fluid, electroytes and acid-base balance
advertisement

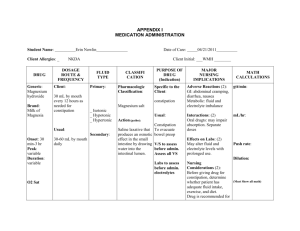
Fluid, Electrolyte, and AcidBase Balance Reference Taylor, C., Lillis, C., & LeMone, P. (2005). Fundamentals of nursing (5th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Chapter 46 Competencies for Ch 46: Fluid, Electrolyte, & Acid-Base Balance By the end of the unit, the student will: 1. Describe the anatomy and physiology related to body fluids, fluid & electrolyte, and acid-base balance 2. Describe age-related differences in body fluid content and effect on fluid balance status 3. Describe how to promote and maintain fluid & electrolyte, and acid-base balance Competencies for Ch 46: Fluid, Electrolyte, & Acid-Base Balance (continued) By the end of the unit, the student will: 4. Describe specific variables that may influence fluid & electrolyte, and acid-base balance 5. Teach clients about specific conditions that can lead to fluid & electrolyte imbalance, and acid-base imbalance 6. Describe care for clients at risk for or with actual problems related to fluid & electrolyte, and acid-base balance Functions of Water in the Body Transporting nutrients to cells and wastes from cells Transporting hormones, enzymes, blood platelets, and red and white blood cells Facilitating cellular metabolism and proper cellular chemical functioning Acting as a solvent for electrolytes and nonelectrolytes Helping maintain normal body temperature Facilitating digestion and promoting elimination Acting as a tissue lubricant Two Compartments of Fluid in the Body Intracellular fluid (ICF) — fluid within cells (70%) Extracellular fluid (ECF) — fluid outside cells (30%) Includes intravascular and interstitial fluids Variations in Fluid Content Healthy person — total body water is 50% to 60% of body weight An infant has considerably more body fluid and ECF than an adult More prone to fluid volume deficits Sex and amount of fat cells affect body water Women and obese people have less body water ELECTROLYTES Terminology Ions Electrolytes Cations Anions Non-electrolytes Solvents Solutes Electrolytes Ions Cations — positive charge Anions — negative charge Homeostasis — total cations equal to total anions Fluid Balance Solvents — liquids that hold a substance in solution (water) Solutes — substances dissolved in a solution (electrolytes and nonelectrolytes) MORE ELECTROLYTES Measurement Based on chemical activity Regulation Water distribution Acid-base balance Neuromuscular excitability COMMON ELECTROLYTES Sodium (Na++) Functions Regulates volume of body fluids Maintains water balance Regulates ECF Influences ICF Generation and transmission of nerve impulses Sodium-Potassium pump POTASSIUM (K+) Major cation in ICF Reciprocal to sodium Functions Regulates cellular enzyme activity and water content Transmission of nerve and muscle impulses Metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates Regulation of acid-base balance by cellular exchange with H+ CALCIUM (Ca++) Most abundant electrolyte in body 99% found in bones and teeth Functions Nerve impulse transmission and blood clotting Catalyst for muscle contraction Thickness and strength of of cell membranes MAGNESIUM (Mg++) Second most important cation in ICF Functions Metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins Vital enzyme actions Protein and DNA synthesis Maintaining intracellular levels of Potassium Maintain electrical activity in nervous tissue and muscle tissue membranes CHLORIDE (Cl-) Chief extracellular anion Functions Works with sodium to maintain osmotic pressure of blood Regulates acid-base balance Buffering action during O2/CO2 exchange Production of Hydrochloric acid in digestion BICARBONATE (HCO3-) Major chemical base buffer Found in ECF and ICF Function Essential for acid base balance. Works with carbonic acid to make up the body’s acid base buffer system PHOSPHATE (PO4-) Major anion in body cells Buffer in ICF and ECF Functions Maintains body’s acid-base balance Cell division and transmission of heredity Chemical reactions use of Vit B, CHO metabolism, nerve and muscle action OTHER ELECTROLYTES Sulfate Anion ICF Excreted in the kidney Lactic acid Anion Facilitates diffusion to and from capillaries FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE MOVEMENT Osmosis – Fluid passes from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration Diffusion – tendency of solutes to move freely from areas of high concentration to low concentration (down hill) Active Transport – requires energy to move through a cell membrane from area of lesser concentration to one of greater concentration Filtration – passage of fluid through a permeable membrane. Movement is from high to low pressure Osmolarity of a solution Isotonic — same concentration of particles as plasma Hypertonic — greater concentration of particles than plasma Hypotonic — lesser concentration of particles than plasma Filtration Colloid osmotic pressure Hydrostatic pressure Source of Fluids for the Body Ingested liquids Food Metabolism Fluid Losses Kidneys — urine Intestinal tract — feces Skin — perspiration Insensible water loss Fluid Imbalances Involves either volume or distribution of water or electrolytes Hypovolemia — deficiency in amount of water and electrolytes in ECF with near normal water/electrolyte proportions Dehydration — decreased volume of water and electrolyte change Third-space fluid shift — distributional shift of body fluids into potential body spaces Fluid Volume Excess Hypervolemia — excessive retention of water and sodium in ECF Overhydration — above normal amounts of water in extracellular spaces Edema — excessive ECF accumulates in tissue spaces Interstitial-to-plasma shift — movement of fluid from space surrounding cells to blood Electrolyte Imbalances Hyponatremia and hypernatremia Hypokalemia and hyperkalemia Hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia Hypophosphatemia and hyperphosphatemia Nursing Assessments Identify patients at risk for imbalances. Determine a specific imbalance is present and its severity, etiology, and characteristics. Determine effectiveness of plan of care. Parameters of Assessment Nursing history and physical assessment Fluid intake and output Daily weights Laboratory studies Lab Studies to Assess for Imbalances Complete blood count Serum electrolytes Urine pH and specific gravity Arterial blood gases Risk Factors for Imbalances Pathophysiology underlying acute and chronic illnesses Abnormal losses of body fluids Burns Trauma Therapies that disrupt fluid and electrolyte balance Nursing Diagnoses Related to Imbalances Excess fluid volume Deficient fluid volume Risk for imbalanced fluid volume Expected Outcomes Maintain approximate fluid intake and output balance (2500mL intake and output over 3 days) Maintain urine specific gravity within normal range (1.010 to 1.025) Practice self-care behaviors to promote balance Implementing Dietary modifications Modifications of fluid intake Medication administration IV therapy Blood and blood products replacement TPN Administering Medications Mineral-electrolyte preparations Diuretics Intravenous therapy Intravenous Therapy Vascular access devices Peripheral venous catheters Midline peripheral catheter Central venous access devices Implanted ports Vein Site Selection Accessibility of a vein Condition of vein Type of fluid to be infused Anticipated duration of infusion Administering Blood and Blood Products Typing and cross-matching A, B, AB, and O type blood Rh Factor Selecting blood donors Initiating transfusion Transfusion reactions HOMEOSTASIS PROCESS OF MAINTAINING A STABLE STATE UNDER VARIABLE CONDITIONS MECHANISMS OF HOMEOSTASIS Kidneys Cardiovascular system Lungs Adrenal Glands Thyroid Gland Parathyroid Gland Gastrointestinal tract Nervous system Primary Organs of Homeostasis Kidneys normally filter 170 L plasma, excrete 1.5 L urine. Cardiovascular system pumps and carries nutrients and water in body. Lungs regulate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels of blood. Primary Organs of Homeostasis, continued Adrenal glands help body conserve sodium, save chloride and water, and excrete potassium. Thyroid gland increases blood flow in body and increases renal circulation. ACID – BASE BALANCE Acid contains hydrogen atoms that can be released Base accepts hydrogen atoms Acidosis too many circulating H+ ions Alkalosis not enough H+ ions in the ECF pH is the unit of measure used to describe acid base balance Buffer prevents ECF from becoming too acidic or too alkaline BUFFER SYSTEMS Carbonic Acid-Sodium Bicarbonate System Phosphate Buffer System Protein Buffer System IMBALANCE IN ACID – BASE BALANCE Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory Acidosis Excess in carbonic acid in the ECF Metabolic Alkalosis Deficit in carbonic acid in the ECF Excess of bicarbonate in the ECF Metabolic Acidosis Deficit of bicarbonate in the ECF EXERCISE #1 For the patient with hyperkalemia related to decreased renal excretion secondary to potassium conserving diuretic therapy” an appropriate expected outcome would be which of the following? a) b) c) d) Bowel motility will be restored within 24 hours after beginning supplemental K+ ECG will show no cardiac arrhythmias within 48 hours after removing salt substitutes, coffee, tea and other K+ rich foods from the diet ECG will show no cardiac arrhythmias within 24 hours after beginning supplemental K+ Bowel motility will be restored within 24 hours after eliminating salt substitutes, coffee, tea, and other K+ rich foods from the diet EXERCISE #2 Which of the following nursing diagnoses would you expect to find based on the effects of fluid and electrolyte imbalance on human functioning? a) Constipation related to immobility Pain related to surgical incision Altered thought processes related to cerebral edema, including mental confusion and disorientation Health risk for infection related to inadequate personal hygiene b) c) d) EXERCISE #3 a) b) c) d) A nurse who diagnoses a patient as having “fluid volume excess” related to compromised regulatory mechanisms (kidneys) may have been alerted by which of the following symptoms? Muscular twitching Distended neck veins Fingerprinting over sternum Nausea and vomiting EXERCISE #4 a) b) c) d) Pumping uphill would describe which of the following means or transporting materials to and from intercellular compartments? Osmosis Diffusion Filtration Active transport