International Business
advertisement

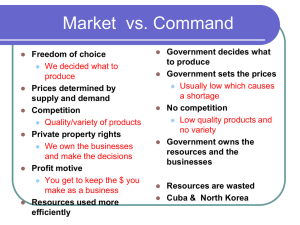
International Business Intro to Business 3/14/2016 Trading Among Nations • Domestic Business – making, buying, selling of goods and services within a country • International Business – all of the business activities necessary for creating, shipping, and selling goods and services across national boarders (aka world trade) Advantages over America Why do we trade? • While America has many natural resources, a skilled labor force, and modern machines and methods of production, we cannot provide ourselves with all of the things we want. • We must go outside of our borders to get some of the things that other countries specialize in. America’s Advantages over other countries Importing • Imports – the things we buy from other countries • Imports account for 100% of: Foreign Trade • Without foreign trade, many of the things we buy would cost more or not be available to our consumers. • Other countries can produce some goods at lower costs because they have the needed raw materials or have lower labor costs. • Some consumers may still purchase foreign goods at higher prices if they perceive the value to be higher. • Or they may simply just enjoy owning foreign products: – French Perfumes, Norwegian Sweaters, Swiss Watches Exporting • Exports – the goods and services we sell to other countries • Exports benefit consumers in other countries – – – – – Factory and farm machinery made in U.S. Food grown on U.S. farms Chemicals, pesticides, medicines and plastics produced in U.S. U.S. Movies, Television (CNN, MTV, ESPN) U.S. Books, magazines, newspapers • 1 out of every 6 U.S. jobs depends on international business International Currency • Each nation has its own banking system and its own type of money – Russia: ruble – India: rupee – Japan: yen • Exchanging one currency for another occurs in the foreign exchange market • The value of each currency in one country compared to another country is called the exchange rate Barriers to International Trade • Governments establish international policies that guide trade with other countries – through control of importing and exporting – Quotas – Tariffs – Embargos Quota • Sets a limit on the quantity of a product that may be imported or exported within a given period of time • Reasons: – Keep supply low = keep prices up – To express disproval of one countries social behavior or policies – To protect one country’s industry from too much competition – Known as shielding infant industries which need protection to get started Tariff • A tax that government places on certain imported products • Ex. A foreign bicycle costs $140 but our government collects a 20% tariff ($28) costing you $168, plus shipping • The increase in price lowers demand • May help consumers decide to purchase domestic product Embargo • Stop on an import or export completely • Reasons: – Protection from international competition (to a greater degree than the tariff or quota) – To prevent sensitive information falling into hands of unfriendly groups or nations (relating to defense) – As well as to express disproval of the actions or policies of another country Measuring trade between nations • Just like people try to spend less than they earn, countries try to maintain a positive balance of trade Balance of Trade • The difference between a country’s total exports and imports • Trade surplus – exports more than imports • Trade deficit – imports more than exports Multinational Company/Corporation (MNC) • An organization that conducts business in several countries and has management capable of doing business worldwide



![Quiz About [Your Topic]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009237721_1-467865351cf76015d6a722694bb95331-300x300.png)