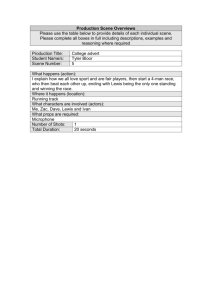
Production Guideline
advertisement

Production Process (Non-Announcement Video Productions) Video Project/Idea assigned 1. Planning the project out- Personal or Group planning meeting- (What? How? When? Where?) Brainstorming Pitching/selling your production idea Research and gather source information Do your homework-research inspirational video production ideas from other video productions (television shows, YouTube videos, cartoons, etc.) 2. Finalize your idea so that it is ready for production (there is no turning back at this point we are ready to begin production (Design the look and style of the show) 3. Finding video location (in-studio green screen or specific on-campus location) Have you scouted a primary and secondary location to shoot your video? Is your location appropriate for what you are shooting-does it match? Is the location in a controlled environment? Are there noises or sounds that will interfere with your recording? 4. Storyboarding-Bring the video production to life Storyboard scene and camera framing (Tight close up, close up, medium, full frame head to toe shot) Your team should discuss and debate the best look for the camera (how the scene should look) Per frame, describe the location and what is happening in the scene Per frame, describe what the character(s) should be feeling and doing in the shot What is the mood of the scene -the look and sound(s) Each storyboard block should be named Scene followed by a brief description (such as, Scene 1: Hallway)(Scene 2: Stairs) Basic sketch of the scene Describe and name the characters in the scene (their roles, what they do, their personality, background/history) Background music or sound effects of each scene (thunder, bells ringing, laughter etc.) Special effects of the scene Storyboard will be done in unison with Scriptwriting to coordinate the scene and production Each story board scene will be checked and tested against what the scripter’s are developing ( in order to make sure the scene still makes sense, scene by scene) 5. Scriptwriting-Bringing your character to life Narration or dialect of the character(s) The script should include the scene or location of the character (ex: Scene 1 Scene 2) Brief description of what’s going on in the scene The script should give the actors their motivation, personality, and emotions (ex: A bubbly energetic soccer player) If needed the script should include background and foreshadowing The script should describe the scenes genre (ex: Mystery, comedy, scary.etc...) Scripts must develop and maintain the characters motivation, personality, and emotions Scripts must also have a relation of the targeting audience Scripts should emphasize that actors must represent their character Scripts must provide factual information to develop, dialects, scenes, and characters (do research to insure that what your saying is real) In the script of the scene the story idea(s) need to flow (ex: teen sitcoms need to be about teen life) Script dialect needs to be read out loud and tested to different individuals (to insure that the story makes sense) Scripting will be done in unison with Storyboarding to coordinate the scene and production Each dialect scene will be checked and tested against what the storyboarders are developing ( in order to make sure it makes sense- scene by scene) 6. Production rehearsal (no camera) On location mock video shooting Walk through rehearsal of scenes and dialogue Frame camera position( the location of character and where it is from the character) Be sure that audio is clear with no distracting sounds or background noise Director gives direction of characters and what each scene represents Time the pacing of each scenes (how long should it take on each scene) In order to make sure the scene is done on pace, perform a real time production run through 7. Live production (with camera) On location or set Scenes directed by the storyboard and script Set up audio and video recording equipment Set up props and lighting Control or block off production area Observe and promote production safety Maintain a professional and structured production environment Keep production on schedule and pace 8. Post-Production (time to edit) Capture footage to the editing computer (firewire capture) Save footage to a designated folder (give the project a specific name) Import the footage into the editing timeline 9. Clean and trim video Adjust audio levels to correct volume Apply green screen effect Add backgrounds for green screen footage Add fade ins and fade outs/ Add transitions Add titles when needed Add sound effects and ambient noise when needed (laughter or claps) Add special effects and color tints when needed Add skit or sitcoms intro and outro Add Credits Rendering and export as a movie file Upload or broadcast movie Begin the process again on the next episode (make adjustments and fine tuning as needed)