Smart Phone [ Case Study ]1
advertisement
![Smart Phone [ Case Study ]1](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009893129_1-199888e5bd9b187a62cd418637127eb6-768x994.png)
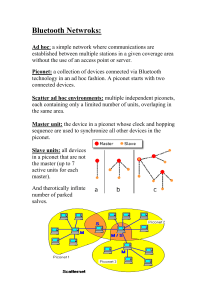
Smart Phone [ Case Study ] Additional Terms-- 1G , 2G , 3G , 4G • 1G-1G is short for first-generation wireless telephone technology. This generation of phones and networks is represented by the brick-sized analog phones introduced in the 1980’s. Subsequent numbers refer to newer and upcoming technology. 1G , 2G , 3G , 4G • 2G--2G phones use digital networks. Going all-digital allowed for the introduction of digital data services, such as SMS and email. 2G networks and their digital nature also made it more difficult to eavesdrop on mobile phone calls. 1G , 2G , 3G , 4G • 3G--3G networks are an in between standard. 3G is seen more as pre4G instead of a standard of its own. The advantage 3G networks have over 2G networks is speed. 3G networks are built to handle the needs of today’s wireless users. This standard of wireless networks increases the speed of internet browsing, picture and video messaging, and handheld GPS use. 1G , 2G , 3G , 4G • • 4G---4G (AKA Beyond 3G) is like the other generations in that its advantage lies in promised increased speeds in data transmission. There is currently no formal definition for 4G, but there are objectives. One of these objectives is for 4G to become a fully IPbased system, much like modern computer networks. The supposed speeds for 4G will be between 100 Mbit/s and 1 Gbit/s. What is Firewire ? • FireWire, also known as IEEE 1394, is one of the fastest peripheral standards ever developed. It was developed by Apple in the 1990s and has been included with Macintosh computers beginning with the Power Macintosh G3 (Blue and White) model. FireWire has been widely adopted as a standard by digital peripheral companies such as Sony, Canon, JVC and Kodak. • FireWire provides a single plug-andsocket connection on which up to 63 devices can be attached with data transfer speeds up to 400 Mbps (megabits per second). The standard describes a serial bus or pathway between one or more peripheral devices and your computer's microprocessor. What is Firewire ? • IEEE 1394 provides two types of data transfer: asynchronous and isochronous. Asynchronous is for traditional load-and-store applications where data transfer can be initiated and an application interrupted as a given length of data arrives in a buffer. Isochronous data transfer ensures that data flows at a pre-set rate so that an application can handle it in a timed way. For multimedia applications, this kind of data transfer reduces the need for buffering and helps ensure a continuous presentation for the viewer. What Makes FireWire Really Special? • FireWire 800 is among the fastest, if not the fastest, general purpose interface you can find. It can reach speeds of up to 800 megabits per second, allowing for the transfer of vast amounts of information in very little time • FireWire also supports multispeed. You can mix all these [age , purpose and quality] on a single bus and still have all devices operate at maximum speed, as the interface can change speeds on a packet-by-packet basis. • FireWire creates peer-to-peer networks and has always done so, meaning devices can talk to each other without requiring a computer, even on complex chains. • FireWire can operate over ultra-long distances—up to 100 meters—opening up possibilities that are unheard of with other technologies. Does FireWire have "plug-andplay" capability? • Answer: Yes, if the FireWire device is designed according to the FireWire standard, the device can be connected and disconnected, while both the device and the Macintosh are turned on. How many FireWire devices can be connected at any one time? • Answer: Fire Wire can work with up to 63 devices on a bus. The number of buspowered devices you can connect depends on the amount of power available from the computer, and the amount of power required by each device. What is i.LINK? • Answer: i.LINK is Sony's name for FireWire. Bluetooth • Bluetooth is a wireless technology for exchanging data over short distances. The chip can be plugged into computers, digital cameras and mobile phones. Bluetooth is a specification for the use of low-power radio communications to wirelessly link phones, computers and other network devices over short distances. Cells( in Mobile phone networks) In half-duplex radio, both transmitters use the same frequency. Only one party can talk at a time. In full-duplex radio, the two transmitters use different frequencies, so both parties can talk at the same time. Cell phones are full-duplex. Channels - A walkie-talkie typically has one channel, and a CB radio has 40 channels. A typical cell phone can communicate on 1,664 channels or more! • In a typical analog cell-phone system in the United States, the cell-phone carrier receives about 800 frequencies to use across the city. The carrier chops up the city into cells. Each cell is typically sized at about 10 square miles (26 square kilometers). Cells are normally thought of as hexagons on a big hexagonal grid, like this: • Because cell phones and base stations use lowpower transmitters, the same frequencies can be reused in non-adjacent cells. The two purple cells can reuse the same frequencies. • Each cell has a base station that consists of a tower and a small building containing the radio equipment. We'll get into base stations later. "cells“-- that make up a cellular system. • A single cell in an analog cell-phone system uses one-seventh of the available duplex voice channels. That is, each cell (of the seven on a hexagonal grid) is using oneseventh of the available channels so it has a unique set of frequencies and there are no collisions What is Frequency hopping ? • FH has mainly the purpose of avoiding interference, • In FH, the information is spread over a bandwidth much larger than is required for its transmission. For this, it is divided into several channels of lower bandwidth. • Knowing the sequence of jumps that must be followed, the receiver and transmitter jump through these channels. What is frequency hopping ? • There are two kinds of frequency hopping • Slow Frequency Hopping (SFH) • Fast Frequency Hopping (FFH) • Slow frequency hopping is a popular technique for wireless LANs. • In GSM telephony, slow frequency hopping can be used, at the discretion of the network control software. It avoids that a stationary terminal that happens to be located in a fade looses its link to the base station. As nearby hopping interferers are unlikely to continuously transmit in the same frequency slot as the reference user, the near-far problem is less severe than in direct sequence (DS) CDMA. Particularly for wireless LANs, where terminals can be located anywhere, this advantage made SFH popular. • In fast Frequency hopping -one data bit is divided over multiple hops. In fast hopping, coherent signal detection is difficult, and seldom used. As a result, using the FH have a signal more robust - interference resistant, and secure - to be very difficult to intercept. What is graffiti ? Graffiti is writing, drawing, or symbols applied to any surface without the permission of the property owner. Graffiti is a form of vandalism and is illegal when it defaces property whether public or private. • SMARTPHONES are being used in the fight against graffiti in Manningham. The new Snap Send Solve app for iPhones allows users to photograph graffiti, vandalism and damaged property and send an instant message complete with location co-ordinates to the relevant council. WIMAX • WiMAX Technology is also one of the emerging wireless technology that provide us high speed mobile data and telecommunication services. WiMAX stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access and it is based on IEEE 802.16 standards.In this technological world, we have so many technologies that help us in every aspect of our daily life such as transportation, communication etc. WiMax is not Wi-fi Nanotechnology • Nanotechnology is an exciting area of scientific development which promises ‘more for less’. It offers ways to create smaller, cheaper, lighter and faster devices that can do more and cleverer things, use less raw materials and consume less energy. Nanotechnology Future smartphone tech: HzO Nanotechnology water-proofing • According to the guys over at PC World, Paul S. Clayson, the CEO of HzO demonstrated the new nanotechnology at a recent New York press preview for CES 2012 in Las Vegas, • Calyson dunks a Samsung Galaxy S II that has been coated HZO’s nanotechnology into a bowl of water, the “nano-scale film barrier” is surrounding the electronics inside the handset and the exterior of the device and allows the device to continue to operate under water. Phishing • Phishing is a fraudulent attempt, usually made through email, to steal your personal information. • Phishing refers to online scams that attempt to trick consumers into revealing personal information, such as check and credit card account numbers, Social Security numbers, or bank account passwords. Most commonly, phishers target unsuspecting users with fake Internet sites or email messages that look startlingly similar to the real thing. This is sometimes referred to as “spoofing.” Scammers may also leverage social networking sites. • Radio is the technology used for communications in Piconet. Radio possesses the • characteristics needed for ad-hoc, peer-to-peer communications in virtually all • configurations and environments Piconet • A network of devices connected in an ad hoc fashion using Bluetooth technology. A piconet is formed when at least two devices, such as a portable PC and a cellular phone, connect. A piconet can support up to eight devices. When a piconet is formed, one device acts as the master while the others act as slaves for the duration of the piconet connection. A piconet is sometimes called a PAN. • The range of Piconet will vary based on the blue tooth device class. The data transfer rate varies around 200 to 2100 KB/S, depending upon the synchronous or asynchronous connection usage, and the number of devices connected in the piconet. Piconet Difference b/w piconet and scatternets • A piconet is the type of connection that is formed between two or more Bluetooth-enabled devices, one device takes the role of 'master', and all other devices assume a 'slave' role for synchronization reasons. • Where as a scatternet is a number of interconnected piconets that supports communication between more than 8 devices. Scatternets can be formed when a member of one piconet (either the master or one of the slaves) elects to participate as a slave in a second, separate piconet. HID- human interface device Thumb wheel • a control for various devices consisting of a partially exposed wheel that can be turned by moving the exposed edge with a finger . USB Port • A USB port is a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronic devices to be connected via cables to a computer • USB is the interface of choice for most home and office peripherals including printers, cameras, modems, and portable storage devices. USB Ports 13 W3 connector DVI-D Dual Co axial BNC “kill” switch • A kill switch is a mechanism used • to shut down or disable machinery or a device or program • Software programs sometimes include encoded kill switches as anti-piracy mechanisms. After installing the software, if a user fails to enter a valid registration key before a specified deadline passes, the software will either stop functioning or continue to function but with reduced capabilities. Microsoft Vista, for example, was designed to operate in "reduced function mode" if the user didn't register the software within 30 days. Kill switch • The kill switch as a "safety lever" or "malware apparatus" used for "removing stuff from devices once it gets out of the perticular market or org[ say Android Market], once it escapes." PDA[ personal digital assistance] • PDAs and smartphones have some similar features and one major difference. A smartphone has a cellular component -- it can be used to make and receive phone calls -- and a PDA cannot. What PDAs can do is organize information. A typical PDA allows you to keep track of your calendar and todo list, it enables you to work on documents, it can be synced with a personal computer or laptop and it can even include Web access or access to specific email programs. Some PDAs can also store and play music and take voice memos. • PDAs are often cheaper than a smartphone over the life of the device. PDA • Smartphones are set up to allow full Web browsing and social networking. Just like PDAs, they can help you organize your life with contact information, calendars, to-do lists and productivity software. Smartphones include a host of multimedia options for storing and listening to music, watching movies and television shows, and taking and sharing photos and video. Another significant difference between PDAs and smartphones is application support. With a smartphone, you can download a wide variety of applications for free or a small fee. Multi touch • Multi-touch is a method of input on a touchscreen that allows two or more fingers to be used on the screen at one time. Apple's iPhone is famous for introducing multi-touch to the cell phone world by using it to allow pinching and stretching gestures on the screen to control zooming. Infra-red • Infrared is an energy similar to visible light, but with a longer wavelength. • The light we see with our eyes is really a very small portion of what is called the "Electromagnetic Spectrum." The Electromagnetic Spectrum includes all types of radiation - from the X-rays used at hospitals, to radio waves used for communication, and even the microwaves you cook food with. Infra-red • PowerPoint presentations and the like are a bit easier to control remotely because, presumably, they are being viewed through a laptop. But the benefit is considerable. No longer tethered to your laptop, you can move around the room while still holding in your hand an image of what’s on the screen behind you. Infra red • Infrared light is even used to heat food sometimes - special lamps that emit thermal infrared waves are often used in fast food restaurants! • Shorter, near infrared waves are not hot at all - in fact you cannot even feel them. These shorter wavelengths are the ones used by your TV's remote control. Jail break • The iPhone, iPod touch & iPad hack that allow users to gain access to the entire Unix filesystem. In Unix terms, this refers to changing the root of the directory tree to . • Jailbreaking is basically modifying the iPhone’s firmware so that you can get access to the internals of its operating system and install a whole slew of third-party applications on your iPhone that are not otherwise available through official channels. Why Would I Want to Jailbreak My Phone? • It lets you do everything from customizing the look of your iPhone to installing third-party applications (such as titles that are not authorized and available in the App Store) and customized ringtones on it. Depending on how far you're willing to go, you can do even more than that: Jailbreaking even lets you to unlock your phone so you can use it with a carrier other than the one from which you purchased it Is Jailbreaking the Same as Unlocking? • No, these are 2 different things, although to unlock your iPhone, you usually have to jailbreak first. As noted above, jailbreaking an iPhone lets you install third party applications and mods on it, while unlocking allows you to use your iPhone with a different carrier Synchronization • Synchronization occurs when a mobile device communicates with applications on a personal computer or a server. This is often referred to simply as a "sync" or a "docking". Research in Motion BlackBerry technicians call it "cradling" when it applies to BlackBerry devices. Synchronization • Synchronization is the process by which Data Protection Manager (DPM) transfers data changes from a protected file server to a DPM server, and then applies the changes to the replica of the protected data. Pharming • Pharming is a scamming practice in which malicious code is installed on a personal computer or server, misdirecting users to fraudulent Web sites without their knowledge or consent. Pharming has been called "phishing without a lure." pharming • Whereas phishing uses fraudulent email messages to lure you to fake Web sites and try to get you to supply personal information like account passwords, pharming attacks redirect you to a hacker's site even when you type the address of a real site into your browser. HAPPY READING !!!!!!