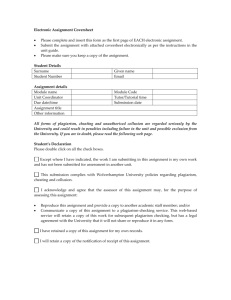
TurnitinUK

Using the Turn
it
inUK Service via
WebCT
Jim Sharp - CAP
Hotline plagiarism@qmu.ac.uk
Overview
• The extent of plagiarism in the UK
• QMU approach – avoiding the “arms war”
• Introduction to the TurnitinUK service
• Embedding TurnitinUk within WebCT
• Student use within WebCT
• Interpreting “originality” reports
• Conclusions
2
The Bigger Picture….
• 17 March 2006 - One in three students cheats, survey finds
One-third of students admit to cheating at university by copying ideas from books or the internet, according to the results of a survey published today in The Times Higher Education Supplement . The statistics come to light only a day after Oxford University warned that plagiarism by its students could threaten the value of its degrees.
The survey, based on 1,022 undergraduates at 119 universities and colleges, found that one in six students admitted they copied work from friends while 10 per cent said they looked for essays online.
Male students were more likely to copy work from their friends (21 per cent) than female students (14 per cent), the study revealed.
Nearly half of male students (45 per cent) said they copied from their friends for group assignments, compared with 29 per cent of female students, the researchers discovered.
3
Student View?
4
Essay Banks (Cheat Sites)
‘Essays’ can be available for as little as £4.99
• www.oxbridgewriters.com
• www.ukessays.com
(notorious
– try it!)
• http://www.academicdb.com/
(does your essay feature here?)
• www.lawteacher.net/essaybank.html
• www.DissertationsAndAssignments.com
• www.essayrelief.co.uk
• www.EssayAcademy.com
• www.nonplagiarizedessays.co.uk
• www.ebay.co.uk
5
Essay Banks (Good Guys)
• www.coursework.info
• www.thestudentroom.co.uk
6
Exercise – your experience
A recent survey of both students and staff at Northumbria University ascertained the proportions of students who believed certain forms of cheating to be common (Dordoy, 2002).
From your experience and intuition complete the supplied pro-forma with your best guess at these proportions (the percentages need not add up to 100%)
Then check your answers with the next slide.
7
Plagiarism in the UK
A recent survey of both students and staff at Northumbria University ascertained the proportions of both staff and students who believed certain forms of cheating to be common (Dordoy, 2002).
Proportion thinking that cheating is ‘common’ (i.e. more than 10% cases)
Copying a few paragraphs from a book/internet un-cited
Copying most of an assignment from some source
Downloading a whole essay from a cheat site on the internet
Buying an essay from a ghost-writing service
Cheating in an exam
Making up data for a project or lab class
Working with another student on work that is meant to be individual
Passing off others’ ideas/images/designs as your own
Staff %
(n=155)
71
15
3
2
4
20
62
45 77
Students %
(n=140)
74
24
11
11
21
60
77
8
The QMU Approach - 1
• One of the key elements of our approach is to avoid a ‘them and us’ situation caused by a perception of being “policed”
• It is tempting to believe that a problem exacerbated by ICT (eg the Internet) can be solved by ICT (eg the TurnitinUK service)
• Cole & Kiss (2000) describe a situation in American
Universities where ‘cheaters’ are using devices such as silent pagers and tiny video cameras to gain marks which in turn requires lecturers to deploy forensic linguistics to detect plagiarism
• They describe this as a ‘dispiriting arms race’ and is certainly something we at QMU want to avoid.
• Already happening in TurnitinUK with Word macros. (YouTube video)
9
The QMU Approach - 2
• Using workshops where appropriate, we are operating what Carroll & Appleton (2001) describe as a “balanced institutional response” including:
– Creating a climate that discourages plagiarism
– Ensuring that students know what plagiarism is
– Teaching students paraphrasing/referencing skills to avoid plagiarism
– Encouraging tutors to ‘design out’ opportunities for plagiarism
Note: persistent plagiarism suggests a problem with an instrument of assessment
– Introducing the judicious use of electronic aids ie TurnitinUK
(Note that these steps should not be confused with the need for a well defined disciplinary procedure for when serious plagiarism is detected.
This procedure should be clearly separated from the assessment process.)
10
The QMU Approach - 3
• In practical terms plagiarism can occur as a result of:
1. Poor academic practice (eg inadequate paraphrasing/referencing)
2. Copying from published material (eg cut & paste from internet)
3. Outright deception (eg purchase/commisioning of work, collusion)
• Two further aspects at marking time are:
1. Intention – the student’s intention to deceive the marker on a scale of 0 to 10
2. Proportionality – the amount of plagiarism expressed as a % of the submission
11
TurnitinUK – An introduction
• QMU is a registered user of the TurnitinUK service available via
WebCT (also available at www.submit.ac.uk
)
• This web-based service compares submitted assignments against
– a database of over 11.4 billion web pages (in 2008)
– plus a range of electronic sources (eg Emerald, Gale InfoTrac )
– The CrossRef database
– plus thousands of previously submitted assignments (> 65 million 2008)
• It then produces an “originality report” that identifies sections of matching text within a submission and providing links to the original sources.
• This service is free to all QMU tutors and students.
• The intention is that students will routinely submit their assignments to the service and use the originality reports generated as re-assurance that they have referenced appropriately.
12
How it works
• John Baillie and some colleagues at Berkeley designed a method of analysing sound patterns which produced an n-dimensioned space
“footprint” or “dot diagram”
• If this process was repeated on other patterns a clear % match could be established between the footprints
• John used this research to develop the software that became TurnitinUK
• Note that the pattern cannot be reverse engineered into a student submission.
13
Submitted Work
Dot Diagram
“Footprint” for matching
14
Turnit
in
UK – the process
1.
For any assessed piece of work, the Tutor uses “Build” mode in a WebCT module to create a TurnitinUk
“assignment”, this appears as a “Content Link”
2. When ready, the student submits work via the relevant assignment link in WebCT. The TurnitinUK service then matches the work against the various databases, generating an “originality report” for the student
3.
Student checks the “matches” in their originality report and makes any necessary changes to the work. The student can resubmit for a further check.
17
18
Sample Report
Print, refresh, download
Fine Tuning
This is OK
– it’s referenced
This is OK – it’s seven words, the minimum match
This is referenced but the paraphrasing could be improved
This is OK – it’s referenced but might be improved with quotes
19
20
• Problem area – no reference, no paraphrasing. This is plagiarism.
Other Class Data Sources
• The matching process includes all previous student submissions to the Service
• This includes those to another tutor’s class area, even in another HE Institution.
• If a match is found across areas, the service will not display the matched text because of the
TurnitinUk privacy policy
• Instead the student is advised to seek permission from the other tutor to view the text
• If this happens you and that tutor might want to consider the implications
21
Adding TiiUK to a webCT module
• Always use one of the “plugins”
• Ready made learning modules that can be imported into any webCT module
• Includes a placeholder for the TiiUK link
• Puts TiiUK in context
• Two versions:
– Study Skills + Plagiarism for levels 2 & 3
– Plagiarism only for levels 3 and above
• Can be downloaded with instructions from QMU plagiarism web site
– http://mcs.qmu.ac.uk/plagiarism
22
Adding Content Link
Select TurnitinUK Assignment
23
TurnitinUK Assignment – First steps
Click on the “Create TurnitinUk Assignment” button
Enter a title eg First Essay and click “Create …” button
24
TurnitinUK – assignment type
Click “next step”
25
TurnitinUK Assignment – setting up
• Enter a title
• Enter a possible mark for this component if using GradeMark
• Start date will be set to current date
•
Due date is the submission deadline
•
Post date is the date that results will be returned to students if using GradeMark
•
Click on (more options) for advanced assignment options
26
TurnitinUK Assignment – options 1
Normally ‘no’ unless using GradeMark
Always ‘yes’
Always set to this
Usually ‘no’ but can be
‘yes’ if required
Usually ‘no’ but can be
‘yes’ if required
27
TurnitinUK Assignment – options 2
Best as ‘yes’ and 1% , makes report easier to read
Always ‘yes (critical)
Always ‘yes’, submission after the due date will be flagged as ‘late’
Always ‘yes for QMU
Leave these sections as is
When complete, click on the
‘submit’ button
28
More options – recommended settings
• Would you like to select a QuickMark set? = no
• Generate Originality Reports for submissions = yes
• Generate Originality Reports for student submissions = "immediately
(can overwrite reports until due date)"
• Exclude bibliographic materials from Similarity Index for all papers in this assignment? = yes (this stops the bibliography being matched)
• Exclude quoted materials from Similarity Index for all papers in this assignment? = no
• Exclude small matches? = yes and set to 1% (makes for a clearer report for students) Be aware that students may get 0% reports!
• Allow students to see Originality Reports? = yes
• Allow submissions after the due date? = yes
• Allow anonymous marking? = yes
29
TurnitinUK Assignment
– the link
• Move the link from the bottom to below the “placeholder”
(“Tutor to put TiiUK link here”) by ticking the select box alongside the link and then the arrow in the leftmost column in the line below the placeholder.
• Now delete the placeholder by choosing “delete” from the drop down arrow to the right of the placeholder.
30
TurnitinUK Assignment – tutor “inbox”
In Teach Mode clicking on the assignment link displays the “assignment inbox”
• To see a student name click on the “Anonymous marking” button. The name will only be displayed if a good reason is given.
• Clicking on the icon will display the contents of that originality report
• The large “Submit Paper” button allows a tutor to submit a piece of work on behalf of a student
• The “Roster Sync” button makes sure that all students on the module are also enrolled on the TurnitinUK assignment (good for late enrolments)
• To edit the assignment settings eg change the dates, click on the “Edit assignment settings” link above the submission lines or the “edit assignment” tab in top row
• If you want to mark a submission online click on the icon in the GRADEMARK column
• .
31
Other tasks
Some actions on the inbox will bring up an additional toolbar similar to this:
These actions are:
1 To download a student submission to your local file space, click on the .doc item in the “file” column and click on the “Download” button
2 To download all the submissions as a single zip file, tick the author column first to select all of them and then click on the “Download” button
3 To delete a submission select it with a tick and click on the “Delete” button (Note that this does not delete the submissions “electronic footprint” from the TurnitinUK database)
32
Please remember …
• Academic judgement is essential when interpreting the report
– % scores can be misleading
– try including/excluding reference list/quotations
– always check matches for referencing
– look out for plagiarism “rings”
– take care with
situations
• The Turnit in UK service is only one tool in the
QMU “plagiarism toolbox”
33
Restrictions
• Please be aware that the TurnitinUK links are only “live” for the lifetime of the module. This means that when the module is archived and restored (or copied forward to a new academic session):
– the link will be there but will not link to the previous student submissions. You can however create a new one and a new assignment.
– If you are using Grademark, you will no longer be able to see the marked-up submissions but the marks will still be in the gradebook.
• In practice this means that current QMU practice via Assignment drop boxes/ School Office downloads should be continued.
34
How Students submit - 1
When a student clicks on the TurnitinUK link for the first time, they will see a screen similar to the following:
They can now click on the “submit” icon to submit a piece of work for checking by
TurnitinUK.
35
How Students submit - 2
• Note the restriction on file types
• First and last names will be provided by webCT
• Student must supply a
“submission title”
• Clicking on “Browse” provides access to the student file space where they can navigate to the piece of work to be submitted
36
Students inbox - 1
The student inbox will now look like this:
They should now click on the “Show details link
37
Students inbox - 2
Until the report is generated there will be a greyed out icon in the student’s inbox:
Once generated the icon will have a colour and a %:
The student can now click on the coloured icon to view the originality report
38
39
Warning !!!
• Please note that while the first submission will come through rapidly, second and subsequent submissions will each be delayed by 24 hours.
• This is deliberate and was introduced to prevent the occasional student repeatedly trying to “wash” their assignment of TiiuK matches by changing odd words and resubmitting again and again
• In other words students should not wait until near the deadline to start using TiiUK.
• Better to put a first draft through and if necessary re-submit for a final check.
Late Submissions
With the option “can submit after due date” set to “yes”:
• Student can submit once and be flagged as “late”
• To submit a second time after the due date the tutor has to delete the existing attempt first.
40
Reminders
• % needs to be investigated
• Is the % to be with or without bibliography/quotes - affects %
• Discard small matches – what % ?
• Check “+options” – can students see reports?
• First submission quick but 24hr delay after
• WebCT Plugins
41
Signposts to Resources
•
Hotline plagiarism@qmu.ac.uk
•
Website http://mcs.qmu.ac.uk/plagiarism
– Examples of originality reports
– This presentation online
– Tutor Quick Start Guide
– Student Quick Start Guide
– List of “Cheat” sites
– Access to referencing guides via Library website
– Access to relevant QMU regulations
– Hints on assessment design (Leeds University)
•
Plagiarism Workshops for staff
– Teaching paraphrasing and referencing skills
– Designing assessments to minimise plagiarism
•
CAP website
– http://www.qmu.ac.uk/cap/appsCAP-TurnitinUk.htm
• Study Skills website
– www.qmu.ac.uk/futurefocus
42
Bibliography
•
Franklyn-
Stokes,A. and Newstead,S. (1995), ‘Undergraduate cheating: who does what and why?’
Studies in Higher Education , 20 (2), 159-172.
• Newstead, S., FranklynStokes, A. and Armstead, P. (1996), ‘Individual differences in student cheating’, Journal of Educational Psychology , 88 (2), 229-241.
• Dordoy, A. (2002), ‘Cheating and Plagiarism: Staff and Student Perceptions at
Northumbria’, University of Northumbria Conference on Plagiarism [on-line] http://www.jiscpas.ac.uk/images/bin/AD.doc
• Carroll, J. and Appleton, J. (2001), ‘Plagiarism: A Good Practice Guide’, Oxford
Brookes University Guide Series [on-line] http://www.jiscpas.ac.uk/apppage.cgi?USERPAGE=6202
• Cole, S. and Kiss, E. (2000), ‘What can we do about student cheating?’, About
Campus , May-June, 5-12.
•
Other reading
– ‘Plagiarism and Poor Academic Practice – A Threat to the Extension of e-
Learning in Higher Education?’
Mike Hart,
King Alfred’s University College,
Winchester, UK, and Tim Friesner, University College Chichester, UK [on-line] http://www.ejel.org/volume-2/vol2-issue1/issue1-art25.htm
43