Science in a Box- Student Page 4 th Grade
advertisement

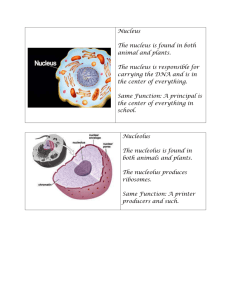
Science in a Box- Student Page 4th Grade Standards GLE 0407.1.1 Recognize that cells are the building blocks of all living things. 90407.1.1 Use illustrations or direct observations to compare and contrast the basic structures of plant and animal cells. SPI 0407.1.1 Compare basic structures of plant and animal cells. Task Objective You should be able to tell the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell. You should also be able to identify the parts of each cell. Materials Needed Science box will include: Plant cell model Diagram of animal cell Blue cards for card sort Outside of the box: Venn diagram and pencil Procedures 1. Take a moment to examine the plant cell model. 2. Then review the diagram of the animal cell model. 3. Use the cards in the box to sort what is in the plant cell and what is in the animal cell by making 2 columns. One for the plant and one for the animal. Then place the remaining cards in the appropriate column. 4. After you put the cards up, complete the assessment. Directions are below the vocabulary. Vocabulary Lysosome Ribosomes Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole Mitochondria Plasma (cell) Membrane Chloroplast Cell wall Assessment Venn diagram: Use the vocabulary above to complete the Venn diagram. Place the completed diagram in your interactive notebook. Clean-up Please make sure that the model, diagram and blue cards are left in the box for the next student. Science in a Box- Teacher Page 4th Grade Standards GLE 0407.1.1 Recognize that cells are the building blocks of all living things. 90407.1.1 Use illustrations or direct observations to compare and contrast the basic structures of plant and animal cells. SPI 0407.1.1 Compare basic structures of plant and animal cells. Task Objective The student should be able to tell the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell. They should also be able to identify the parts of each cell. Explanation At this stage, the students are learning that all living things are made of cells that perform functions necessary for life. A very important aspect of this is knowing the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell. They share some of the same parts and even have different parts. This activity should help compare and contrast the two cells. They will do this by visually comparing the animal cell and the plant cell provided. Then they will complete a “card sort” for practice. They will be assessed by filling out a Venn diagram. Vocabulary- These words were chosen because they are the parts of an animal and a plant cell and they will be used to differentiate them by using “card sorts” and the Venn diagram. Lysosome- digest food or the cell itself when it dies. Ribosomes- These are like construction guys who connect one amino acid at a time and build long chains of protein. Cytoplasm- The fluid that fills a cell Nucleolus- The center of the nucleus Nucleus- the brain of the cell Vacuole- stores nutrients or food that the cells might need to survive. Mitochondria- the “power house of the cell”. It digests nutrients and breaks them down to create energy for the cell. Plasma (cell) Membrane- outer layer that holds all of the pieces and fluid inside Chloroplast- food producers of the plant cell. Cell wall- made of cellulose (specialized sugar); only in plant cell Common Misconceptions One common misconception in regards to this lesson is that the animal cell and the plant cell both have the same parts and function the same. They do not contain all of the same parts. Both have a Lysosome, Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Nucleolus, Nucleus, Vacuole, Mitochondria and Plasma Membrane. Only the plant cells have a Chloroplast and Cell Wall. Page 1 Real World Connection The students could connect the cell to their school. For example, the principal is the Nucleus. The Nucleolus is the office with the secretary. The Mitochondria could be the teachers and the students could be the vacuole or the cytoplasm. This could be debatable but a legitimate class discussion. Connections across the Curriculum Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity 10. Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts independently and proficiently. Grade 4 Reading Standards for Foundational Skills Strand Standard Foundational Skills Phonics and Word Recognition 3. Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words. a. Use combined knowledge of all letter-sound correspondences, syllabication patterns, and morphology (e.g., roots and affixes) to read accurately unfamiliar multisyllabic words in context and out of contrast. Fluency 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. a. Read grade-level text with purpose and understanding. b. Read grade-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c. Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary. References The information I received in regards to Cell Walls, came from the below web site: http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_wall.html I received my vocabulary definitions/information from the below web page: http://teachertech.rice.edu/Participants/dawsonm/cells/partsdef.htm I used the below reference to get the idea on card sorts: Science Formative Assessment, by Page Keely; pages 56-59 Page 2