F.6 Chemistry Project Dipole-dipole interaction and its application
advertisement

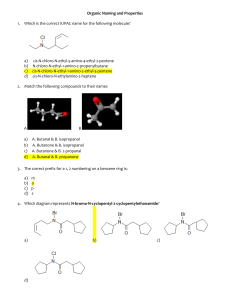
F.6 Chemistry Project Dipole-dipole interaction and its application Fung Chun Yu (8) Kwok Chun Nga (9) Chan Wai Sum (5) Introduction • What is dipole-dipole interaction? – The difference in electronegativities between elements in a covalent bond produces a certain degree of polarization – The electron cloud is distorted, and a dipole is produced Introduction • What is dipole-dipole interaction? – example can be seen in hydrogen chloride (HCl) – Cl, being more electronegative, pulls the electron cloud towards it Distortion of electron cloud – The positive end attracts the negative end the molecules are packed regularly in a head-to- tail fashion Introduction An illustration of the head-to-tail arrangement of molecules due to dipole-dipole interaction Introduction An extraordinarily simple animation showing the interaction between HCl molecules Application of dipole-dipole interaction –LCD –Biological field Liquid Crystal Display • consists of two sheets of polarizing material with a liquid crystal solution in between • can be orientated into a a desired direction under current. • light will be polarized by this pattern Why can the liquid crystal be arranged by electricity? Liquid Crystal Display • liquid crystal molecule used is introduced below • Methoxybenzilidene Butylanaline (MBBA) • p-decyloxybenzylidene p'- amino 2-methylbutylcinnamate (DOBAMBC) Liquid Crystal Display • The molecules are dipoles • they twist the plane of polarization originally • They are aligned regularly in a head-to-tail fashion as mentioned above when electric field is applied formed a polaroid • light is then blocked Biological Field • Molecular arrangement of protein There are four levels of protein structure Primary level arrangement of amino acid Secondary structure helical coiling of the peptide Biological Field Tertiary structure spatial relationship of different secondary structures Quaternary structure How can we stabilize the protein structure??? Biological Field • Polypeptide is a long chain molecule • Dipole is present in polypeptide • Interactions including Dipole – dipole interaction stabilize the structure Biological Field • Example: Haemoglobin Consists of four protein subunits + haem molecule Formation of haemoglobin involved dipole-dipole interaction Dipole-dipole interaction allow the haemoglobin to take its final shape Acknowledgement • Wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/ • http://www.gullwinguk.com • http://bucarotechelp.com/computers/anatom y/91060003.asp The End