Name: :______ Period:______ Fundamentals of Business Review
advertisement
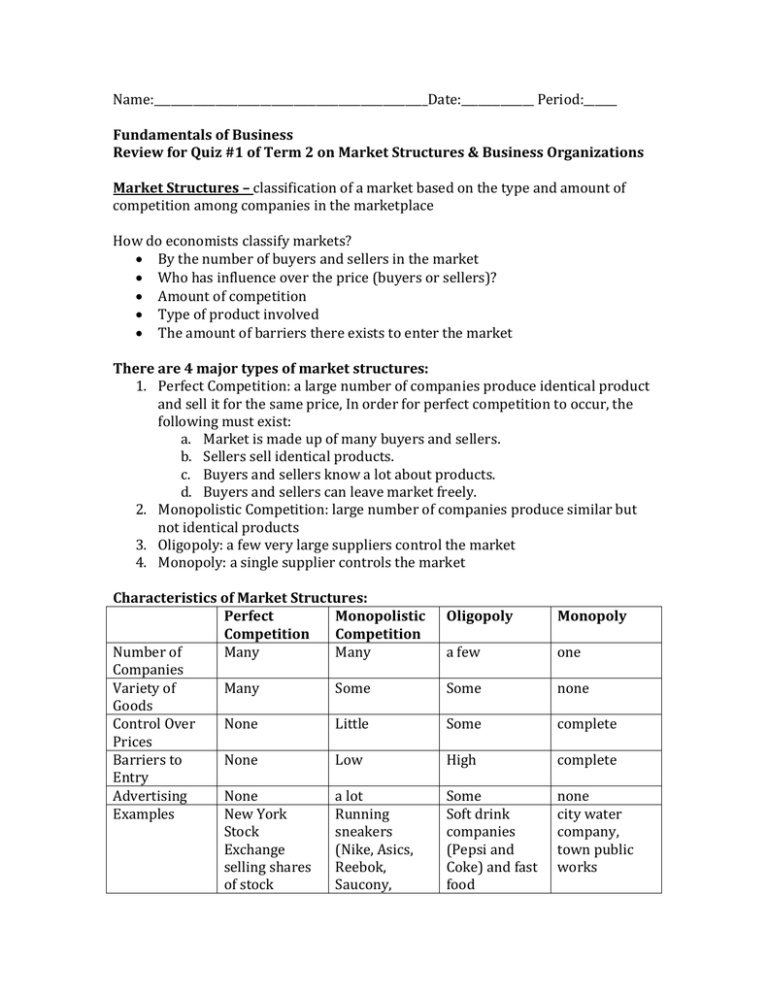
Name:_________________________________________________Date:_____________ Period:______ Fundamentals of Business Review for Quiz #1 of Term 2 on Market Structures & Business Organizations Market Structures – classification of a market based on the type and amount of competition among companies in the marketplace How do economists classify markets? By the number of buyers and sellers in the market Who has influence over the price (buyers or sellers)? Amount of competition Type of product involved The amount of barriers there exists to enter the market There are 4 major types of market structures: 1. Perfect Competition: a large number of companies produce identical product and sell it for the same price, In order for perfect competition to occur, the following must exist: a. Market is made up of many buyers and sellers. b. Sellers sell identical products. c. Buyers and sellers know a lot about products. d. Buyers and sellers can leave market freely. 2. Monopolistic Competition: large number of companies produce similar but not identical products 3. Oligopoly: a few very large suppliers control the market 4. Monopoly: a single supplier controls the market Characteristics of Market Structures: Perfect Monopolistic Competition Competition Number of Many Many Companies Variety of Many Some Goods Control Over None Little Prices Barriers to None Low Entry Advertising None a lot Examples New York Running Stock sneakers Exchange (Nike, Asics, selling shares Reebok, of stock Saucony, Oligopoly Monopoly a few one Some none Some complete High complete Some Soft drink companies (Pepsi and Coke) and fast food none city water company, town public works Under Amour,) (McDonalds and Burger King) Types of Business Organizations 1. Sole Proprietorship: is a business owned by one person who is responsible for all debts and profits. It can be run from a person’s home, or storefront. Examples include small local restaurants, barber shop, small local landscaping business. a. Advantages Easy to start Obtain a business license Complete control over business Owner is responsible for all debts and keeps all profits b. Disadvantages Owner has unlimited personal liability (individual may have to sell own personal property if business fails Difficult to obtain financing 2. Partnership: is a business that is owned by 2 or more people. A contract details the roles and responsibilities of each partner. (Examples include law firms, small medical or dental office and accounting firms.) a. Advantages Easy to start Obtain a business license Shared control over business, risks and rewards Easier to obtain financing than Sole Proprietorships b. Disadvantages Partners need to work cooperatively for a successful business venture to work. 3. Corporation: is a business organization that has all the rights of an individual. It has the right to buy and sell property and enter into legal contracts. 20% of businesses in the US are corporations but they make up 90% of all sales. Businesses need a charter, an official paper from the government to start the corporation. It states how many shares of stock the corporation has. People who own stock in company are called stockholders. a. Advantages Easy to raise capital Owners can hire professional managers to run their company Shared control over business, risks and rewards Easier to obtain financing than Sole Proprietorships b. Disadvantages Difficult to start More regulated than other business organizations Functions of Business Include: Production: process of creating, expanding , manufacturing or improving goods or services Marketing: process of planning, pricing, promoting, selling and distributing ideas, goods, and services Management: process of achieving company goals by planning, organizing, directing controlling and evaluating resources Finance: business or art of money management Accounting: involves maintaining and checking records, handling bills and preparing financial reports for a business Types of Businesses by Activities Producers: business that gathers raw or natural goods Processors: changes raw materials into more finished product Manufacturers: business that makes finished product out of processed goods Wholesalers: distributor of good Retail: purchases goods from a wholesaler and sells them to consumer









