Unit III - WordPress.com
advertisement

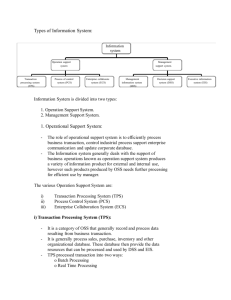
UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA Unit III Information Systems in Business and Management: Transaction Processing System: Information Repeating and Executive Information System. INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT Introduction There are many ways to use information system in business. The word information system represents variety of information system like TSS, DSS, Information reporting etc. The information support the business function such as accounting, finance, marketing, and HRM Marketing information system Marketing information system is one of the most important information system. The basic function of marketing is concerned with planning, promotion of existing products in the existing markets and promoting new products in the new markets. The major applications and objective of various sub-system in marketing information system are 1. Sales promotion:- sales manager must plan, monitor and support the performance of the sales people in their organization 2. Sales force automation:- Increased computer based information system are providing the basis for sales force automation. 3. Advertising and promotion:- Marketing managers need information to help them achieve sales objective at the lowest possible cost for advertising and promotion 4. Product management:- Product managers need information to plan and control the performance of specific product, product lines and brands 5. Sales forecasting:- sales forecasting can be grouped in to two. Short range forecasting:- Deals with the forecast of sales up to a period on one year Long range forecast:- deals with forecast of sales more into future. 6. Market research:- The market research information system provides marketing intelligence to help managers make more effective marketing decision. 7. Marketing management:- Marketing managers make use of information system to develop short or long range plans outlining product sales, profit and growth objectives Human resource information system HRIS functions involve the recruitment, placement, evaluation, compensation and development of employees in an organization. HRIS supports the following 1. Recruitment:- Recruits the people at the proper time to satisfy the organizational needs 2. Placement:- It matches the available personnel with the requirement, hence the effective use of labour is achieved. 3. Training and development:- The technology changes demands new skills, hence the employees need to be trained in the advanced technological changes. 4. Compensation:- The pay and other values for the satisfactions of individual . 5. Maintenance:- To control work standards, and to ensure that personnel policies and procedures are achieved. By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 1 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA Production/Manufacturing information system This information system provides information on production/operation activities of an organization and thus facilitates the decision making process of production managers of an organization The main decisions to be taken in manufacturing system are given below 1. Product design 2. Plant location and layout 3. Production planning and control 4. Quality control By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 2 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA Inventory control system Inventory refers to the stock of raw materials and finished products available in the firm for production or sales. An inventory control system ensures that the proper stock levels of each item are maintained. By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 3 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA Sales order processing systems Sales order processing is an important information system that captures and processes the customers’ orders and produce invoice for the customers. Accounting information system These are the oldest and most widely used information system in the business. They record and report the business transactions and other economic events. The functions of AIS includes the following 1. Order processing 2. Inventory control 3. Accounts receivable 4. Accounts payable 5. Payroll 6. General ledger Financial information system Financial information system is a subsystem of organizations management information system. Financial information system support the financial managers in decision concerning 1. The financing of a business 2. The allocation and control of financial resources within an business Payroll system Payroll system receives and maintains data from employee time card and other work records. They produce pay checks and other documents such as earning statement, payroll reports, labour analysis report etc. TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEM Transaction processing system is a computerised system that performs and records the daily routine transactions necessary to conduct the business. Examples or TPS are sales order processing, shipping, client information etc. Transactions Transactions are the events that occurs as a part of doing business such as sales, purchase, deposits, withdrawals, refunds and payments. Transaction processing cycle By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 4 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA The TPS captures and processes data describing business transactions. Then they update organizational files and databases and produce a variety of information products for internal and external use The five stages in TPS cycle are 1. Data entry 2. Transaction processing 3. File and database maintenance 4. Document and report generation 5. Inquiry processing Data entry:- The first step of data processing cycle is the capture of business data. Transaction processing:- Here the actual process of processing the transaction takes place. There are two types of transaction processing. They are 1 Batch Processing 2 Online processing Database maintenance:- the organization’s database must be maintained by the TPS so that they are always correct and up-to-date. TPS update the corporate database of the organization to reflect changes resulting from day-to-day activities. Document and report generation:- TPS produces a variety of documents and reports. Examples of TPS documents includes purchase orders, pay checks, slaes recipts etc. Inquiry processing:- Many TPS allow the public to use internet, intranets, extranets and we browsers or database management system query languages to make inquires and receive responses. Types of TPS There are two types of TPS. They are 1 Batch processing 2 online/real time processing By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 5 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA 1 Batch processing:- Here the data are accumulated over a period of time and processed periodically. 2 Online / real time processing: - Here the data are processed immediately the transaction occurs. TPS Applications Order Processing Purchasing Accounts Receivables & Accounts Payables Receiving & Shipping Inventory on Hand Payroll General Ledgers Two feature of TPS 1. Spans the boundary between the organization and its environments 2. Major producer of information for other types of systems By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 6 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA Role of TPS in a business A Transaction Processing Model By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 7 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA INFORMATION REPEATING AND EXECUTIVE INFORMATION SYSTEM Executive information systems are information systems that combine many if the features of the management information system and decision support system. They were first developed with the focus of meeting the information needs of the top management. Most popular alternative names of executive information system are executive support system, enterprise information system and management support system. Components of EIS The components of an EIS are 1. Hardware 2. Software 3. Network 4. Data resources Executive workstations in an EIS are typically networked to mainframe for the access of EIS software. The EIS package works with the database management and telecommunication software to provide easy access. Characteristics of EIS Are suitable for individual executive users Extract, filter, compress and track critical data Provide online status access, trend analysis, exception reporting. Access and integrate a broad range of internal and external data Are user friendly and require minimal or no training to use Are directly used by executives without intermediaries Present graphical, tabular and textual information EIS Operational Success Factors Deliver timely information Improve efficiency Provide accurate information Provide relevant information Ease of use Provide access to the status of the organization Provide improved communications By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 8 UNIT III MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM III BCOMCA Most Popular EIS Uses – Decision making (by providing data) – Scheduling (to set agendas and schedule meetings) – Email and electronic briefing (to browse data and monitor situations) EIS/ESS and DSS Executive information sources Information is collected from two major sources 1. Internal 2. External External sources on-line databases newspapers industry newsletters government reports other personal contacts Internal sources • Financial • accounting • personnel • other internal reports By Mr M. Suresh M.C.A., M.E (C.S.E) Asst. Prof., DOC NASC., NGI Page 9