Platonic Solids PowerPoint
advertisement

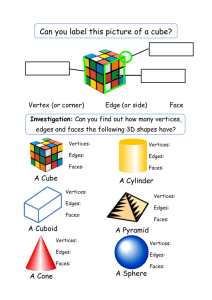
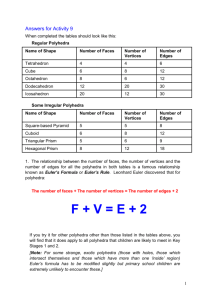
In Perspective • Objects that are symmetrical look the same from several different views, or two sides are mirror images of each other. • Symmetric solids are referred to as regular, or Platonic solids. • For centuries, the Platonic solids were associated with mystical powers. • Euclid wrote about these regular solids. However, they are named after Plato because he tried to relate them to the five elements: fire, earth, wood, metal, water. • The Pythagoreans knew there were only 5 and held them in awe. • Remembered best for laws of planetary motion. • In his time there were 6 known planets and he showed that it is possible to take the 5 regular solids, put one inside the other, and have the sizes of inscribed and circumscribed spheres about these solids reveal the sizes of the orbits of the planets. • Once Uranus was discovered in 1781 his theory fell apart. • Made up of 4 identical equilateral triangles. • Four identical faces, four vertices, and six edges. • The most famous of the Platonic solids, we see it as dice most frequently. • Six faces, 12 edges, 8 vertices • Constructed from 8 identical, equilateral triangles. • Eight faces, 12 edges, 6 vertices • The only solid with pentagonal faces. • Twelve faces (do = 2, dec = 10, dodec = 2+10), 20 vertices, 30 edges. • Constructed from 20 identical equilateral triangles. • Twenty faces, 12 vertices, 30 edges. # Vertices # Edges # Faces # Faces at each vertex # sides at each face Tetrahedron 4 6 4 3 3 Cube 8 12 6 3 4 Octahedron 6 12 8 4 3 Dodecahedr on 20 30 12 3 5 Icosahedron 12 30 20 5 3 • The number of faces of the cube equals the number of vertices of the octahedron; the number of vertices of the cube equals the number of faces of the octahedron. • The number of edges of both figures is the same. • Why is that? • From the cube we can construct an octahedron using midpoints of the cube faces. This is called a dual. • The process of creating one solid from another is duality. • Cube – octahedron, dodecahedron – icosahedron, tetrahedron is self dual. • Have you ever looked down a long road, or train tracks, and noticed that it looked like it was getting “thinner” in a way? • This is an optical illusion created by perspective. • Perspective is defined as the way in which objects appear to the eye. • To draw an image in perspective, we need to have a horizon and a vanishing point. • The horizon is an imaginary line in which the ground “ends” and the sky “begins” in relation to your image. • The vanishing point is an imaginary point in which everything seems to disappear, or vanish.