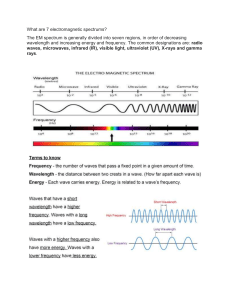
Electromagnetic Spectrum
advertisement

Electromagnetic Spectrum Range of Behavior Electromagnetic waves are characterized by their wavelength or frequency. c • Linked by the speed of light The frequency is associated with an energy. • High frequency is high energy E h hc The common unit is the electron-volt (eV). • Work done by 1 V potential on one electron hc = 1.240 keV nm Electromagnetic Radiation Traditional upper boundaries for types of EM radiation: Radio waves Microwaves Infrared Visible light Ultraviolet light X-rays Gamma rays (m) 1 110-3 0.7510-6 0.410-6 1.210-8 1.410-11 (Hz) E (eV) 3108 1.2410-6 31011 1.2410-3 41014 1.65 7.51014 3.1 2.41016 1102 31019 1.2105 (highest energy) Radio Waves Radio waves primarily come from the oscillation of currents in conductors. A 1 MHz frequency has an energy of 6.6 x 10-28 J. The long wavelengths travel easily and are not interfered by atoms. • Except conductors Microwaves Microwaves are very short wavelength radio waves. Microwaves are associated with the vibrations of some atoms and molecules. Water molecules act as a dipole. • Motion increased by microwaves • Causes heating Radiation from Heat Heated objects give off electromagnetic waves. • Higher temperature has more radiation A hot object gives off a spectrum of frequencies. intensity low energy high energy • Shifts based on temperature This is called blackbody radiation frequency Infrared Wavelengths longer than visible light are called infrared rays. • Come from warm objects Molecules are heated by infrared waves. • Radiant heat Visible Light Visible light is radiation in a narrow band of wavelength. • 400 nm to 800 nm • Narrower ranges are colors Corresponds to maximum output from the Sun. intensity low energy high energy Many atoms and molecules have specific behavior at unique frequencies of light. frequency Ultraviolet Ultraviolet rays have shorter wavelengths than visible light. • Higher energy • Often with visible light Some molecules absorb ultraviolet and reemit visible light. • Fluorescent light X-Rays X-rays are associated with energetic transitions in atoms. electrons target Continuous spectra result from electron bombardment. x-ray The short wavelength x-rays can penetrate materials. • Stopped by dense atoms Gamma Rays Gamma rays are photons associated with nuclear or particle processes. • Energy range overlaps: soft gamma equals hard x-ray g e e Z Acceleration of a very energetic charged particle gives x-rays and gamma rays. • Called bremsstrahlung next