Faith and Religion
advertisement

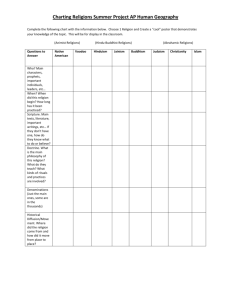
Introduction to SCTR 19 Prof. Felix Just, S.J. Religion & Religious Studies What Is “Religion”? Theological Beliefs? Spiritual Practices? Ethical Injunctions? Communal or Individual? Believing in God (or gods)? Defining “Religion” Quality of Definitions (cf. Kessler, pp. 17-20) Usefulness (applicable to reality) Precision (not too broad, nor too narrow) Lack of Bias (as much as possible) Types of Definitions Essential Defs. (Theoretical, Deductive) Descriptive Defs. (Experiential, Inductive) Dictionary Definitions Dictionary.com Thesaurus.com What are “Religious Studies”? “Insider” Perspectives by adherents, believers, members “Outsider” Perspectives by scholars, observers, adherents of other religions Qualities necessary for academic study: Openness & Honesty Critical Intelligence & Tolerance Careful Reading & Listening Asking Questions / Seeking Understanding Religion < Latin religio ("fidelity"); religare ("to bind fast, adhere to") "adherence to someone (a god) or something (a belief)" Theology < Greek theos ("God") + logos ("word, sentence, speech") "study of God; talking about God" & related topics Philosophy < Greek philos ("friend; lover") + sophia ("wisdom") “love of wisdom” or quest for knowledge and truth Studying God & Religion through the Centuries Ancient World: no specialized “theologians” Greece: Philosophers Israel: Prophets & Priests Other Cultures: Magi, Physicians, Kings, etc. Medieval Universities: Four Main Disciplines: Philosophy, Theology, Medicine, Law Modern Universities: Liberal Arts, Humanities, Social Sciences, Natural Sciences, Engineering, Art, Business, Education, Religious Studies, etc. Post-Modern World: More interdisciplinary: “Religion and XYZ” Religious Questions – vs. – Religious Studies Questions Questions Religions seek to answer: God? World? Humans? Life? Death? Afterlife? Heaven / Hell? Good vs. Evil? Holy / Sacred? Revelation & Prayer? Questions scholars ask about Religion(s): Anthropological, Psychological, Sociological, etc. Comparative, or about particular religions, their: Foundations, History, Beliefs, Practices, Structures Studying World Religions: History & Development Historical Foundations & Growth Branches, Divisions, Demographics Beliefs & Practices Scriptural & other Foundational Texts Theological & Ethical Teachings Liturgical & Spiritual Practices Structures & Relationships Organization & Leadership Internal Rules; External Relations World Religions: Main Eastern Religions South Asia: Buddhism, Hinduism, Sikhism, Jainism East Asia: Taoism, Confucianism, Buddhism, Shinto Main Western Religions (“Religions of the Book”?) Judaism; Christianity; Islam Local/Tribal Religions: Animist Practices, Ancestor Worship New Religious Movements: Cults, Sects, Splinter Groups “Religion” in Bible and Qur’an Judaism: “Shema” (Deut 6:4-9) “Decalogue” (Exod 20; Deut 5) Christianity: “Greatest Commandment” (Luke 10:27 & par.) “Religion” in James (1:26-27) Islam: “Fatihah” (Qur’an 1:1-7) “Shahada” (cf. Qur’an 38:65; 33:40) Questions for Group Discussion and/or Personal Reflection: What is religion? How would you define “religion”? In what ways is religion important/influential in our world today? …in our own country? …in your own community? …in your own family? What are some of the positive effects or benefits of religion? In what ways has religion helped people and/or improved our world? What are some of the negative effects or downsides of religion? In what ways has religion harmed people and/or impaired life? In which religion were you raised, if any? How well do you understand it? How actively do you practice it? Have you chosen a different religion? What aspects of your former religion did not satisfy you? What aspects of the new religion most attracted you?