Blood Composition
advertisement

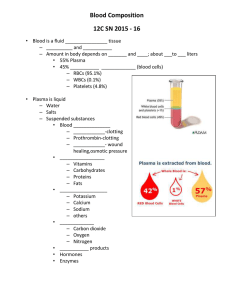
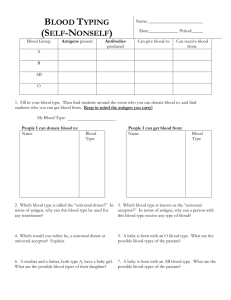
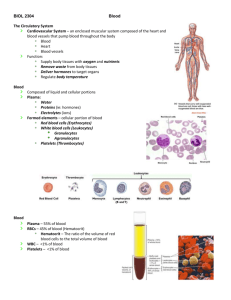
Blood Composition 2015 - 2016 12 C Flurkey Blood composition • Blood is a fluid connective tissue – Liquids and solids – Amount in body depends on size and sex; about 4 to 6 liters • 55% Plasma • 45% formed elements (blood cells) –RBCs (95.1%) –WBCs (0.1%) –Platelets (4.8%) Blood Composition • Plasma is liquid – Water – Salts – Suspended substances • Blood proteins – Fibrinogen - clotting – Prothrombin - clotting – Albumin – wound healing & osmotic pressure • Nutrients – Vitamins – Carbohydrates – Proteins – Fats • Electrolytes – – – – Potassium Calcium Sodium others • Gases – Carbon dioxide – Oxygen – Nitrogen • Waste products • Hormones • Enzymes Centrifuge Blood Composition • Major components are plasma and formed elements Blood Functions • Regulates homeostasis: – Body temperature – Water content of cells – pH level • Acidity or alkalinity – Blood pressure • Protects – Clotting – Immunity • Phagocytosis • Makes Antibodies Blood Functions • Transports to and from 75 trillion body cells – Oxygen from lungs to body cells – Carbon dioxide from body cells to lungs – Nutrients from digestive tract to body cells – Metabolic and waste products from body cells to organs of excretion (kidneys, lungs, skin, GI tract) – Heat produced by muscles – Hormones produced by endocrine glands to targeted tissues or organs Blood • All blood cells are formed in bone marrow through a process called hemopoiesis • Three main types of Formed Elements (blood cells): – Erythrocytes – Leukocytes – Thrombocytes Blood Cells – Formed Elements • Erythrocytes – RBCs – Produced in red bone marrow • ~1 million/min. – Live ~120 days – 4.5 – 5.5 million per mm3 (1 drop) or 25 trillion in body – Mature cells • lack nucleus (cannot reproduce by mitosis) • shaped like a disc • thinner center – Hemoglobin (Hgb) • Complex protein – Iron compound – heme – Protein – globin • Carries oxygen and carbon dioxide Leukocytes / WBCs • Leukocytes guard from invasion, infection (major part of immune system) • • • 5 Main types: • • • • • Neutrophils Basophils Eosinophils Monocytes Lymphocytes Respond to different types of infections As infections occur, numbers increase, can run blood test to determine type of infection pt has Leukocytes / WBCs Polymorphonuclear (multi-lobed nuclei) granulocytes (granules in cytoplasm) originate from red bone marrow (Myeloid tissue) Neutrophils Basophils Eosinophils Mononuclear (single nucleus) cells originate from myeloid tissue also, but mature in lymphoid tissue. They are agranular. Lymphocytes Monocytes Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes / WBCs • Neutrophils: • • • • • Nucleus with 3-5 lobes (poly morpho nuclear) Cytoplasmic granules 1st responders to arrive, highly motile Innate immune system (not specific) Consume/phagocytize – – – – • Harmful bacteria Fungi Other foreign invaders/antigens Phagocytosis - process in which neutrophils surround and ingest invader (antigen) by using lysosomes to release powerful enzymes Increased number of neutrophils indicates a non-specific infection Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes / WBCs • Basophils: • • • • • Irregular shaped, bi-lobed nucleus (polymorphonuclear) Blue-black granules in cytoplasm Participate in innate immune response toward • • Allergies – release histamines that produce allergy sxs and inflammation Parasites Important also because they secrete a chemical, heparin, which thins blood Increased number indicates allergy or parasitic invasion Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes / WBCs • Eosinophils: • • • • • Coarse granules Bi-lobed nucleus (polymorphonuclear) Circulate • • in blood 8 – 12 hours In tissue up to 12 days Produce antihistamines to • • Combat allergy sxs Remove toxins Increased numbers usually indicates an allergy Mononuclear Leukocytes / WBCs • Monocytes – Largest WBC – Considered agranular, mononuclear – Circulate in blood plasma 1-3 days – Become Macrophages when travel to tissue • Takes 8 – 12 hours to get to target tisse – Increased number with chronic infections Mononuclear Leukocytes / WBCs • Macrophages (in tissue) – Multi-purpose: • Take longer to arrive than neutrophils, but greater in number • Destroy invaders/antigens in tissue, phagocytosis – Innate/ Non-specific immune system • Antigen Presenting Cells (APC) to Helper T Cells – Specific/Adaptive immune system » Bacteria, fungus, virus, parasites • Active in wound healing by clearing dead cells • Can suppress immune system & promote inflammation – May hold key to autoimmune diseases • Maintain insulin sensitivity in adipose cells of normal wt people; cause insulin resistance in overweight people • Macrophages in lungs are alveolar macrophages, in the liver are Kupffer cells, and in the kidney are called mesangial cells Mononuclear Leukocytes / WBCs • Lymphocytes • • • • • Small WBCs Can pass through capillary walls Agranular, mononuclear In blood plasma and lymph tissue Produce specific antibodies to fight specific antigens – Provide Specific/Adaptive Immunity • Three types of Lymphocytes: – B Cells – T Cells – NK Cells Lymphocytes • B Cells – Release antibodies into blood • Provide Specific/Adaptive Immunity – Produced in bone marrow and mature in bone marrow – Cloned by mitosis when antigens present – Some live for years and have memory • Faster response if infected by same antigen in future Lymphocytes • T Cells – Produced in bone marrow, mature in Thymus gland • Helper T Cells (CD 4+ cells) • bind to antigens, release lymphokines, creates inflammation to wall off & destroy antigens • Activate B Cells, Macrophages, & Cytotoxic T Cells • Cytotoxic T Cells (CD 4+ and CD 8+ cells) • Bind to antigens & destroy them • Destroy cancer • Induce programmed cell death (Apoptosis) – only way to destroy invader living inside a cell • Viruses • Cytoplasmic bacteria, parasites Lymphocytes • T Cells continued • Regulatory T Cells, also called Suppressor T Cells • Tell immune system when to stop • When this malfunctions, can have long-term inflammation or lead to autoimmune disease • Memory T Cells • May live for years • Remember the strategy used to destroy a specific antigen previously Lymphocytes • NK Cells (Natural Killer Cells) – Detect stress-induced molecules – Do not attack invading organisms directly but instead destroy the body's own cells that have either become cancerous or been infected with a virus Thrombocytes / Platelets • Anucleated cell fragments from WBCs called megakaryocytes • Formed in bone marrow • Vary in shape and size; smallest of formed elements • Critical for clotting process – Vessel cut> platelets collect> secrete serotonin so blood flow slows> release thromboplastin> thrombin with fibrinogen> fibrin> fibers form clot Dendritic Cells • Dendritic cells – phagocytic – antigen-presenting cells (APCs) • process antigen material and present it to the surface of T cells • initiate antigen-specific/Adaptive immune responses Blood Composition - Label Blood Types – Fill In Table If you have blood type: RBC Antigen Present Plasma Antibodies A A Anti-B B B Anti-A AB AB None O None Anti-A & Anti-B Universal Recipient Universal Donor Recipient Donor type Donor type Donor type blood type: A B AB A Donor type O Anti-B B AB (Universal Recipient) O (Universal Donor) = Agglutinated blood = Normal blood Type & Cross match • Typed – Recipient cells & serum mixed with known serum type – Clumping if not a match d/t antigens on RBCs – If same type, proceed to cross match • Cross matched – Recipient cells mixed with donor blood – Clumping/ agglutination indicates incompatibility – If compatible (no clumping), may transfuse • Incompatibility can lead to Transfusion reaction – – – – – Fever Hemolytic anemia Renal failure Shock Death • • • • • O pos is most common blood type AB is rarest major blood type AB Universal recipient O Universal Donor Type O can only accept type O • Are about 46 other types, they are rare Rh Factor Blood type RBC Antigen Present Antibodies Present Rh Pos D None Rh Neg None D • First found in the Rhesus monkey • If have Rh factor, called Rh positive • If don’t have it, are Rh negative Pregnancy • Rh pos father and Rh neg mother – 70% of time, fetus inherits Rh pos – During pregnancy or at birth, baby’s blood can mix with mother’s Pregnancy • If Mother and baby mix blood – Mother makes Rh antibodies – With a second pregnancy the mother’s antibodies attack the fetus • • • • Anemia (erythroblastosis fetalis) Brain damage Miscarriage Still birth • Precautions – Know blood types – Take Rho gam shots 3rd trimester and after delivery • Prevents antibody formation in mother