Proprietorships,
Partnerships, and
Corporations
Chapter 8
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
8-2
Learning Objective 1
Identify the primary characteristics of
sole proprietorships, partnerships, and
corporations.
8-3
Forms of Business Organizations
A sole proprietorship
is owned by a
single individual.
A corporation is a
separate legal entity
created by the authority
of a state government.
A partnership is
owned by two or
more individuals.
Each state has
separate laws governing
establishing corporations.
Partnerships require
clear agreements about
authority, risks, and
the sharing of profits
and losses.
8-4
Regulation
Few laws govern the operations
of proprietorships and partnerships.
Corporations are subject to regulations.
Large, publicly traded corporations
are much more heavily regulated than
smaller closely held corporations.
SEC Acts of 1933 and 1934
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
Exchange listing requirements.
8-5
Comparing Corporations with
Proprietorships and Partnerships
Corporate Advantages
Separate legal Entity
Limited liability of stockholders
Continuous life
Management Structure
Easily transferable ownership rights
Ability to raise capital
Corporate Disadvantages
Governmental regulation
Corporate double taxation
8-6
Corporate Management Structure
Stockholders
(Owners of voting shares)
Appointed
by directors
Board of Directors
Internal (managers) and
External (non-managers)
Elected by
shareholders
President
Vice President
(Production)
Vice President
(Marketing)
Vice President
(Finance)
Vice President
(Personnel)
8-7
Learning Objective 2
Analyze financial statements to identify
the different types of business
organizations.
8-8
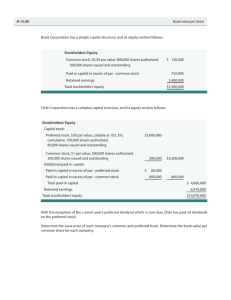
Appearance of Capital Structure in
Financial Statements
The ownership interest (equity)
in a business is composed of:
Owner/investor contributions.
Retained earnings.
8-9
Learning Objective 3
Explain the characteristics of major
types of stock issued by corporations.
8-10
Characteristics of Capital Stock
Par Value
Nominal
Amount
Legal
capital
Legal capital is the amount of capital,
required by the state of incorporation, that
must remain invested in the business.
8-11
Characteristics of Capital Stock
No-par Stock
Some states
do not
require a par
value to be
stated in the
charter.
8-12
Characteristics of Capital Stock
Par value is an
arbitrary amount
assigned to each
share of stock when
it is authorized.
Market price is the
amount that each
share of stock will
sell for in the market.
8-13
Authorized, Issued, and
Outstanding Capital Stock
Authorized
Shares
The maximum
number of shares of
capital stock that can
be sold to the public.
8-14
Authorized, Issued, and
Outstanding Capital Stock
Authorized
Shares
Issued
shares are
authorized
shares of
stock that
have been
sold.
Unissued
shares are
authorized
shares of
stock that
never have
been sold.
8-15
Authorized, Issued, and
Outstanding Capital Stock
Authorized
Shares
Issued
Shares
Outstanding shares are
issued shares that are
owned by stockholders.
Outstanding
Shares
Treasury
Shares
Unissued
Shares
Treasury shares are
issued shares that have
been reacquired by the
corporation.
8-16
Classes of Stock – Common Stock
Common stockholders have the rights to:
Buy and sell stock.
Share in the distribution of profits.
Share in the distribution of assets in
the case of liquidation.
Vote on significant matters that affect
the corporate charter.
Participate in the election of directors.
8-17
Classes of Stock – Preferred Stock
• A separate class of stock, typically having
priority over common shares in . . .
– Dividend distributions.
– Distribution of assets in case of liquidation.
Usually has a stated
dividend rate.
Normally has no
voting rights.
25%
75%
Corporations
with preferred
stock
Corporations
without
preferred stock
8-18
Preferred Stock Dividends
Cumulative
Noncumulative
Dividends in arrears
must be paid before
dividends may be
paid on common
stock.
Undeclared dividends
from current and
prior years do not have
to be paid in future
years.
Most preferred stock
is cumulative.
8-19
Preferred Stock Dividends
• In addition to common stock, Dillion, Incorporated
has the following stock outstanding:
• Preferred stock, 4%, $10 par, 10,000 shares
Common stock, $10 par, 20,000 shares
• Dividends have not been paid in two years. In the
current year, the board of directors declared
dividends of $22,000.
• How much will each class of stock receive?
It depends on whether the preferred stock is cumulative.
8-20
Preferred Stock Dividends
First, let’s assume the
preferred stock is cumulative.
Total dividend declared
Preferred stock (cumulative)
Arrearage
1st year ($10 par × 4% × 10,000 shares)
2nd year ($10 par × 4% × 10,000 shares)
Current Yr. ($10 par × 4% × 10,000 shares)
Remainder to common stockholders
$ 22,000
$ 4,000
4,000
4,000
12,000
$ 10,000
8-21
Preferred Stock Dividends
Now, let’s assume the preferred stock is noncumulative.
Total dividend declared
Preferred stock (noncumulative)
Arrearage
1st year
2nd year
Current Yr. ($10 par × 4% × 10,000 shares)
Remainder to common stockholders
$ 22,000
$
0
0
4,000
4,000
$ 18,000
8-22
Learning Objective 4
Explain how to account for different
types of stock issued by corporations.
8-23
Issuing Stock, $10 Par Value
Nelson, Incorporated issued 100 shares of
$10 par value stock for $22 per share.
The effects on the financial statements would be:
Assets
Cash
2,200
= Liabilities +
=
=
n/a
+
+
Equity
Com.
+
Stk.
1,000 +
PIC in
Excess
1,200
Revenue
n/a
-
Expenses =
n/a
=
Net
Income
n/a
Cash
Flow
2,200 FA
100 shares × $22 per share = $2,200
100 shares × $10 par value = $1,000
8-24
Issuing Stock, $20 Par Value
Assume that Nelson has another class of
common stock, $20 par value Class B.
The company issues 150 shares of Class B
common stock at $25 per share.
The effects on the financial statements would be as
follows:
Assets
Cash
3,750
= Liabilities +
=
=
n/a
Equity
+ Com. Stk. +
+
3,000 +
PIC in
Excess
750
Revenue
n/a
-
Expenses
n/a
=
=
Net
Income
n/a
Cash Flow
3,750 FA
150 shares × $25 per share = $3,750
150 shares × $20 par value = $3,000
8-25
Issuing Stock, $10 Stated Value
Assume that Nelson issues 100 shares of 7 percent
cumulative preferred stock with a stated value of
$10 per share at a price of $22 per share.
The effects on the financial statements would be as
follows:
Assets
Cash
2,200
= Liabilities +
=
=
n/a
+
+
Equity
Pfd. Stk. +
1,000 +
PIC in
Excess
1,200
Revenue
n/a
-
Expenses
n/a
=
=
Net
Income
n/a
Cash Flow
2,200 FA
100 shares × $22 per share = $2,200
100 shares × $10 par value = $1,000
8-26
Issuing Stock with No Par
Value
Assume that Nelson issues 100 shares of no
par common stock at a price of $22 per share.
The effects on the financial statements would be as
follows:
Assets
Cash
2,200
= Liabilities +
=
=
n/a
Equity
+ Com. Stk. +
+
2,200 +
PIC in
Excess
n/a
Revenue
n/a
-
Expenses
n/a
=
=
Net
Income
n/a
100 shares × $22 per share = $2,200
Cash Flow
2,200 FA
8-27
Financial Statement Presentation
8-28
Learning Objective 5
Show how treasury stock transactions
affect a company’s financial
statements.
8-29
Treasury Stock
No voting
or
dividend
rights
Contra
equity
account
Treasury
shares are
issued
shares that
have been
reacquired
by the
corporation.
When stock is reacquired, the corporation
records the treasury stock at cost.
8-30
Treasury Stock
Why would
a company
buy its
own stock?
Common reasons include:
Employee stock option plans.
Preparation for a merger.
To increase earnings per share.
Supporting the stock price.
To avoid a hostile takeover.
8-31
Treasury Stock
Assume that Nelson paid $20 per share to buy
back 50 shares of the $10 par value stock that
it originally issued at a price of $22 per share.
The effects on the financial statements would be as
follows: (since Treasury Stock is a contra-equity account, the
accounting equation is in balance)
Assets
= Liabilities +
Cash
=
(1,000) =
n/a
+
+
Equity
Other
Equity
Accts.
n/a
-
Treasury
Stk.
1,000
Revenue
n/a
-
Expenses
n/a
=
=
50 shares × $20 per share = $1,000
Net
Income
n/a
Cash Flow
(1,000) FA
8-32
Treasury Stock
Assume Nelson resells 30 shares of its treasury
stock at a price of $25 per share.
Cash
750
=
=
n/a
+
+
Other
Equity
Accts.
n/a
PIC from
Treasury
Treasury
Stk.
+
Stk.
+
150
(600)
Revenue - Expenses =
n/a
n/a
=
Net
Income
n/a
Cash
Flow
750 FA
30 shares × $25 per share = $750
30 shares × $20 cost = $600
No gain or loss is recognized on sale of treasury stock.
8-33
Learning Objective 6
Explain the effects of declaring and
paying cash dividends on a company’s
financial statements.
8-34
Cash Dividends
• Corporations are not required to pay
dividends, but once declared, dividends
are legal obligations.
Stockholders
Corporation
Dividends
8-35
Cash Dividends
Declaration Date
Date of Record
Payment Date
Record liability
for dividend.
No entry
required.
Record payment of
cash to stockholders.
• Three important dates
8-36
Declaration Date
On October 15, 2013, Nelson’s Board of
Directors declared a cash dividend on the 100
outstanding shares of 7 percent, $10 par
preferred stock. The dividend will be paid on
December 15 to stockholders of record on
November 15. The effects on the financial
statements would be as follows:
Assets
Cash
n/a
= Liabilities +
= Div. Pay. +
=
70 +
Equity
Com.
Stk.
n/a
+
+
Ret.
Earn.
(70)
Revenue - Expenses =
n/a
n/a
=
Net
Income
n/a
Declaration
Date
Record liability for dividend.
0.07 × $10 par × 100 shares = $70
Cash Flow
n/a
8-37
Date of Record
On October 15, 2013, Nelson’s Board of
Directors declared a cash dividend on the 100
outstanding shares of 7 percent, $10 par
preferred stock. The dividend will be paid on
December 15 to stockholders of record on
November 15. The effects on the financial
statements would be as follows:
Date of Record
No entry
required.
No entry required on
November 15.
8-38
Payment Date
On October 15, 2013, Nelson’s Board of
Directors declared a cash dividend on the 100
outstanding shares of 7 percent, $10 par
preferred stock. The dividend will be paid on
December 15 to stockholders of record on
November 15. The effects on the financial
statements would be as follows:
Payment Date
Assets
= Liabilities +
Cash
= Div. Pay. +
(70) +
(70) =
Equity
Com.
Stk.
n/a
Record payment of
cash to stockholders.
+
+
Ret.
Earn.
n/a
Revenue - Expenses =
n/a
n/a
=
Net
Income
n/a
Cash Flow
(70) FA
8-39
Learning Objective 7
Explain the effects of stock dividends
and stock splits on a company’s
financial statements.
8-40
Stock Dividends
Distribution of additional shares
of stock to stockholders.
No change in total
stockholders’ equity.
All stockholders retain
same percentage
ownership.
No change in
par values.
8-41
Stock Dividends
Nelson’s Board of Directors decided to issue a 10 percent
stock dividend on the 150 outstanding shares of its $20 par
value, Class B common stock. Market value at the time of the
stock dividend was $30 per share. The effects on the
financial statements would be as follows:
Assets
n/a
= Liabilities +
=
=
n/a
+
+
Equity
Com.
PIC in
Stk.
+ Excess +
150 +
300 +
Ret.
Earn.
(450)
Revenue - Expenses =
n/a
n/a
=
Net
Income
n/a
0.10 × 150 shares × $20 par = $300
0.10 × 150 shares × $30 per share = $450
An amount from
Retained Earnings is moved to other equity accounts.
Cash Flow
n/a
8-42
Stock Splits
Stock splits replace existing shares
with a greater number of new shares.
Companies use stock splits to reduce
market price per share of their
outstanding stock.
The number of outstanding shares
increase and par value is decreased
proportionately.
Retained earnings is not affected.
8-43
Stock Splits
Nelson’s Board of Directors declared a 2-for-1 stock split on
the 165 outstanding shares of its $20 par value, Class B
common stock.
Before
Split
Common Stock Shares
165
Par Value per Share
$
20
Total Par Value
$ 3,300
After
Split
8-44
Stock Splits
Nelson’s Board of Directors declared a 2-for-1 stock split on
the 165 outstanding shares of its $20 par value, Class B
common stock.
Before
Split
Common Stock Shares
After
Split
165
Par Value per Share
$
20
Total Par Value
$ 3,300
330
$
10
$ 3,300
Increase
Decrease
No Change
No journal entry required – Change par value
and number of shares authorized and outstanding.
8-45
Learning Objective 8
Show how the appropriation of retained
earnings affects financial statements.
8-46
Appropriation of Retained Earnings
• A corporation’s directors can voluntarily limit
dividends because of a special need for cash.
• Assume that Nelson’s Board of Directors
appropriated $1,000 of retained earnings for future
expansion. The effects on the financial statements
follow:
Assets
n/a
= Liabilities +
=
=
n/a
+
+
Com.
Stk.
n/a
+
+
Equity
Ret.
App. Ret.
Earn. + Earn.
(1,000) +
1,000
Revenue - Expenses =
n/a
n/a
=
Net
Income
n/a
Cash Flow
n/a
8-47
Financial Statement Presentation
Beginning Balance $
5,000
Net Income
6,000
Cash dividend
(70)
Stock dividend
(450)
Ending Balance
10,480
8-48
Learning Objective 9
Explain some uses of accounting
information in making stock
investment decisions.
8-49
The Financial Analyst
Stockholders benefit in two ways
when a company generates earnings.
Dividends
Increase in market
price per share
8-50
End of Chapter Eight