The media team was challenged to develop a package that best
advertisement

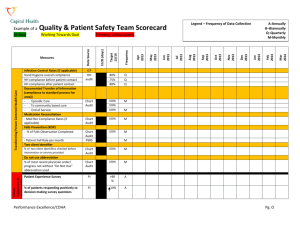
Measuring the Effectiveness of Employee Communications A General Motors Case Study Kathy Collins Director, Communications Research GM’s PR measurement process captures inputs from many constituents Asia-Pacific Business Partners Communities Customers Employees Financial Community Influentials Media Policy Makers Shareholders Europe LAAM North America GM’s recent history GM’s Market Share Key Events Competitive pressures increase 50.0% 45.0% Market share declines 40.0% 35.0% Major internal reorganizations 30.0% 25.0% Management goes through phases of denial, reorganizations, then recommits to business basics 20.0% 15.0% 10.0% 5.0% 1999 1980 0.0% Employees make a huge impression …. 1 in 5 adult Americans knows and regularly talks with a GM employee Employee contact is one of the most credible sources of information about products about the company A two-day corporate benchmarking symposium: GM hosts 13 world-class communicators 3M AT&T Florida Power and Light Hewlett-Packard IBM Motorola Ritz-Carlton Royal Bank of Canada Royal Bank of Scotland Southwest Airlines SRC Holdings Corporation Texas Instruments Whirlpool The process is based on seven building blocks of effective internal communication Actively Engage Employees In The Business Leaders Must Drive Communications Focus On Deeds Not Words Craft Clear, Relevant Messages Use FaceTo-Face Communications Communicate With Measure Employees Communication Openly, Performance Frequently, And First Performance GM “deep dives” into key communication elements Improvement Process Objective To establish a communications structure and process to improve business performance Improvement Process Structure Message Content Message Development Process External Benchmarking Common Process Media Measurements The communication improvement plan starts with best practices • Business leaders will drive communications using face-to-face meetings and “Winning Together” theme • Sites will implement a common communications process — Common activities — Overarching theme and six key messages — Upgraded media tools and technology — Site Business Communications Integrators • Each site’s process, capability and overall effectiveness will be measured and tied to business results Goal • Actively engage all employees • Improve business performance Management leads communication measurement with these requirements One number per location that local and divisional leaders can manage Added to the overall divisional performance measurement process Structured around common processes to be implemented at every site in North America The internal communication process will be measured and tied to business plan objectives Communication Plan In Support Of Business Plan Measurements Process Audit Problem Resolution Communicate Messages Process Capability Scorecard And Insight Generation Overall Effectiveness Metrics Staged to Accommodate Variability of Site Communications Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Minimum measurements across the sites Raise the bar Part of the performance scorecard • Communications Activity Inventory • Communications Activity Inventory • Communications Activity Inventory • Activity Process Audit • Activity Process Audit • Activity Process Audit • Mechanism Evaluation • Mechanism Evaluation • Mechanism Evaluation • Environmental Surveys • Environmental Surveys • Environmental Surveys • Business Goal Attainment • Business Goal Attainment • Process evaluations • Business Goal Attainment • Process evaluations • Standardized, numerically based metric for sites Communication Scorecard Outline Common Process Activity Frequency Actual Occurrences Planned Occurrences Content Standards Effectiveness Score Department/Team Meetings Diagonal Slice Meetings ____% (X) ____% (X) Number (=) Number Newsletters/Written Communications Quarterly Business Updates State of the Business Meetings Environmental Survey Environmental Score Total Score The frequency audit measures actual vs. planned occurrences of each common process activity Common Process Activity Minimum GMNA Level Planned Occurrences (Inventory) Department/Team Meetings • Monthly = 12 Diagonal Slice Meetings • Each employee = 1 (execs w/ >100, monthly; execs with <100, quarterly) Newsletters/Written Communications • Site newsletter — weekly = 48 • Division newsletter — monthly = 12 Quarterly Business Update • Quarterly = 4 State Of The Business Meetings • Annual = 1 Each process activity’s capabilities will be based on specified attributes and established goals Exploded View of Standards for Department/ Team Meetings Common Process Activity Department/ Team Meetings Content Standards Capability Goal Attendance Operations content Area/Dept goals content External content Dialogue, Q&A time 100% 35% 25% 10% 30% Total Each process is measured by degreesfrom being informed - to taking action Score/level of action taken by employee Communication Action Strategy Correlation 0 = No business information available through this process 1 = Business information is barely available through this process 2 = Occasional reference to business goals in this process Information 3 = Business information is generally available in this process 4 = Dialogue is taking place regarding business issues in response to this process 5 = This process helps explain how business goals affect employees Understanding 6 = Employees can describe how local leadership is involved in supporting business goals as a result of this process 7 = Employees can articulate personal role in business issues Commitment 8 = Employees can explain what actions they personally need to take in support of their locations business goals as a result of this process 9 = Employees can describe what actions they took to support business goals as a result of this process 10 = Employee actions resulting from this process have improved business performance Action Business performance improves A communication scorecard for a site could look like this… Common Process Activity Frequency Actual Occurrences Planned Occurrences Content Standards Department/Team Meetings 90% 80% 6 =4.3 Diagonal Slice Meetings 100% 90% 8 =7.2 Newsletters/Written Communications 95% 75% 6 =4.3 Quarterly Business Updates 100% 70% 5 =3.5 State of the Business Meetings 100% 90% 5 =4.5 Environmental Score Total Score Effectiveness Score 6.5 =30.3 Relevant to Msgs, SW, & Media The math behind the single communication scorecard-type metric Standardized Work Mechanism Capability Actual Occurrences Planned Occurrences Process Effectiveness(1) Score (Inventory & Audit) Newsletters (Written Communications) Actual Planned Department & Area Managers Meetings Actual State of Business Meetings Actual Diagonal Slice Meetings Actual Business Updates (Satellite Broadcasts) Actual Planned Planned Planned Planned Capability Goal Attain 0 = __% Total Capability (Xi)/n = __% Goal Attain 0 = __% Total Capability (Xi)/n = __% Goal Attain 0 = __% Total Capability (Xi)/n = __% Goal Attain 0 = __% Total Capability (Xi)/n = __% Goal Attain 0 = __% Total (Xi)/n = __% 2 4 6 8 10 Max = 10.0 = __ (number) 2 4 6 8 10 Max = 10.0 = __ (number) 2 4 6 8 10 Max = 10.0 = __ (number) 2 4 6 8 10 Max = 10.0 = __ (number) 2 4 6 8 = __ (number) 10 Max = 10.0 Viewpoint Score Max = 10.0 Total Score Max = 60.0 Notes: (1) Gathered from CC Integrator Process Evals & Standardized Work feedback: obtain general level of EE understanding of key information Key Communications Effectiveness Measures (Base for Environmental Score) My supervisor acts on my ideas, suggestions and concerns. I have the opportunity to participate in solving problems that affect my job. My supervisor is kept well-informed by upper management. Communication here is well-planned and efficient. My plant or staff is well-organized and efficient. Management and employees here are all working toward the same objectives. I have the tools and information I need to make a full contribution here. My plant or staff provides me with information about the company. I understand the reasons for decisions within my plant or staff that affect me. Top management is visible and accessible. Overall communications are improving in my plant or staff. Is the effectiveness score over or under five? Under Over Always do, regardless of score Identify common processes that do not meet the standard Review survey and/or focus group data. Identify environmental elements that contribute to communication effectiveness Review viewpoint survey and/or focus group data. Identify environmental elements that Do Not contribute to communication effectiveness Low scores on effectiveness should generate insight and new business and communications plans define corrective action Put plans in place to maintain good communication environment Prioritize those elements that make most significant negative Impact on communication effectiveness Develop corrective action plan to address environmental issues. involve site steering committee Summary points Process GM has a common process for communications across North America Management and Communications have a common process they can communicate through together Scorecard Scorecard balances different elements (frequency, content, effectiveness and third-party surveys) to create credibility Management has a measurement tool that they understand and accept Management drives the process and manages the measurement Scorecard facilitates implementation and improvements Communications people now have data to take to management — not just “feelings”