Customer Service in the aviation industry
advertisement

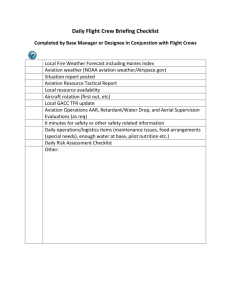
Customer Service in the aviation industry P5,P6,M1 Plan for today Time Topic 9.30-10.00 Recap of P4 Learning outcomes today 10.00-10.45 P5 review different customer service models appropriate for use in the aviation industry 10.45-11.00 Break 11.00-12.00 P6 Compare customer service strategies developed by aviation organisations 12.00-12.30 M1 Analyse how customer service provision is implemented in aviation organisations Module Overview Week No Week commencing Topic 1 12 Sept P1 2 19 Sep P1 3 26 Sep 4 3 Oct 5 10 Oct 6 17 Oct P1 and P2 P3 P4, P5, P6, M1 D1 P4, P5, P6, M1 D1 7 24 Oct Presentations Half term 8 7 Nov 9 16 Nov 10 23 Nov 11 30 Nov Role-plays 12 5 Dec Role-plays 13 12 Dec Role-plays P7 P8 P9 M2, M3, D2 Christmas Holidays Recap of P4 Task 5 (provides evidence for P5 and P6) Review different customer service models appropriate for use in the aviation industry Compare customer service strategies developed by aviation organisations P5 You must produce a Power-point presentation in pairs which reviews different customer service models appropriate for use in the aviation industry. P6 You must compare service strategies developed by aviation organisations. You must research a minimum of two aviation organisations and compare their customer service strategies. An example could be comparing a low-cost scheduled airline strategy as opposed to that for a full service scheduled airline. In this presentation, please also include methods of communicating with customers, using examples from aviation organisations: Task 6 (provides evidence for M1) To achieve M1, you must examine the provision of customer service in at least two aviation organisations and analyse how it is implemented. Learning outcomes for today List different customer service models appropriate for use in the aviation industry Compare customer service strategies developed by aviation organisations Presentation Skills • Please consider the tips on the factsheet when delivering a presentation • Your presentation will be assessed • You will receive feedback from your tutor and the rest of your peers • The presentation should be a maximum of 10 minutes and include 10 slides or less Customer interfaces ways of communicating with customers Premium rate numbers On-line services Mobile & Text E-check-in Fax Text Letters E-mail Methods of communicating with customers Work in four groups. Each group to summarise the different methods of communicating with customers and feedback to the rest of the group. • face to face • written, e.g. letter, email • telephone • web based Customer Service Models • Customer Relationship Management (CRM) • Institute of Customer Service – world-class customer service • RATER model • RESPECT model • Moments of Truth • company-developed models CRM In response to this new environment, aviation organisations are undertaking initiatives focussed on identifying, developing and retaining high-value customers, under the overall banner of customer relationship management or CRM. Customer Relationship Management is a strategy which focuses on creating and maintaining lasting relationships with its customers. CRM In response to this new environment, aviation organisations are undertaking initiatives focussed on identifying, developing and retaining high-value customers, under the overall banner of customer relationship management or CRM. Customer Relationship Management is a strategy which focuses on creating and maintaining lasting relationships with its customers. CRM • Customer relationship management (CRM) is a widely implemented model for managing a company’s interactions with customers. • The overall goals are to find, attract, and win new customers, service and retain those the company already has, entice former clients to return, and reduce the costs of marketing and client service. CRM • Customer relationship management describes a companywide business strategy including customer-interface departments as well as other departments. • Measuring and valuing customer relationships is critical to implementing this strategy CRM • Customer relationship management describes a companywide business strategy including customer-interface departments as well as other departments. • Measuring and valuing customer relationships is critical to implementing this strategy Institute of Customer Service – world-class customer service The Institute of Customer Service is the professional body for customer service. The main purpose is to lead customer service performance and professionalism. They are a membership body with a community of more than 350 organisational members from across the private, public and third sectors - and over 5,000 individual memberships Institute of Customer Service – world-class customer service Activity: Follow the link to the ICS website to the ‘about us’ page and find out what they do and how they support their customers. Summarise the information and feedback http://www.instituteofcustomerservice.com/453/About-us.html RATER Model Zeithaml, Parasuraman & Berry • RATER is a service delivery quality framework • RATER focuses on the dimensions of customers expectations • The RATER factors help provide specific dimensions which can be used to analyse and measure customer expectations. RATER Model • Reliability • • • • "Do what you say you will do, reliably and consistently" Relates to timeliness, consistency, regularity, accuracy Assurance "I need to be confident of the knowledge and courtesy of your staff" Relates to competence, knowledge, respect, credibility, honesty, confidentiality, safety, security Tangibles "Make sure your facilities, equipment, communication materials look attractive and are user friendly" Relates to appearance of facilities, staff, communication facilities Empathy "Treat me as an individual, in a caring and empathic way; understand my needs" Relates to access to staff and information, clear, appropriate and timely information, individualised attention Responsiveness "Be flexible and willing to help me; resolve my problems promptly and effectively" Relates to prompt service, willingness to help, problem resolution RATER Model • In groups • You are the owner of a new airline-rate the points of the RATER scale in order of importance to your airline and explain your reasons for your decision • Thinking about an existing airline, state the order of importance of the RATER scale to them RESPECT Model Paul Marciano • • • • • • • Responsive Educate Solve Personalize Empathize Courteous Teamwork • See full brochure • http://www.paulmarciano.com/wpcontent/uploads/2010/07/Paul_Marciano_RESPECT_Custome r_Service_7-7-10.pdf Moments of Truth In any customer service procedure there are several points when customer awareness of the quality of customer service is particularly high. These points have a greater effect on customer perceptions of the customer service they have received. It is usually appropriate to pay particular attention to these moments of truth because they form customer opinions about customer service as a whole. Moments of Truth 'Moments of truth' means the points in a transaction, service delivery or customer relationship at which customer expectations are at their sharpest and most demanding e.g. airlines - as you reach check-in, settling down for take-off etc. e.g. restaurant - waiter takes order, food arrives at table Moments of Truth What a customer remembers about a service is not just dependent on the usual suspects of first and last impressions. It is dependent on the "moments of truth", a phrase coined by Jan Carlson from Scandinavian Airlines. For an organisation in the service industry, there may be twenty or thirty moments of truth in its provision of service. A moment of truth is when an interaction occurs between a customer and the service provider that can leave a lasting positive or negative impression on a customer. Moments of Truth Moments of truth in the hospitality industry, for example, will undoubtedly include, but not be limited to, booking the room, check-in, check-out, dinner reservations, dinner ordering, dinner presentation, eating (quality and quantity of food) and laundry receipt. Understanding the moments of truth that are important to an organisation's customers by segment is the key to understanding what is good customer service Moments of truth • Think of all the points of a customer journey where there could be ‘moments of truth’ Company developed models of customer service P6 P5, P6 and M1 • You must compare service strategies developed by aviation organisations. You must research a minimum of two aviation organisations and compare their customer service strategies. An example could be comparing a low-cost scheduled airline strategy as opposed to that for a full service scheduled airline. • In groups: spend 5 minutes discussing which airlines you could compare in your presentation • In pairs :begin your research for P6 and ensure that you understand P5 in order to include this in your presentation. You must include a minimum of two of the models from P5 in your presentation • Please include M1 in your presentation Presentation P5, P6 and M1 A customer service strategy covers, for example: • new and existing customers • different customer interfaces • training requirements for staff at different levels • links to organisational business model You must compare at two different customer service strategies Points that may be included in a customer service strategy • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Organisation procedures and strategies Customer loyalty schemes Employee Training Advertising Monitoring of customer feedback Company image/reputation Consideration of customer needs Employee incentives OTP CRM KPI’s Benchmarking Use of technology Monitoring of consistency of quality of service Customer profiling Updating company policies and procedures Presentation P5, P6 and M1 M1 Analyse how the provision is implemented in the organisations that you have researched