:04 1:05 1:06 1:07 1:08 1:09 1:10 0:12 0:13 0:14 0:15 0:16 0:17 0:18 0:19 0:20 0:21 0:22 0:23 0:24 0:25 0:26 0:27 0:28 0:29 0:30 0:31 0:32 0:33 0:34 0:35 0:36 0:37 0:38 0:39 0:40 0:41 0:42 0:43 0:44 0:45 0:46 0:47 0:48 0:49 0:50 0:51 0:52 0:53 0:54 0:55 0:56 0:57 0:58 0:59 0:01 0:02 0:03 0:04 0:05 0:06 0:07 0:08 0:09 0:10 1:11 0:11 End www.A6training.co.uk The reasons why we need a balanced diet. Anagrams • a) ovdepisr ynrgee Answers • Provides energy • b) thorwg • Growth • c) persair sutsei • Repairs tissue • d) omtepros dogo ealhth • promotes good health Nutrition • Nutrition is based upon the chemical breakdown of food. • We therefore need to know the content of foods to understand its role and function within our bodies. • Nutrients are required in varying amounts. • A diet must contain adequate amounts of all the essential nutrients. Activity 3. Complete section on your worksheet giving 2 examples. Extension activity – provide another example for each group. 1:12 1:13 1:14 1:15 1:16 1:17 1:18 1:19 1:20 1:21 1:22 1:23 1:24 1:25 1:26 1:27 1:28 1:29 1:30 1:31 1:32 1:33 1:34 1:35 1:36 1:37 1:38 1:39 1:40 1:41 1:42 1:43 1:44 1:45 1:46 1:47 1:48 1:49 1:50 1:51 1:52 1:53 1:54 1:55 1:56 1:57 1:58 1:59 2:00 1:00 1:01 1:02 1:03 1:04 1:05 1:06 1:07 1:08 1:09 1:10 0:12 0:13 0:14 0:15 0:16 0:17 0:18 0:19 0:20 0:21 0:22 0:23 0:24 0:25 0:26 0:27 0:28 0:29 0:30 0:31 0:32 0:33 0:34 0:35 0:36 0:37 0:38 0:39 0:40 0:41 0:42 0:43 0:44 0:45 0:46 0:47 0:48 0:49 0:50 0:51 0:52 0:53 0:54 0:55 0:56 0:57 0:58 0:59 0:01 0:02 0:03 0:04 0:05 0:06 0:07 0:08 0:09 0:10 1:11 0:11 End www.A6training.co.uk Essential Nutrients • • • • • • • Carbohydrates Protein Fat Vitamins Minerals Water Fibre (not a nutrient but aids digestion and excretion) Figure 10.1 www.mypyramid.gov Key Point • The eatwell plate & MyPyramid.gov are excellent starting points from which to evaluate the adequacy of a diet. • If a diet provides a variety of foods from each group, it is likely adequate for vitamins and minerals. However, if the diet excludes an entire food group, specific nutrients may be lacking. Acceptable nutrient distribution. The amount of energy each individual needs will depend on their age, gender and lifestyle. No more than 10% should come from saturated fat. Figure 1. Acceptable macronutrient distribution for carbohydrate, fat and protein (Institute of Medicine 2002). Carbohydrates, Protein and fats are macronutrients (nutrients required in significant amounts). Kcals provided per gram Carbohydrates 4kcals Protein 4kcals Fat 9kcals Activity 4. Complete section 3 on your worksheet. Extension activity – List some of the foods next to each group. 1:12 1:13 1:14 1:15 1:16 1:17 1:18 1:19 1:20 1:21 1:22 1:23 1:24 1:25 1:26 1:27 1:28 1:29 1:30 1:31 1:32 1:33 1:34 1:35 1:36 1:37 1:38 1:39 1:40 1:41 1:42 1:43 1:44 1:45 1:46 1:47 1:48 1:49 1:50 1:51 1:52 1:53 1:54 1:55 1:56 1:57 1:58 1:59 2:00 1:00 1:01 1:02 1:03 1:04 1:05 1:06 1:07 1:08 1:09 1:10 0:12 0:13 0:14 0:15 0:16 0:17 0:18 0:19 0:20 0:21 0:22 0:23 0:24 0:25 0:26 0:27 0:28 0:29 0:30 0:31 0:32 0:33 0:34 0:35 0:36 0:37 0:38 0:39 0:40 0:41 0:42 0:43 0:44 0:45 0:46 0:47 0:48 0:49 0:50 0:51 0:52 0:53 0:54 0:55 0:56 0:57 0:58 0:59 0:01 0:02 0:03 0:04 0:05 0:06 0:07 0:08 0:09 0:10 1:11 0:11 End www.A6training.co.uk Activity 5. In groups decide which is the most important to the least important on the diamond template. End www.A6training.co.uk Weight and Body Composition • Energy Requirements – Energy is commonly measured in kilocalories (kcal or calories). – Energy (caloric) requirement is defined as energy intake equal to expenditure, resulting in constant body weight BMR – Basal Metabolic Rate – the energy required to stay alive, awake, to function and maintain a comfortable body temperature. Energy Requirements • Factors affecting energy requirements include: • • • • Resting Metabolic Rate (BMR) Thermic Effect of Food Physical Activity Age / Height / Weight (Body Composition) Energy Intake Energy Expenditure Activity 6. Complete section 4 on your worksheet. Extension activity complete number 5 1:12 1:13 1:14 1:15 1:16 1:17 1:18 1:19 1:20 1:21 1:22 1:23 1:24 1:25 1:26 1:27 1:28 1:29 1:30 1:31 1:32 1:33 1:34 1:35 1:36 1:37 1:38 1:39 1:40 1:41 1:42 1:43 1:44 1:45 1:46 1:47 1:48 1:49 1:50 1:51 1:52 1:53 1:54 1:55 1:56 1:57 1:58 1:59 2:00 1:00 1:01 1:02 1:03 1:04 1:05 1:06 1:07 1:08 1:09 1:10 0:12 0:13 0:14 0:15 0:16 0:17 0:18 0:19 0:20 0:21 0:22 0:23 0:24 0:25 0:26 0:27 0:28 0:29 0:30 0:31 0:32 0:33 0:34 0:35 0:36 0:37 0:38 0:39 0:40 0:41 0:42 0:43 0:44 0:45 0:46 0:47 0:48 0:49 0:50 0:51 0:52 0:53 0:54 0:55 0:56 0:57 0:58 0:59 0:01 0:02 0:03 0:04 0:05 0:06 0:07 0:08 0:09 0:10 1:11 0:11 End www.A6training.co.uk Weight and Body Composition • Energy Requirements – Estimating Energy Requirements • Brooks (2004) recommends calculating BMR by multiplying body weight in pounds by 10. • Activity 7: Calculate and note answer. • Energy needs (including BMR) can be loosely estimated using the guidelines found in table 10.7. • Food diaries could also be used during periods of stable body weight to estimate requirements. Table 10.7 Calculate your estimated total daily calorie requirements using the table provided. Extension activity: divide your calories into the percentages recommended for carbohydrates, fats and proteins. (Put your answers under the pie chart.) 1:12 1:13 1:14 1:15 1:16 1:17 1:18 1:19 1:20 1:21 1:22 1:23 1:24 1:25 1:26 1:27 1:28 1:29 1:30 1:31 1:32 1:33 1:34 1:35 1:36 1:37 1:38 1:39 1:40 1:41 1:42 1:43 1:44 1:45 1:46 1:47 1:48 1:49 1:50 1:51 1:52 1:53 1:54 1:55 1:56 1:57 1:58 1:59 2:00 1:00 1:01 1:02 1:03 1:04 1:05 1:06 1:07 1:08 1:09 1:10 0:12 0:13 0:14 0:15 0:16 0:17 0:18 0:19 0:20 0:21 0:22 0:23 0:24 0:25 0:26 0:27 0:28 0:29 0:30 0:31 0:32 0:33 0:34 0:35 0:36 0:37 0:38 0:39 0:40 0:41 0:42 0:43 0:44 0:45 0:46 0:47 0:48 0:49 0:50 0:51 0:52 0:53 0:54 0:55 0:56 0:57 0:58 0:59 0:01 0:02 0:03 0:04 0:05 0:06 0:07 0:08 0:09 0:10 1:11 0:11 End www.A6training.co.uk Table 10.1 Checking Learning • Using the cards provided. • Create revision flash cards. • Create 1 question per card on the front. Q. Define Basal Metabolic Rate. >> Flip Card Checking Learning • Pass to the next group who will complete the answer on the back. • When prompted, ask the questions to another group. A. The amount of calories the body needs just to function on a daily basis. Q&A • Homework • Complete a food diary for the week, bring to the next lesson. • To write down as many fad diets as you know and bring to the lesson next week. • Ask your friends and family if they have tried any of the fad diets and if they were successful in losing weight and keeping it off. Your food intake for a week (include snacks and drinks) Day Mon Tue Wed Thur Fri Sat Sun Breakfast Lunch Dinner References • Brooks, D.S. (2004). The Complete Book of Personal Training. Leeds. Human Kinetics. • National Health Service (2009). http://www.nhs.uk. • World Health Organisation.(1999). http://www.who.int