The Rock Cycle
advertisement

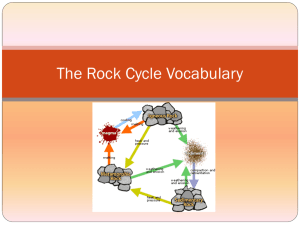
The Rock Cycle No …. Yes….. Rocks Defined • Solid mixture of crystals of one or more minerals SO…. What are “minerals” and “crystals”? • Minerals = anything with a definite chemical compound and definite structure and always inorganic (never was “living”) which are typically found in the earth (ex quartz, calcite, feldspar….) Rock Cycle Processes Erosion • Deposition • Compaction and Cementation • Metamorphism • Melting • Cooling • Solidification • Weathering • Crystals…. a solid object/piece of inorganic substance having a definite internal structure and characterized by identifiable geometric patterns SO…. Rocks are loose combinations of crystals of any variety of minerals Do we have samples? Rock Classification • How they are formed • Where they are formed • Composition – Minerals that make up a rock • Texture – Sizes, shapes, and positions of the grains Value of Rock ‐ History • Important to scientists – Help answer questions about the history of earth and the solar system. • Record of what the Earth used to be • Fossils Value of Rock • Natural resource – Used as tools and weapons (hammers, spears,knives) – Used in buildings, roads, and monuments Rock Cycle Processes • Weathering – Rocks attacked by weather • Air, moisture, and living things – Rocks broken down into sediments • Erosion – Sediment is transported by wind, water, ice or gravity Rock Cycle Processes • Deposition – Sediments settle to the bottom • Compaction and Cementation – Compaction • Layers form on top of each other • Air and water pushed out – Cementation • Loose sediments are glued together by natural glue Melting – Rocks deep in Earth melt and become magma • Cooling – Magma cools • Solidification – Rock solidifies Rock Cycle Processes • Metamorphism – Means changed form – Increased heat and pressure – Changes a rock into a metamorphic rock Who can tell us what is happening at each star?