The Human Body
advertisement

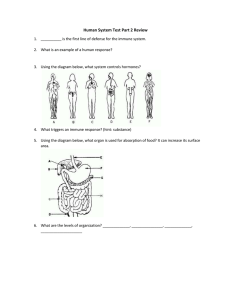
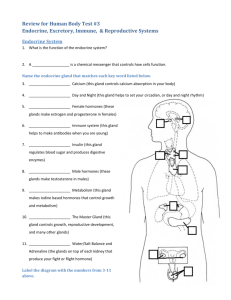
The Human Body Body Organization • Organ Systems – groups of organs in the body that work together to form a specific task • Homeostasis – the maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM skin, hair, and nails Functions of the Skin • Protects you by keeping water in the body and foreign substances out • Sense of touch • Helps regulate body temperature with sweat glands • Gets rid of waste • Largest organ of the body Layers of the Skin • Epidermis • very thin top layer of the skin • most epidermal cells are dead • Dermis • lies beneath the epidermis • contains many other small structures • Subcutaneous Fat • bottom layer Parts of the Skin • Hair follicle – where hair grows • Sweat gland – releases sweat, which regulates the body and gets rid of waste • Oil gland – releases oil, which keeps hair flexible and makes the skin waterproof • Blood vessels – transport blood to the skin; regulate body temperature Other Parts of the Skin • Hair & Nails • both grow from the base of a follicle or root • only living cells are at the base and push old cells up • provide protection and hair helps regulate body temperature About the Skin • Melanin • chemical that determines color of the skin • a lot of melanin = darker skin • helps protect against UV radiation from the sun • Skin Cancer • abnormal growth of skin cells • can develop from prolonged exposure to UV radiation Structure & Movement The Musculoskeletal System Kinds of Muscle • Smooth Muscle • found in the digestive tract and walls of blood vessels • involuntary (not under your control) • Cardiac Muscle • found only in the heart • involuntary (not under your control) • Skeletal Muscle • attached to your bones and allows you to move • can be involuntary or voluntary (you control the movement) Tendons • Tendons • connective tissue that attaches muscles to bones • when the muscle contracts, the bones are pulled up • Ex. contracting your bicep makes your arm move upward Muscle Fatigue • Lactic Acid • chemical produced by muscle cells during respiration • if muscles are worked too hard too quickly lactic acid can build up, this causes the muscles to burn or ache Function of Skeletal System • Protection • ex. ribs protect heart, skull protects brain • Storage • store minerals and fat • Movement • muscles pull on bones to make them move • Blood cell formation • marrow inside the bones makes blood cells Bone Structure • Compact Bone • dense and rigid structure • no pores or open spaces • stores minerals (calcium and phosphorus) • Spongy Bone • many open spaces • provides strength and support Bone Structure • Cartilage • soft, flexible tissue usually replaced by bone • also found on the ends of bones to ease friction and absorb shock • Marrow • soft tissue inside bone • red marrow produces blood cells • yellow marrow is found in long bones and stores fat Joints - a place where two or more bones meet - held together by ligaments- connective tissue that connects bone to bone. • Three kinds of joints: • Gliding Joint - bones gliding over one another (ex. wrist, vertebrae) • Ball-and-Socket Joint - allows movement in all directions (ex. shoulder, hip) • Hinge Joint - allows for bending at right angles (ex. knees, elbows) Skeletal System Injuries & Disorders • Sprain • when a ligament is stretched too far or torn • Osteoporosis • bones become less dense and weak due to age or poor diet • Arthritis • swelling or stiffening of the joints Communication & Control The Nervous & Endocrine Systems The Nervous System • The nervous system acts as the body’s central command post. • It detects , processes, and responds to information in the body • Communication occurs using electrical impulses. Neurons • The basic unit of the nervous system is the Neurona specialized nerve cell that transfers messages in the form of electrical impulses. • Three parts of a neuron: • cell body – normal cell structure • dendrite – branch-like structures used to receive impulses • axon – long, tail-like structure covered in a myelin sheath (fat) used to send impulses Information Collection & Delivery • Sensory Neurons – gather information about what is happening in and around the body • Motor Neurons – send impulses from the central nervous system to other systems of the body • Nerve – collection of axons bundled together with blood vessels and connective tissue Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • all of the parts of the nervous system except the brain and spinal cord • uses specialized structures call nerves to carry information between parts of the body Central Nervous System (CNS) • Central Nervous System (CNS) • receives messages from the peripheral nervous system and responds by sending messages to the motor neurons • made up of the brain and spinal cord The Brain • Main control center of the nervous system • Three main parts of the brain: • Cerebrum • Cerebellum • Medulla Cerebrum • largest part of the brain • where you think and carry most memories • location of all your senses • divided into two hemispheres • right side controls left side of the body, and vice versa Parts of the Brain Cerebellum • second-largest part of the brain • located beneath the back of the cerebrum • processes sensory information from muscles and joints (i.e. balance) Parts of the Brain Medulla • part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord • controls involuntary things like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature Parts of the Brain Spinal Cord • made of bundles of neurons that pass impulses to and from the brain • surrounded by the vertebrae (protective bones of the spine) • sensory neurons spinal cord brain spinal cord motor neurons The Endocrine System pituitary, thyroid, gonads • a collection of glands that secrete hormones into the body that regulate growth, development, and homeostasis Function Hormones • chemical messengers released by an endocrine gland and carried through the blood to different parts of the body • ex. adrenaline - released when you are scared, angry, or excited to increase your heart rate and breathing • Pituitary gland • “master gland” that controls other endocrine glands • located in the brain • makes human growth hormone (HGH) • Thyroid gland • controls how you use energy (metabolism) • in the neck • Parathyroid gland • regulates calcium levels in the blood • behind the thyroid gland Endocrine Glands • Thymus gland • regulates the immune system to help fight disease • behind the heart • Adrenal glands • produces adrenalin to help the body respond to danger • sit atop the kidneys • Pancreas • regulates blood sugar levels by secreting insulin Endocrine Glands • Ovaries (female) • produce estrogen to aid in female reproduction • released during puberty • Testes (male) • produce testosterone to aid in male reproduction • released during puberty Endocrine Glands • Diabetes • the pancreas does not make insulin properly so the body cannot regulate blood sugar levels • patients must take insulin injections • Hormone Imbalances • Thyroid – controls metabolism, so this can lead to obesity • Pituitary – controls growth, so this can lead to stunted growth or being abnormally tall Diseases & Disorders The Respiratory System lungs, bronchi, diaphragm • The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between living cells and their environment • Includes breathing and cellular respiration • The respiratory system is a group of organs that take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide Respiration • Nose • air enters and exits through the nose • hairs and mucus in the nose trap dirt and particles • Pharynx (Throat) • splits into two tubes – the esophagus (leads to the stomach) and the trachea (leads to the lungs) • a tiny flap called the epiglottis covers the trachea to prevent food from going into the lungs when swallowed • Larynx • location of the vocal cords – two muscles stretched over the trachea that vibrate when air passes through them Upper Respiratory System • Trachea • also known as the windpipe • Bronchus • the trachea splits into two separate bronchi, going to each lung • the bronchi split further into smaller tubes bronchioles one called • Alveoli • tiny air sacs located at the ends of each bronchiole • Covered in blood vessels so gas exchange can take place Lower Respiratory System • the diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle underneath your lungs • when it pushes downward you inhale, when it pushes upward you exhale • spasm of the diaphragm gives you hiccups Breathing • Asthma • swelling and narrowing on the bronchioles • makes breathing more difficult • Emphysema • damage to the alveoli • trouble getting oxygen to the body • Lung cancer • can be caused by smoking Respiratory Disorders The Circulatory System heart, blood, arteries & veins • moves blood throughout the body • carries nutrients to your cells • removes waste from your cells • carries chemicals through your body • regulates body temperature Functions • Made of cardiac muscle • Right side of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs • Left side pumps oxygenrich blood to the body Four chambers separated by valves: Upper = atriums (right and left) Lower = ventricles (right and left) Heart Path of Blood • Three types of blood vessels: • Artery • Carries blood AWAY from the heart • Vein • Carries blood TO the heart • Capillary • Tiny blood vessels that allow for gas and waste exchange between the blood and cells Blood Vessels • Two types of circulation • Pulmonary Circulation – between the heart and lungs • Pulmonary artery – carries blood from heart to lungs • Pulmonary vein – carries blood from lungs to heart • Systemic Circulation – between the heart and body • Aorta – carries blood from heart to body • Superior/Inferior Vena Cava – carries blood from body to heart Circulation Diseases & Disorders of the Circulatory System • Atherosclerosis • build up of cholesterol in blood vessels • clogs pathways and blood flow becomes blocked • Heart Attacks • arteries going to the heart itself become blocked • heart muscle cells die • Fluid that carries nutrients, waste, and gases throughout the body • Made up of four parts: • • • • plasma red blood cells platelets white blood cells Blood Plasma Red Blood Cells • Fluid part of the blood • Most of what blood is made of • A mixture of water, minerals, nutrients, sugars, proteins, and other substances • Hemoglobin in your red blood cells helps carry oxygen to your body. • All other parts of the blood are found within plasma Parts of the Blood Platelets White Blood Cells • Pieces of larger cells floating among blood cells • Destroy pathogens (bacteria and viruses) that attack your body • Release chemicals that form a net at damaged vessel to stop blood flow and clot • Some release antibodies which identify and destroy pathogens Parts of the Blood • Refers to the types of chemicals (antigens) you have on the surface of your red blood cells • • • • Type A = A antigens Type B = B antigens Type AB = both antigens Type O = neither antigen Can Receive From Can Donate To A A, O A, AB B B, O B, AB All types AB only O only All types AB O Blood Types Universal Receptor = Type AB Universal Donor = Type O The Digestive System stomach, liver, intestines • organs that break down food to be used by the body • Mechanical Digestion – breaking, crushing, mashing of food particles • Chemical Digestion – large molecules are broken down into specific nutrients Function Teeth • chew and mash food beginning mechanical digestion • hardest substances in the body Saliva • liquid made in the salivary glands of the mouth • contain enzymes that begins the chemical digestion of food Digestion in the Mouth • long, straight tube connecting the throat and stomach • squeezes food down to the stomach using muscle contractions called peristalsis Esophagus • muscular, saclike organ where food continues to get broken down mechanically and chemically • releases small amount of enzymes and acid to break down food • slowly releases the soupy mixture, now called chyme, into the small intestine The Stomach • located between the stomach and small intestine • released enzymes into the small intestine to continues digestion • also releases hormones to regular blood sugar levels Pancreas Liver Gallbladder • located beside and above the stomach on the right side • produces bile to help break down fats • also breaks down toxins Helper Organs • small, green, saclike organ located behind the liver • stores the bile • Small Intestine • muscular tube that is about 6 meters long • inside is covered in small projections called villi where nutrients are absorbed • Large Intestine (Colon) • stores and compacts undigested material by absorbing water • feces (poop) are stored in the rectum and eliminated through the anus Small & Large Intestine • • • • • • • • • Mouth Esophagus Stomach Pancreas Liver Gallbladder Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum What to Know • Essential needs for human development: • Carbohydrates – give energy • Examples: fruits, vegetables, grains • Proteins – build muscle • Examples: meat, dairy, beans • Fats – protect body • Examples: oils, nuts, lard • Vitamins & Minerals • Examples: zinc, calcium, potassium, vitamin A, vitamin C Nutrition • calories = how much energy is contained in food • determined by using a calorimeter – food is burned to see how much heat (energy) is released Calories The Excretory System kidneys, urinary bladder • removal of waste materials from the body • Parts of the Excretory System: • skin – sweating • lungs – exhaling • kidneys – urine Function • a pair of organs that constantly clean the blood • inside each kidney are about one million nephrons • Nephrons - microscopic filters that remove harmful substances from the blood, including urea • Urea - a nitrogen-based substance that is formed when cells use protein for energy Kidneys • renal artery brings blood into each kidney • tiny blood vessels bring blood to the nephrons • blood gets filtered • cleaned blood exits kidneys through a renal vein • waste material leaves nephrons as urine How Kidneys Work • urine leaves the kidneys through tubes called ureters • ureters lead to the urinary bladder where urine is stored • it will eventually leave the body through a tube called the urethra Exiting the Body • Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) • bacteria gets into the urinary tract (urethra, bladder, ureters) and cause pain • Kidney disease • damage to nephrons prohibits normal filtering of the blood • a machine must be used to filter the blood, called a dialysis machine Kidney Diseases & Disorders • salts and other waste build up in the kidneys and make a hard stonelike substance that interferes with urination • can be passed naturally or must be removed surgically Kidney Stones The Immune System disease, T & B cells, antibodies Noninfectious Infectious • cannot be spread from one individual to another • can be spread from one individual to another • can be caused by genetics, habits (ex. smoking), poor diet • ex. cancer, heart disease Disease • caused by pathogens (virus or organism that causes disease) • some organisms that cause disease: bacteria, fungi, protists, worms • Ways Pathogens Get Transferred: • • • • • Air Contaminated objects (ex. doorknobs, keyboards) Person to person Animals (ex. dogs, ticks) Food and water (ex. meat) Pathogen Pathways • List some ways pathogens can be spread from one individual to another. BELLWORK Viruses • Microscopic • can be spread from one individual to another • need the cells of living things to reproduce, therefore are not considered a living thing themselves • Are treated with Vaccines. Bacteria • Some bacteria are pathogens • Some bacteria that normally live in the body cause illness only when the person's immune system is weakened. • They can enter the body through a cut, in the air, or on food. After they are in the body, they reproduce and cause disease. • Some can: • make people sick by damaging tissue. • cause illness by releasing toxins. • Antibiotics are medicines that stop the growth and reproduction of bacteria The Immune System • Function • cells and tissues that recognize and attack foreign substances in the body • Parts of the Immune System • Macrophages • T-cells • B-cells • If pathogens get past your first line of defenses (skin, oil, mucus) your body will respond to destroy them. • Macrophage • engulf and destroy the virus • engulf and destroy cells infected by the virus • display viral antigens (substances that stimulate an immune response) • Helper T-Cells • recognize the viral antigen and begin two responses: • T-Cell Response • B-Cell Response Responding to a Virus T-Cell Response B-Cell Response • activation of killer T-cells • recognize antigens on infected body cells • kills the cells so they cannot replicate • activation of B-cells • b-cells divide and create anitbodies (proteins that attach to specific antigens) • antibodies cause viruses to clump together and become marked for destruction Immune Responses • normal B-cells create antibodies against a pathogen within two weeks • some B-cells become memory B-cells, which means the next time your body encounters that pathogen your Bcells “remember” how to create the antibodies for it and you will be protected within 3 or 4 days Memory B-Cells • Allergy • an overreaction to a harmless or common substance by the immune system • Autoimmune Diseases • diseases in which the immune system mistakes body cells for pathogens and attacks them • ex. rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, lupus Challenging the Immune System • Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) • causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) • infects the cells of the immune system, specifically the helper T-cells, and destroys them • killer T-cells and B-cells do not get activated, therefore the body cannot defend itself against the virus or any other pathogens • Most people die from other diseases that their body could not fend off HIV/AIDS The Reproductive System ovaries, testes, egg, sperm • Testes – sperm is produced here • Epididymis – sperm is stored here • Vas Deferens – sperm leave the testes through these tubes • Prostate Gland – other fluids are added here to make semen • Urethra – semen leaves the body through this tube out the penis Male Reproductive System • Ovaries – eggs are produced here • Fallopian Tubes – eggs travel down these to get to the uterus • Uterus – fertilized eggs attach here and this is where the fetus develops Female Reproductive System • beginning at puberty eggs are released from the ovary once a month to be fertilized • the uterus begins to prepare for pregnancy by building up blood vessels in the uterine walls • if the egg does not become fertilized the uterus will release the egg along with the all the uterine lining through the vagina Menstruation • An egg becomes fertilized when a sperm enters the egg cell. The fertilized egg is now called a zygote. • The zygote begins to divide into many cells and implants itself into the uterine wall. It is now called an embryo. Fertilization • The placenta gives the embryo nutrients and picks up any waste products. • It is attached to the placenta by the umbilical cord. • The embryo develops inside a sac called the amnion which is filled with amniotic fluid. Pregnancy