The Future of the Internet
advertisement

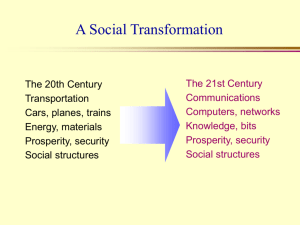
Exploring the Internet The Future of the Internet 91.113-021 Instructor: Michael Krolak 91.113-031 Instructor: Patrick Krolak See also http://www.cs.uml.edu/~pkrolak/ Authors: P. D. & M. S. Krolak Copyright 2005 Tonight • The Internet and the Future • A capstone for the course Before the Internet – http://xo.typepad.com_ blog_amusing_.htmB Class Announcements • . The Future of the Internet The Internet has gone through many changes in the last 30 years. We are now in the transformation from its primarily as a communications network and webbed structure of documents to a wireless applications driven age. The applications are driven by computers controlling networks of computers and smart devices to create: 1. intelligent cars and homes, 2. create and find information on the deep web, 3. provide greater homeland security and safety 4. allow people greater production and efficiency in order to compete in the global economy. Technologies driving the Age of Connection • • • • • • Internet2 -- orders of magnitude faster than 58Kb. SAND storage technology fast cheap storage in Terabytes. Array computing – a super computer in a box. The merger of large flat screen TV, computer displays, and 3D graphics cards. The merger of telephone and computer devices. The creation of micro-sensors, wireless integration of phones and smart sensors (blue-tooth), computers networked for command & control of machines. Internet2 • A project launched in 1996 to create and develop the applications for a network thousands of times faster than the 58Kb modem. • Allows 200 member universities to share data and facilities for research. • The Internet2 Commons allows high band width video conferences to hold major teaching and learning events, research meetings at multiple sites. Internet2 (more) Internet2 Internet2 is a collaboration among more than 200 U.S. universities to develop networking and advanced applications for learning and research. Since much teaching, learning, and collaborative research may require real-time multimedia and high-bandwidth interconnection, a major aspect of Internet2 is adding sufficient network infrastructure to support such applications. But Internet2 also intends to investigate and develop new ways to use the Internet and the Internet2 infrastructure for its educational purposes. Although Internet2 is not envisioned as a future replacement for the Internet, its organizers hope to share their developments with other networks, including the Internet. Internet2 will include and further develop the National Science Foundation's very high-speed Backbone Network Service (vBNS) that currently interconnects research supercomputer centers in the U.S. The involved institutions plan to continue using the existing Internet for "ordinary" services such as e-mail, personal Web access, and newsgroups. http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/0,,sid9_gci214029,00.html The Intelligent Home The home of the future will have far more computer appliances and use a home network for security, energy efficiency, etc. The Intelligent Home • The intelligent home is a networked collection of computers, sensors, and smart appliances. • The user can use the web cams and security devices to monitor the house and inspect it via wireless devices, e.g. PDAs. Check on latch key children and sitters. Turn on heat/AC from a cell phone while driving home to save energy turn on the lights and set the mode to match the guests, etc. Intelligent Home – Smart Appliances • Ovens that turn on from your phone or Internet, it holds the food at a cool temperature until you call. • Smart cribs you can watch baby from other rooms, http://www.pcmag.com/slideshow_viewer/0,2393,l=&s=400&a=142290&po=10,00.asp The Intelligent Car • The modern car can have 20 computers. In the near future cars will have LANs that will do more than just monitor and control basic functions such as braking and exhaust emissions. • In the near future cars will have wireless connections to road side (Bluetooth), other cars, and to the internet and celluar systems that will allow two way communications. • OnStar is now a feature of GM luxury vehicles. Next Generation of Cruise Control • A prototype “fusion processor” from Fujitsu Ten Ltd. depends on optical and radar sensors to move a car automatically at the varying speeds of traffic. A camera and radar report on the width, distance , and speed of objects ahead, • and the processor combines the data, feeding it to a unit that controls the car. • Millimeter-wave radar • Image-processing unit and stereo camera Keeping Cars from Crashing September 2001 article in IEEE Spectrum on adaptive cruise controls. Discussion focuses on radar and lidar sensors. © IEEE (PDF, 432Kb). Intelligent car (more) • • In Minnesota, state police cars, ambulances, and government vehicles will soon carry a small piece of extra cargo—a sensing device that collects data as it rolls down the state's roadways. Ford Motor Company officials call the program a prototype for a nextgeneration travel-advisory system. During their daily rounds, stateowned vehicles will gather trafficrelated data like speed, location, and direction of travel. The sensors will also record weather information, such as windshield-wiper and headlight use, outside temperature, and traction-control-system data. • Ford Motor Company's Smart, Safe Research Vehicle is an enhanced version of the company's Explorer model. The concept automobile includes such "intelligent" safety features as a navigation system that uses real-time traffic information to suggest alternate routes around congested areas. Photograph courtesy Ford Motor Company http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/05/0521_040521_smartcars.html The Cyber Military and Home Defense • • • • The military is changing its theory, order of battle, and deployment strategies in the post cold war world. The Stryker Brigade which was deployed in late 2004 in Iraq. It is an example of how information over an enterprise network allows units at the point of the spear to adjust and take the imitative without the usual hierarchical chain of command. The network allows satellite, robotic vehicles, and other sensors are integrated in intelligence network. Vehicle locations and GIS data are also known. Striker vehicles have wheels rather than treads and are designed to be air mobile. This has required some modification to deal with the Iraq urban battlefield. the steel rails on the sides to prevent exposure to RPGs). The Future of the Internet and media One of the bigger arguments about the future is how the media will adapt to the challenge of the Internet. In prior material we discussed how blogs effected the political news in the last two elections. Record and movie sales are dramatically down this year despite a major legal attack on peer to peer web sites. In the 90s the traditional brick & mortar retailer ignored then modified their business model to adjust to this new marketing and sales channel. Can the media make similar adjustments to compete successfully in the future. The Media Epic 2014 • In this vision of the world -- Google and Amazon.com merge to become the global retailer of information and by 2014 drive the current news media (newspapers, television, and news magazines) into bankruptcy. • The deep web is mined for ideas, facts, and options that are created into customized information products. • Some dismiss this as the ravings of the artificial intelligence geeks. Attempts to define a new search process to replace the current based text ones has not lead to any promising concrete methodology at this moment. The Factory of the Future and the Post-industrial Age In the 80’s the Japanese factories were making better, cheaper cars and appliances than the US. This caused the US industries to change many of their manufacturing practices. Fixed automation was replaced being replaced by robotic assembly. Unionized workers were negotiating for earlier retirements, higher heath care benefits, and more job security. They were so successful that some have commented that the Big 3 auto makers are pension funds that happen to make cars. Free trade and Globalization have seen manufacturing move rapidly off shore supported in large part by the Internet. Union membership has dropped from 1 in 3 Americans to 1 in 7 and the new members largely come from service industry. Pensions are in doubt and health care benefits are becoming less common. The Global Economy will increase the reliance on the Internet • Concepts like “Just-in-Time” (JIT), Six Sigma, etc. pioneered by the Japanese were adopted by other industrialized nations in the 80s & 90s. • The rise of China and India with a large skilled educated workforce will soon advance from outsourcers to major competitors. • The need for increased productivity, demands for greater port security, and higher fuel costs will drive the industrialized nations to place greater demands on their supply chains. • The consumer will demand greater freedom in selection and more individuality for their life styles. • The Factory of the Future will be driven by customers designing their purchases online and a highly automated robotic factory making it, with shipping and order processing being done by computerized systems, e.g. today’s state of the art newspaper production is a leading example. Internet and the Future Society Without doubt the Internet will play the role as a major change agent in society. The findings in the material that follows were taken from Pew Internet & American Life Project, 1615 L Street, NW, Suite 700, Washington, DC 20036 202-419-4500 http://www.pewinternet.org Summary of PEW Experts’ Forecasts 56% of them agreed that as telecommuting and home-schooling expand, the boundary between work and leisure will diminish and family dynamics will change because of that. 50% of them believe that anonymous, free, music file-sharing on peer-topeer networks will still be easy to perform a decade from now. Just 32% of these experts agreed that people would use the internet to support their political biases and filter out information that disagrees with their views. Half the respondents disagreed with or disputed that prediction. Only 32% agreed with a prediction that online voting would be secure and widespread by 2014. Half of the respondents disagreed or disputed that idea. • In the emerging era of the blog, experts believe the internet will bring yet more dramatic change to the news and publishing worlds. They predict the least amount of change to religion. Summary (more) “Connections across media, entertainment, advertising, and commerce will become stronger with future margins going to a new breed of ‘digital media titans’ … Wellbranded innovators such as Google and Starbucks have a chance to build all-new new distribution models tied to ad revenue and retail sales.” “Health care is approximately 10 years behind other endeavors in being transformed, and will experience its boom in the next 10 years.” “Government will be forced to become increasingly transparent, accessible over the Net, and almost impenetrable if you're not on the Net.” “Digitization and the Internet make for a potent brew ... TiVo kills the commercial television format. Napster, Kazaa, and iPod kill the ‘album’ format. In the future, everyone will be famous for fifteen minutes in their own reality show.” “Hyperlinks subvert hierarchy. The Net will wear away institutions that have forgotten how to sound human and how to engage in conversation” “The ‘always-on’ internet, combined with computers talking to computers, will be a more profound transformation of society than what we've seen so far.” “The next decade should see the development of a more thoughtful internet. We've had the blood rush to the head, we've had the hangover from that blood rush; this next decade is the rethink.” “The dissemination of information will increasingly become the dissemination of drivel. As more and more ‘data’ is posted on the internet, there will be increasingly less ‘information.’” Forecast of Internet on Society Civic engagement • • Prediction: Civic involvement will increase substantially in the next 10 years, thanks to ever-growing use of the internet. That would include membership in groups of all kinds, including professional, social, sports, political and religious organizations – and perhaps even bowling leagues. Experts’ reactions – Agree 42% – Disagree 29 – Challenge 13 – Did not respond 17 Since results are based on a non-random sample a margin of error cannot be computed. • Note: An extended rundown of the written answers to this question can be found at: http://www.elon.edu/predictions/q11.aspx Future of the Internet - 20 - Pew Internet & American Life Project Part 6. Civic engagement Civic Involvement • Rose Vines, a technology journalist, wrote, “Involvement won't necessarily increase in numbers, but it will in depth and richness of experience. As more groups discover ways to use the internet to connect, disseminate and influence, a new element will be added to group interaction. We'll also see those traditionally excluded from participation, including the physically disabled and elderly, being brought on board.” Tobey Dichter, founder of Generations on Line, went even further, writing, “This is one of the most effective uses of the internet – building community. Exciting global connections will do more for international understanding and intergenerational respect than any tool since the printing press.” Future of the Internet - 20 - Pew Internet & American Life Project Part 6. Civic engagement Security and the Internet Society Prediction: As computing devices become embedded in everything from clothes to appliances to cars to phones, these networked devices will allow greater surveillance by governments and businesses. By 2014, there will be increasing numbers of arrests based on this kind of surveillance by democratic governments as well as by authoritarian regimes. Experts’ reactions – – – – Agree 59% Disagree 15 Challenge Did not respond 8 17 Since results are based on a non-random sample a margin of error cannot be computed. Source: Future of the Internet - p22Pew Internet & American Life Project Part 7. Embedded Networks Education and the Internet Society Prediction: Enabled by information technologies, the pace of learning in the next decade will increasingly be set by student choices. In ten years, most students will spend at least part of their “school days” in virtual classes, grouped online with others who share their interests, mastery, and skills. Experts’ reactions •Agree 57% •Disagree 18 •Challenge 9 •Did not respond 17 Since results are based on a non-random sample a margin of error cannot be computed. Future of the Internet – p35- Pew Internet & American Life Project Part 8. Formal Education Health Care & Internet Health system change • • Prediction: In 10 years, the increasing use of online medical resources will yield substantial improvement in many of the pervasive problems now facing health care—including rising health care costs, poor customer service, the high prevalence of medical mistakes, malpractice concerns, and lack of access to medical care for many Americans. Experts’ reactions – – – – Agree 39% Disagree 30 Challenge 11 Did not respond 19 • Since results are based on a non-random sample a margin of error cannot be computed. • A December 2002 Pew Internet & American Life Project survey showed that 80% of internet users, or about 102 million Americans, have searched online for at least one of 16 major health topics. An educated consumer stands a better chance of getting good treatment and the internet can be a significant resource for that health education process. An increase in the use of internet health resources is not a cure-all, however. See “Internet Health Resources” (Pew Internet & American Life Project, July 16, 2004). Available at: http://www.pewinternet.org/PPF/r/95/report_display.asp Politics and 2014 Prediction: By 2014, most people will use the internet in a way that filters out information that challenges their viewpoints on political and social issues. This will further polarize political discourse and make it difficult or impossible to develop meaningful consensus on public problems. • Experts’ reactions – – – – Agree 32% Disagree 37 Challenge 13 Did not respond 18 Since results are based on a non-random sample a margin of error cannot be computed. Future of the Internet - Pew Internet & American Life Project p 33