Domino's Pizza
advertisement

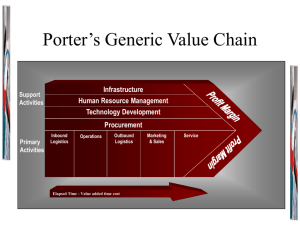
Business-Level Strategy: How do we compete? Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Cost Breadth of Competitive Scope Broad Target Market Narrow Target Market Cost Leadership Uniqueness Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Cost Breadth of Competitive Scope Broad Target Market Narrow Target Market Uniqueness Cost Leadership Differentiation Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Breadth of Competitive Scope Broad Target Market Narrow Target Market Cost Uniqueness Cost Leadership Differentiation Focused Low Cost Focused Differentiation Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Cost Breadth of Competitive Scope Broad Target Market Narrow Target Market Uniqueness Cost DifferenLeadership tiation Integrated Low Cost/ Differentiation Focused Focused DifferenLow Cost tiation Profit = (P – C) × Q The Experience Curve The “Law of Experience” 1994 1995 Cost per unit of output The unit cost value added to a standard product declines by a constant % (typically 20-30%) each time cumulative output doubles. 1996 1997 1998 Cumulative Output 1999 2000 Examples of Experience Curves 75% UK refrigerators, 1957-71 Price Index 50 100 200 300 1960 Yen 15K 20K 30K Japanese clocks & watches, 1962-72 70% slope 100K 200K 500K 1,000K Accumulated unit production (millions) 5 10 50 Accumulated units (millions) Choices that Drive Costs Economies of scale Product features Asset utilization Performance Capacity utilization pattern Mix & variety of products - Seasonal, cyclical Interrelationships - Order processing and distribution Value chain linkages Service levels Small vs. large buyers Process technology Wage levels - Advertising & Sales Product features - Logistics & Operations Hiring, training, motivation Value Chain of Firm Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Service Marketing & Sales Outbound Logistics Operations Inbound Logistics Procurement Value Creating Activities common to a Inbound Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Logistics Inbound Logistics Support Activities Highly Efficient Systems to Link Suppliers’ Products with the Firm’s Production Processes Located in Close Proximity with Suppliers Primary Activities Value Creating Activities common to a Operations Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Effective Training Programs to Improve Worker Efficiency and Effectiveness Human Resource Management Timing of Asset Purchases Investments in Technology in order to Reduce Costs Associated with Manufacturing Processes Technological Development Policy Choice of Frequent Evaluation to PlantProcesses Technology Procurement Outbound Logistics Operations Efficient Plant Delivery Schedule Scale to Minimize that Reduces Manufacturing Costs Costs Selection of Low Timing of Asset Cost Transport Purchases Carriers Policy Choice of Efficient Order Plant Technology Sizes Organizational Learning Primary Activities Organizational Small, Highly Trained Sales Learning Force Products Priced to Generate Sales Volume Service Monitor Suppliers’ Performances Inbound Logistics Support Activities Firm Efficient Plant Scale to Minimize Infrastructure Mfg. Costs Relatively Few Management Layers to Reduce Overhead Value Creating Activities common to a Cost Leadership Business LevelOutbound Strategy Logistics Delivery Schedule that Reduces Costs Human Resource ManagementSelection of Low Technological Development Cost Transport Carriers Efficient Order Frequent Evaluation Processes to Procurement Monitor Suppliers’ Performances Sizes Effective Product Interrelationships Installations to Reduce Frequency with Sister Units Marketing & Sales Service Delivery Schedule Small, Highly that Reduces Trained Sales Costs Force Outbound Outbound Logistics Logistics Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Selection of Low Cost Transport Carriers and Severity Products Priced to of Recalls Generate Sales Volume Efficient Order Sizes National Scale Advertising Interrelationships with Sister Units Primary Activities Value Creating Activities common to a Marketing Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy & Sales Human Resource Management Technological Development Primary Activities Small, Highly Trained Sales Force Products Priced to Generate Sales Volume National Scale Advertising Marketing & Sales Marketing & Sales Service Outbound Logistics Operations Procurement Inbound Logistics Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Effective Product Installations to Management Reduce Recalls Technological Development Primary Activities Marketing Service & Sales Service Outbound Logistics Procurement Inbound Logistics Operations Support Activities Value Creating Activities common to a Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Service Firm Infrastructure Value Creating Activities common to a Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Procurement Systems and Procedures to Find the Lowest Cost Products to Purchase Raw Materials Primary Activities Marketing & Sales Service Outbound Logistics Inbound Logistics Operations Procurement Procurement Frequent Evaluation Processes to Monitor Suppliers’ Performances Value Creating Activities common to a Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Human Resource Management Technological Development Marketing & Sales Outbound Logistics Easy-to-Use Manufacturing Technologies Operations Technological Development Service Procurement Inbound Logistics Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Investments in Technology in order to Reduce Costs Associated with Manufacturing Processes Primary Activities Value Creating Activities common to a Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Human Procurement Resource Management Primary Activities Service Marketing & Sales Effective Training Programs to Improve Worker Efficiency and Effectiveness Outbound Logistics Operations Inbound Logistics Consistent Policies to Reduce Turnover Costs Value Creating Activities common to a Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Firm Infrastructure Primary Activities Service Relatively Few Management Layers to Reduce Overhead Marketing & Sales Outbound Logistics Simplified Planning Procurement Practices to Reduce Planning Costs Operations Inbound Logistics Cost Effective MIS Systems Effective Cost Leaders can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Rivalry Among Competing Firms in Industry Threat of Substitute Products Bargaining Power of Buyers Effective Cost Leaders can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of New Entrants Can frighten off New Entrants due to the need to: * Enter at large scale to be Cost Competitive * Take time to move down the “Learning Curve” Effective Cost Leaders can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of New Entrants Can mitigate Buyer Power by: * Driving prices far below competitors may cause exit and shift power back to firm Bargaining Power of Buyers Effective Cost Leaders can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of Substitute Products Threat of New Entrants Well positioned relative to Substitutes in order to: * Make investments to create substitutes first * Buy patents developed by potential substitutes * Lower prices to maintain value position Bargaining Power of Buyers Effective Cost Leaders can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Bargaining Power of Suppliers Threat of New Entrants Can mitigate Supplier Power by: * Low cost position makes them better able to absorb cost increases large purchases * More likely to make very Threat of which reduces chance Substitute of supplier power Products Bargaining Power of Buyers Effective Cost Leaders can remain profitableavoid Competitors even when the Five Forces appear unattractive price wars with Cost Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Rivalry Among Competing Firms in Industry Threat of Substitute Products Leaders, which creates higher profits for entire industry Bargaining Power of Buyers The Major Risks involved with a Cost Leadership Business Level Strategy Dramatic technological change could take away your cost advantage Competitors may learn how to imitate Value Chain Focus on efficiency could cause Cost Leader to overlook changes in customer preferences Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Breadth of Competitive Scope Broad Target Market Narrow Target Market Cost Uniqueness Cost Leadership Differentiation Differentiation Business Level Strategy Key Criteria Value provided by unique features and value characteristics Command premium price High customer service Superior quality Prestige or exclusivity Rapid innovation Drivers of Differentiation Some Examples: Unique product features Unique product performance Exceptional services New technologies Quality of inputs Exceptional skill or experience Detailed information Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Human Resource Management Technological Development Primary Activities Service Marketing & Sales Outbound Logistics Operations Procurement Inbound Logistics Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Value Creating Activities common to a Inbound Differentiation Business Level Strategy Logistics Primary Activities Service Outbound Logistics of incoming raw Human Resource Management materials to minimize damage and Development improve the Technological quality of the final product Procurement Inbound Logistics Inbound Logistics Operations Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Superior handling Value Creating Activities common to a Operations Differentiation Business Level Strategy Human Resource Management Technological Rapid responses to customers unique Development manufacturing specifications Primary Activities Service Outbound Logistics Procurement Inbound Logistics Operations Operations Support Activities Firm Consistent manufacturing of Infrastructure attractive products Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Outbound Strategy Logistics Human Resource Accurate and responsive order Managementprocessing procedures Technological Development Primary Activities Rapid and timely product deliveries to customers Marketing & Sales Service Outbound Outbound Logistics Logistics Procurement Inbound Logistics Operations Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Value Creating Activities common to a Marketing Differentiation Business Level Strategy & Sales Human Resource Management Outbound Logistics Procurement Primary Activities Strong Coordination among functions in R&D, Marketing and Product Development Extensive personal relationships with buyers Marketing & Sales Marketing & Sales Service Technological Development Inbound Logistics Operations Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Premium Pricing Human Resource Complete field stocking of Management replacement parts Technological Development Primary Activities Marketing Service & Sales Service Outbound Logistics Procurement Inbound Logistics Operations Support Activities Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Service Firm Infrastructure Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Procurement Systems and procedures used to find the highest quality raw materials Purchase of highest quality replacement parts Primary Activities Marketing & Sales Service Outbound Logistics Inbound Logistics Operations Procurement Procurement Located in Close Proximity with Suppliers Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Marketing & Sales Service Procurement Coordination among R&D, marketing and product development Outbound Logistics Inbound Logistics Operations Technological Development Investments in technologies to produce highly differentiated products Primary Activities Strong capability in basic research Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Human Procurement Resource Management Primary Activities Marketing & Sales Service Extensive use of subjective performance measures Outbound Logistics Inbound Logistics Operations Compensation programs which encourage worker creativity and productivity Superior personnel training Value Creating Activities common to a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technological Development Firm Infrastructure Primary Activities A companywide emphasis on producing high quality products Marketing & Sales Service Outbound Logistics Inbound Logistics Operations Highly developed Information Systems to better Procurement understand customers’ purchasing preferences Differentiation Business Level Strategy Effectiveness with Differentiation grows out of Value Chain activities Examples: Heineken beer Raw materials – brand name Steinway pianos Raw materials & Workmanship Mercedes Benz autos Technology and Workmanship Intel microprocessors Technological superiority Caterpillar tractors Service buyers’ needs quickly anywhere in the world Effective Differentiators can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of New Entrants Can fend off New Entrants because: * New products must surpass proven products * Or be equal to performance at lower prices Effective Differentiators can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of New Entrants Can mitigate Buyer Power because: Well differentiated products reduce customer sensitivity to price increases Bargaining Power of Buyers Effective Differentiators can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of Substitute Products Threat of New Entrants Well positioned relative to Substitutes because: * Brand loyalty tends to reduce new product trial and brand switching Bargaining Power of Suppliers Effective Differentiators can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Bargaining Power of Suppliers Threat of New Entrants Can mitigate Supplier Power by: * Absorbing price increases due to higher margins Well positioned relative to Substitutes because: prices * Passing on higher supplier Threat of Brand loyalty tends to * because buyers are brand loyal Substitute reduce new product trial and brand switching Products Bargaining Power of Suppliers Effective Differentiators can remain profitable even when the Five Forces appear unattractive Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of Buyers Rivalry Among Competing Firms in Industry Threat of Substitute Products Can fend off New Entrants because: Brand loyalty New products must * surpass proven products overcomes much * Or be equal to performance price competition at lower prices Bargaining Power of Suppliers The Major Risks involved with a Differentiation Business Level Strategy Customers may decide that the cost of “uniqueness” is too great Competitors may learn how to imitate Value Chain The means of uniqueness may no longer be valued by customers Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Breadth of Competitive Scope Cost Uniqueness Broad Target Market Cost Leadership Differentiation Narrow Target Market Focused Low Cost Focused Differentiation Focused Business Level Strategies Focused Business Level Strategies involve the same basic approach as Broad Market Strategies * However..... Opportunities may exist because: * Large firms may overlook small niches * Firm may lack resources to compete industry wide May be able to serve a narrow market segment more effectively than industry-wide competitors Focused Business Level Strategies Focused Business Level Strategies involve the same basic approach as Broad Market Strategies - Bang & Olufsen - Snap-On tools - IAMS * May be able to retrofit old factories to keep costs down * Minimize R&D costs by copying innovators Upscale electronic components High quality mechanics’ tools Premium pet foods Focused Business Level Strategies Focused Business Level Strategies involve the same basic approach as Broad Market Strategies * Focused Differentiators may thrive by selecting a small market that is underserved by large players Custom manufacturers of parts for Harley-Davidson motorcycles Firm may be “outfocused” by competitors The Major Risks involved with a Focused Differentiation Business Level Strategy Large competitor may set its sights on your niche market Preferences of niche market may change to match those of broad market Generic Business Level Strategies Source of Competitive Advantage Cost Breadth of Competitive Scope Broad Target Market Narrow Target Market Uniqueness Cost DifferenLeadership tiation Integrated Low Cost/ Differentiation Focused Focused DifferenLow Cost tiation Integrated Low Cost/Differentiation Strategy Recognize that the Integrated Low Cost/ Differentiation business level strategy involves a Compromise The risk is that the firm may become “Stuck in the Middle” lacking a strong commitment to or expertise with either type of generic strategy Integrated Low Cost/Differentiation Strategy Southwest Airlines Low Cost Use a single aircraft model (Boeing 737) Use secondary airports Fly short routes No meals 15 minute turnaround time No reserved seats No travel agent reservations Integrated Low Cost/Differentiation Strategy Southwest Airlines Low Cost Use a single aircraft model (Boeing 737) Use secondary airports Fly short routes No meals 15 minute turnaround time No reserved seats No travel agent reservations Differentiation Focus on customer satisfaction High level of employee dedication New flight services for business travelers (Phones and faxes) What is the Strategy? Friendly Robotics