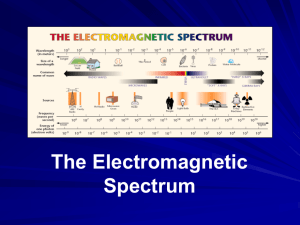
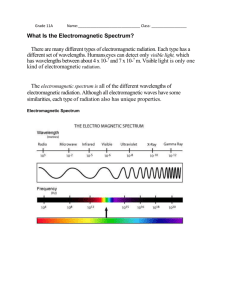
More Good Stuff About the Electromagnetic Spectrum
advertisement

THE Electromagnetic Spectrum Webquest I what are the “ranges” for the different forms of energy? http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/science/know_l1/spectrum_chart.html 1. As we move from radio to gamma, wavelength __________________, frequency ____________________ and (photon) energy ________________________ (Use terms increase, decrease) NOTE: To learn more about each property, use these links: Wavelength: http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/Communications/1-what-is-wavelength.html Frequency: http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/Communications/1-what-is-frequency.html Photon Energy: http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/quantumzone/photoelectric2.html II What forms of E-M energy reach the earth’s surface? Consult the chart on this page (near bottom): http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/science/know_l1/emspectrum.html III For more details on each of the forms of E-M energy, use the link below and answer the questions for each section. Unfortunately, you will not be able to take the video tour, as it is on Youtube. http://missionscience.nasa.gov/ems RADIO (Read first two sections) 2. Radio wavelengths can range from the length of a _________________ to ______________ ________________________ . 3. True or false: in our solar system, only the sun creates radio waves. Humans have created machines that produce radio waves of different wavelengths/frequency. Who can use what is controlled by the FCC. http://www.ntia.doc.gov/osmhome/allochrt.pdf 4. What frequency range does the United States use for FM broadcasting? For AM broadcasting? 5. What frequency does television channel 7 broadcast at? 6. How large a band of frequencies does each television broadcasting channel get? MICROWAVES (Read first two sections): http://missionscience.nasa.gov/ems 7. Microwave ovens produce waves with _______________ wavelengths. 8. How do microwaves “cook” food? 9. Why are microwaves good for transmitting information? B: RADAR, and acronym for ______________ ________________ _____ _________________ actually uses microwaves. B: What is “Doppler Radar?” INFRARED (read first three sections: 10. Infrared radiation is not visible to humans, but we do experience it as ___________________ . 11. Short infrared waves are used in your TV’s _______________ _______________. 12. In the dog picture, the warm areas are: VISIBLE LIGHT (read first section) 13. Visible light is made up of the colors of the visible spectrum. ______________ light has the longest wavelength ( ) and ___________________ light has the shortest (_______________ ). 14. When white light (a mixture of all of the colors) passes through a prism, the colors will be pulled apart, because: ____________________________________________________________________ ULTRAVIOLET WAVES (read first section and “Ultraviolet Astronomy.) 15. Ultraviolet UV-B waves are responsible for causing our ________________________. 16. Though the sun produces much U-V radiation, little reaches the surface because: 17. Cosmic objects are recorded by different devices sensitive to U-V or visible light. This is because: B: U-V radiation exposure is liked to what human physical problems? X-RAY (Read first three sections.) 18. The x-ray photos that we see after an injury have light and dark areas. Why? 19. What determines the wavelengths of radiation produced by an object? B. What is the annual “safe” dosage of X-rays and how does it compare to what we get at the dentist’s office? Gamma (read first two sections) 20. What produces gamma rays here on earth? 21. What produces gamma rays outside of the earth? 22. Why do gamma rays not reflect like other forms of E-M energy? B: Describe HOW gamma rays are used in medicine.