Global Economics–Chapter 7
advertisement

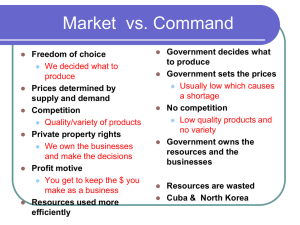
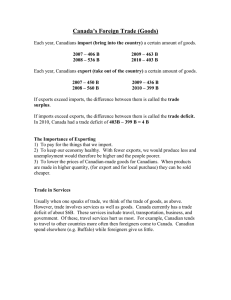
GLOBAL ECONOMICS Chapter 7 IMPORTS AND EXPORTS Imports—products brought in from a foreign country. Exports—products sent to a foreign country for sale. WHY WE TRADE…. To get products we don’t have. To specialize in items we make efficiently and import those we do not. BENEFITS OF TRADE….. More consumer choice Increased competition Expanded markets Improved International relations Increased prosperity and peace NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE… Loss of jobs to countries that can produce cheaper products. Poor quality of imported products INTERNATIONAL TRADE IS DEPENDENT ON A FLEXIBLE EXCHANGE RATE…. Trading partners must exchange currency when they trade. They must use and exchange rate- (the cost on one currency expressed in terms of another currency) A flexible exchange rate changes from day to day. It is determined by supply and demand for various currencies. Can make the cost of doing international business difficult and unpredictable. FACTORS AFFECTING A FLEXIBLE EXCHANGE RATE… Changes in interest rates—(a high interest rate increases the demand for the currency) Economic and political stability The strength or weakness of a nation’s currency affects the willingness of other nations to trade with it. (If the US dollar is weak, exports increase and the apposite is true as well.) BALANCE OF TRADE… The difference between the value of a nation’s imports and exports is called its Balance of Trade. IF a nation imports more than it exports it has a trade deficit. BALANCE OF PAYMENTS… This is an accounting of a nation’s financial transactions that involve other countries during a particular time period. U.S. TRADE DEFICIT…. We have been running a trade deficit since the 1970’s. Oil consumption appears to be a leading reason. TRADE RESTRICTIONS: Protective Tariffs A tax on imports Purpose is to reduce purchases of imported goods Quotas A government limit on the quality or value of certain imported products Tend to raise consumer prices. Embargos Government order prohibiting trade Mainly used for political reasons. PROTECTIONISM VS. FREE TRADE Protectionism is a policy of using trade restrictions to protect domestic businesses from global competition. Free trade is a policy of minimizing trade restrictions. ARGUMENTS FOR PROTECTIONISM National Security Job Security for workers Encourage new industries Protecting the environment To eliminate unfair advantages from other countries. ARGUMENTS FOR FREE TRADE Prevents retaliation by other countries Protectionism creates higher prices for consumers Allows for specialization More competition=lower prices or better products to consumers Protection of national industries can be better helped through subsidies (a form of financial assistance) rather than tariffs. TRADE AGREEMENTS…. GATT (General Agreements on Tariffs and Trade) agreement renewed in 1994 to reduce or remove barriers to trade. WTO ( World Trade Organization) is an international organization that governs trade between 140 member countries that was developed as a result of GATT. NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) is a regional agreement between the US, Canada, and Mexico which tries to make trade between these three countries easier. EU (European Union) is an organization of independent European countries which is trying to create a unified and strong European market. They have been removing trade restrictions between member nations.