Unit 11 - Enderoth
advertisement

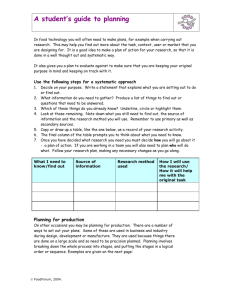
Unit 11 – Maintaining Computer Systems J/601/7329 LO2 - Know how to plan computer system maintenance This unit will give learners an understanding of the role of an IT services practitioner. Learners will identify that in the role the IT services practitioner has to be able to make good judgement based on advantages and disadvantages of any planned changes to a company system. The practitioner will have to be able to monitor and balance the improvements/ maintenance to the computer system, without the company having too much disruption. The aim of this unit is to introduce learners to the role and responsibilities of an IT practitioner with a focus on the field of computer systems maintenance. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Learning Outcome (LO) The learner will: Pass The assessment criteria are the pass requirements for this unit. The learner can: 1 P1 Explain the issues organisations must consider when planning computer systems Maintenance P2 Assess the health and safety risks facing the practitioner when maintaining computer Systems M1 - Identify the precautions that should be taken during routine maintenance procedures M2 - Create a plan for scheduled maintenance Activities D1 - Explain the benefits to an organisation of regular maintenance activities M3 - Test the functionality of the system after upgrade D2 - Compare the improvements and restrictions of the upgraded system against the original installation Understand the organisational issues related to computer system maintenance 2 Know how to plan computer system Maintenance P3 Describe a planning technique that can be used to schedule maintenance activities 3 Be able to perform routine housekeeping on computer systems P4 Perform routine housekeeping on a computer system 4 Be able to monitor and improve systems Performance P5 Use monitoring tools to assess system Performance P6 Improve a system by upgrading hardware and software Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 Merit For merit the evidence must show that, in addition to the pass criteria, the learner is able to: 7 8 Distinction For distinction the evidence must show that, in addition to the pass and merit criteria, the learner is able to: Assessment Criteria P3 Learners should describe a planning technique that could be used by an organisation to schedule their maintenance activities. This could be in the form of a report supported by examples and details of the technique that could be used and why this is the best option; alternatively it could be evidenced as a presentation. Assessment Criteria M2 Learners should create a detailed plan that shows the activities for the scheduled maintenance. This could be evidenced showing the planning documents with route maps, upgrade paths, schedules, Gantt charts etc. Assessment Criteria D1 Learners will need to give detailed explanations of the benefits to an identified organisation of regular maintenance activities identifying the problems that can be avoided. This could be evidenced with detailed explanations of what problems could occur without regular maintenance, to include a range of problems for hardware and software. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The learner needs to be introduced to the planning techniques that could be used and should be taught and be made aware as to why planning is needed and to look at the different techniques and documents that could be used such as; route maps, upgrade paths, schedules, Gantt charts. Learners will benefit having practical exercises in creating and using some of these documents. Learners will need to look at the operational and the tactical planning and to have knowledge and understanding of the differences, this could be reinforced by group working and discussions. Learners will also need to investigate what problems could occur without regular maintenance which could involve looking at what happens if updates are not regularly updated, virus protection not updated, dust build up without regular cleaning, loss of space without careful organisation of files and how these could relate to the computer not performing correctly and how the regular maintenance of equipment would help the organisation. This could be an exercise where they create small presentations explaining the cost savings and benefits to an organisation. The learners will benefit from a mixture of case studies and detailed investigations to provide scope to their learning. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 All planning of projects from computer maintenance to building a stadium have plans that vary from task to task, Gantt charts for the whole project, route maps for problem solving, schedules that are linked to other documents, upgrade paths that show when things should be done and maintenance schedules showing when things should be looked at. All of these are useful as business tools, specifically when a new member of staff or a team joins and needs to know when to do things and in what order things get done. For this project you will need to create a series of plans for the maintenance, upgrade and schedule repairs of computer equipment. These projects may take only an hour to achieve or might need to last years as a plan of replacement. For this project you will need to create at least two plans but need to understand the benefits of dealing with each to a project manager or line manager in order to maintain a routine. P3.1 – Task 01 – Describe, explain and evaluate planning techniques that can be used to schedule maintenance activities. Route maps Scenario Criteria Maintenance schedules Tasks 1 2 3 Upgrade paths 4 5 6 7 Upgrade schedules 8 Gantt charts/ project plans Route Maps - Like Gantt charts Route maps are used as a visual means for a broader staff range to analyse timings and duties. Route Maps are a means of pathing alternative routes to a final conclusion. Similar to a flow diagram, they indicate a path between A to B taking into account all the actions necessary to achieve the task along the line and considering junctures, parts of the path that are vital to achieve before moving on to the next part or force repeating the stage until a successful conclusion is made or a by-pass is achieved. Upgrade Schedule – This is a form of planning similar to a Gantt chart in layout but loops, there is usually no end to the schedule and takes into consideration company policy on rolling replacements. For instance, machines in one room will be upgraded for certain components as the need arises or time can predict, the process of replacing the equipment every three years is superseded by replacing hard drives every 2 years, memory upgrades every 2 years and keeping the monitors after replacement for another 2 years, cascading them down to other rooms where the usage load is not as high or the need not as great. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Upgrade Paths – This is the route a company has to take to change or upgrade hardware or software that is currently in place. This can take the form of a table that costs, designs and plans the upgrade components, when they should be replaced and plan for contingencies. The second form of this is a pathing plan, a chart of what gets replaced, how it is replaced, the timing and scheduling of the method of replacement, the purchase, the testing, the action, the evaluation. It should take into consideration overlapping duties, redundant procedures and timescales. Gantt Charts – These are dependant on the size of the project and the intricacies involved. For instance internal events will have competition for available resources, usually on a first come first served basis or on how important the person wanting the resources is. Similarly rooms can be overbooked, staff are given different priorities, internal conflicts and politics can break up teams. Anything can change, contracts are not written in stone and priorities often shift. Similarly larger projects and longer term projects often risk changing because of the nature of time and funding, new technologies come on the market, new products released can shift a companies focus, economies can change and influence budgeting. In a similar way the success criteria can alter through the life cycle of a project, primary focus can change with the change of client, increased and decreased public interest can alter the budgeting and staffing. And not all outcomes can be predicted or managed. From something as small as Vanilla Ice Microphone to the Kyoto Earthquake, anything can have an impact on the success of a project. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Maintenance schedules - All equipment needs maintenance and the two times it is most necessary is before a problem arises or as a problem is building to the point where repair will pre-empt damage. Hardware Maintenance – charts that plan hardware maintenance can happen as routine or non-routine. Routine maintenance can be a matter of a technician switching every machine on in a room and logging in, either through RDS or in person, a series of software checks like Scandisk, Defragmentation and Drive imaging will pre-empt most of the damage that will happen to the machines or is already happening. It is basically like resetting a computer and the hard drive files, back to default. Charts drawn like those on the right will plan when this happens, what money it will cost, how long they should take, what times they can happen, who will carry them out and track the predicted and actual results. When there is a hardware audit by a company, these plans will show what has been looked at, when things are due and fault report those complete. Software maintenance – Like hardware there are reasons for doing this, a software audit is a legal audit of a companies programs, it tracks through system registry what is legal and covers the company against liability. Charts are drawn up, when the registers took place, what the results are, what was checked and what was done to those with faults, reimaging, reinstalling and reconfiguring then happens to protect a company. P3.1 – Task 02 – Describe which planning techniques should be used to schedule software and hardware maintenance, and software and hardware upgrade activities within your 2 companies. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Before the medium and longer term planning of repairs and scheduling takes place and can become an action plan, operational considerations have to be negotiated. No point planning to replace the whole memory on 30 computers unless there is a budget in place, network staff around, duty staff clear of the rooms and contingencies set aside for potential downtime. Three operational considerations will be in place: Scope of maintenance - Scope is just another word for range. Basically a company will need the technicians to research and explain the range of maintenance tasks involved in keeping a Computer Network healthy. The scope declared will need to include issues such as Time, Cost, Man Hours, Contingencies, Allowances, Safety Procedures, Wastage and possible external application (outside help). This will include: ◦ Hardware Maintenance - Keeping the PC components physically clean, replacing faulty/ out-dated parts, disk defragmenting and disk clean-up, and possible replacement of redundant architecture etc. This can also cover upgrades, replacements and repairs. ◦ Software Maintenance - keeping all software up to date, Imaging, reinstalling, upgrading, fault checking, logging and compatibility testing. This also includes ensuring a computer is protected against viruses by installing anti-virus software and firewalls etc. The Scope document provided is an important management document as it is taken into consideration at a time of budgets being drawn up, it is the network Departments way of stating the costing needs and considerations. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Frequency (e.g. routine, non-routine) - this is where the user maintains the computer without it being on the systems scheduled list of things to do. EG. Checking all the components are in working order. It is a set of service or procedures performed to keep a computer in good working conditions. ◦ Routine maintenance may be needed if you see your system is running slow like a virus scan or if you can tell if something is wrong, then defrag. Routine maintenance can be predicted and planned for, backups, schedules checks, imaging, replacement and upgrades and so it can also be budgeted and planned for, staff, location, room allowance etc. ◦ Non routine maintenance isn't scheduled unlike routine maintenance which is done on a regular basis. This cannot be planned for, involves things like on the spot repairs, replacements, one off decisions. 30% of all network faults are those that can be repaired by a technician going to the room and fixing it but this cannot be budgeted for and allowances vary between businesses on the tolerable and intolerable expense leading to replacement rather than repair. Other e.g. use of maintenance specialists – Put simply, those employed by the company may not be the best people for the job to fix or replace things. Certain IT jobs are specialist like laying down fibre optic cabling, electrical installation, advanced client management support. The support externally can be either telephone which is time consuming but can lead to benefitting the network support team as they will still be involved in the repair process, through RDC, which adds a security risk to the process but is usually quite safe and successful, or hiring in on contract. Contractual work is expensive so it is usually limited to when it needs to happen. Certain external technicians can charge £250 an hour, more than plumbers and electricians, sometimes they charge by the contract. They are professional, will get the job done and should be cost effective. They are also highly skilled. P3.2 – Task 03 – Describe, explain and evaluate the operational planning techniques that can be used to schedule maintenance activities. Scope Frequency Maintenance Specialists P3.3 – Task 04 - Describe how these operational planning techniques can influence the decisions on software and hardware upgrade and maintenance activities within your 2 companies. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Now that you have considered the five different planning mechanisms in place you will need to plan for the maintenance and u[grading of the system for this project. As part of the project you should be given a system to manage. This system should be a single base unit with the OS installed from scratch. The system will have MSOffice or OpenOffice, an installed motherboard, working monitor, keyboard and mouse and perhaps has been in place and working before. For LO3 you will be configuring and scanning the computer for problems and issues, for LO4 you will be adding three pieces of hardware and updating the machine to make it better. You will also be adding software to protect the machine and prepare schedules for the maintenance of the computer. These pieces of software and hardware are of interest to us now. M2.1 - Task 05 - Create a plan for scheduled maintenance Activities, scanning, checking system Integrity, defragmentation, virus checking, installing firewalls and verification for your selected company. For this you will need to draw up two flow diagrams, either a Route Map or maintenance Schedule for the software tasks. The list can be gained from the software task list in LO3 and LO4. The diagrams need to contain alternative pathing for fault finding. M2.2 - Task 06 - Create a Gantt or Upgrade Schedule Chart that outlines all the stages of upgrading and testing 3 device cards and drivers for your selected company. For this you will need to draw up one diagram, either a Gantt or Upgrade Schedule Chart for the hardware tasks that needs to include concurrent, contingencies, deadlines and milestones. You may wish to use OpenProj or Project Manager for this of create the pathing within Excel. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Companies would not run these software and hardware routines unless it was necessary. Decisions made about what to how, how to avoid issues, how to keep things running smoothly are made by management teams in all medium sized companies. Costs are negotiated and plans drawn up, at least for larger projects. On the network side everything has to be micro managed, staff indicate faults on the system, events get added to a list, detailed, assigned and then someone comes and fixes it. At the end of the year all the lists are added up, counted, jobs completed are analysed in terms of time and success rates. But there are other benefits other than job justification: Updates maintained – all updates on a system either supersede previous versions or add to the installation version. When a drive is imaged (a ghost version of a working machine is copied directly over a cleaned hard drive) the updates will be part of that image, replacing everything that went before. This way machines are completely up t date when imaged, newest drivers, most compatible software, most reliable versions and a cleaner, smaller, sleeker OS. This also reduces the backdoor access for hackers and viruses. Reduced risk of viruses – With the newest .dat files and an up to date firewall, the risk of viruses and threats from the outside are massively reduced. There are up to 5000 new viruses and variants every week, it only takes one to destroy the information on a machine, the need for the best version cannot be emphasised enough. Better to avoid the threat than to treat the damage. Updated hardware and new cards with better drivers reduces the number of backdoor or OS holes that allow hackers to gain access. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Equipment clean and dust free – For health and safety reasons as well as computer speed and welfare, this is good to have. Fans will get clogged up, causing crashes, slow downs and risk of fire. Similarly, a clean computer sets a standard, especially when computers are hotswopped by staff and customers. Maximised efficiency of equipment – At the end of the day all upgrades, cleans, images, repairs, scans etc. are designed to make the computers better at what they do. Maximising their potential, their speed, their efficiency, maximising the icons, the accessibility, the speed at which it takes to open files and find information will only benefit a business. When a customer rings up or stands at a desk asking for help from the system, they do not care that your machines are slow, they want to know their answer. Bosses with deadlines do not care about the excuses, just the results, especially when it impacts them. D1.1 – Task 07 - Give detailed explanations of the benefits to your selected company of regular software maintenance activities identifying the problems that can be avoided. D1.2 – Task 08 - Give detailed explanations of the benefits to your selected company of upgrading, adding and replacing legacy hardware. For this your explanation needs to be detailed and include what problems could occur without regular maintenance, to include a range of problems for hardware and software. Updates maintained Scenario Criteria Reduced risk of viruses Tasks 1 2 3 4 Equipment clean and dust free 5 6 7 8 Maximised efficiency of equipment P3.1 – Task 01 – Describe, explain and evaluate planning techniques that can be used to schedule maintenance activities. P3.1 – Task 02 – Describe which planning techniques should be used to schedule software and hardware maintenance, and software and hardware upgrade activities within your 2 companies. P3.2 – Task 03 – Describe, explain and evaluate the operational planning techniques that can be used to schedule maintenance activities. P3.3 – Task 04 - Describe how these operational planning techniques can influence the decisions on software and hardware upgrade and maintenance activities within your 2 companies. M2.1 - Task 05 - Create a plan for scheduled maintenance Activities, scanning, checking system Integrity, defragmentation, virus checking, installing firewalls and verification for your selected company. M2.2 - Task 06 - Create a Gantt or Upgrade Schedule Chart that outlines all the stages of upgrading and testing 3 device cards and drivers for your selected company. D1.1 – Task 07 - Give detailed explanations of the benefits to your selected company of regular software maintenance activities identifying the problems that can be avoided. D1.2 – Task 08 - Give detailed explanations of the benefits to your selected company of upgrading, adding and replacing legacy hardware. Scenario Criteria Tasks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8