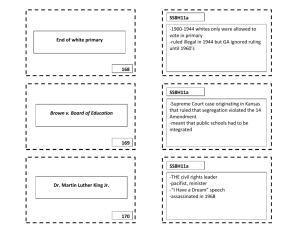
To help poverty and civil rights
advertisement

Welcome to Contemporary U.S. and World History Pg Assignment Date Date: 1/16/15 81 Please Do Now 1/6 82 Vietnam Study Guide 1/6 Activity: Civil Rights Review 83 Legacy of the War Rdg 1/7 84 Legacy of the War Notes 1/7 85 Social Changes Vocab 1/9 86 Culture and Counterculture 1/13 87 Counterculture & Music 1/14 88 Civil Rights Timeline 1/16 Warm Up: While you are waiting to get started, skim through the timeline and see what you remember Homework: ALL LATE WORK DUE BY TUES 1/20 OR ZERO *End of MP Friday 1/23 *Quarterly Exam Th 1/29 Brown vs. Board of Education • Who argued the case? What did the Supreme Court declare? – Thurgood Marshall -Ruled segregation in school was an unconstitutional violation of the 14th Amendment’s equal protection under the law • Why did Chief Justice Warren rule the way they did? – Warren went against Plessy vs. Ferguson and “separate but equal”, stating it can never be equal in the case of school. It would affect the Montgomery, Alabama • What are Jim Crow laws? What does the 14th amendment promise? – Jim Crow laws are ones that segregate African Americans in public. – The 14th amendment grants all persons born or naturalized in US citizens and grants Montgomery Bus Boycott What was Rosa Park’s role in the Montgomery Bus Boycott? – Rosa Parks refused to give her seat to a white person and was arrested. She helped the efforts of the boycott. What is a boycott? How are both sides hurt by a boycott? – To stop using a service or buying products to hurt the industry. The consumers can’t have the product or use the service, but the industry loses money by losing customers. What kind of support did the boycotters receive? How did it all end? Martin Luther King Jr. • – Describe MLK’s background – MLK was a preacher (minister) and was treated poorly by whites. He vowed to hate the whites. • Describe his methods: – He used non-violent protests and speeches to gain support for his cause of gaining Civil Rights. • What is his organization and what did they do? – SCLC: Southern Christian Leadership Conference. To Little Rock, Arkansas • How did some whites resist desegregation? – KKK boycotted businesses who supported integration – students (and parents) picketed outside the schools • What was the “crisis” in Little Rock? What happened with Elizabeth Eckford? – Crisis came after Brown vs. Board of Ed; school board and superintendent were going to start desegregation, but Governor Orval Faubus called in National Guard to turn away the “Little Rock Nine.” Elizabeth Eckford had to enter the school on her own and was terrified by the abusive crowd taunting her. Welcome to Contemporary U.S. and World History Pg Assignment Date Date: 1/20/15 85 Social Changes Vocab 1/9 Activity: Civil Rights Review 86 Culture and Counterculture 1/13 87 Counterculture & Music 88 Civil Rights Timeline 89 Civil Rights Movement Changes Warm Up: What was the first accomplishment of 1/14 the Civil Rights Movement that really 1/16 ‘got the ball rolling’ for future changes? 1/20 Homework: *Read and take notes on “The Great Society” for tomorrow *End of MP Friday 1/23 *Quarterly Exam Th 1/29 Little Rock, Arkansas • How did the government become involved? – Eisenhower put Arkansas National Guard under federal control and ordered 1,000 paratroopers in to oversee the 9 going to school. • What did the Civil Rights Act of 1957 do? – It gave the Attorney General greater power over school desegregation and gave federal government the authority over violations of African American voting Sit Ins What group led many of the sit-ins? SNCC: Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee. What are “sit-ins?” What makes them effective? When people would sit somewhere and not get up to prove a point. They are effective at gaining peoples’ attention What effect did they have? They were on the national news and showed the ugliness of racism and gained a lot of support from people in our nation (especially those up North who protested the segregation in the South) Freedom Riders What were the Freedom Riders trying to do? – Trying to non-violently protest segregation on busses and bus terminals. Why is Kennedy forced to take action? What does he do? – Kennedy had the Justice Dept send 400 U.S. marshals to protect the riders to Jackson, Mississippi, AND the attorney general and the ICC banned segregation in all interstate travel facilities, including waiting rooms, restrooms, and lunch counters. Integrating Ole Miss Why is the following quote shocking by today’s standards: “I call on every Mississippian to keep his faith and courage. We will never surrender”? – For someone to be that adamantly racist is shocking today. Why is James Meredith brave? – Because he was willing to go to a school where no one wanted him in order to help the Civil Rights movement, even if it meant being escorted to class by federal officials and having his home shot at. Birmingham, Alabama Describe Birmingham: – Reputation for racial violence & strict segregation laws, in fact- the most segregated city in the nation. What happens with MLK, children and Bull Connor? – MLK organized a peaceful march on Birmingham, with over 1,000 children. 959 children were arrested. The next day, a second “children’s crusade” marched and the police (Bull Connor was was police commissioner) hosed them down and sent dogs after them and clubbed those who fell. How does the media affect the situation, Kennedy and the rest of the nation? – The media shed light to the rest of the nation about how bad things were & it influenced the need for more laws toward racial justice 1963 – March on Washington Who marches on Washington? What do they want? – They marched on Washington to try to get JFK’s Civil Rights Act passed What famous speech is given? – MLK’s “I Had a Dream” speech ***Civil Rights Act of 1964 What does this law do? – LBJ vowed to get JFK’s legislation passed after his death. Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibited discrimination based on race, religion, national origin, and gender. It gave all citizens the right to enter public accommodations. Freedom Summer What was the goal of “Freedom Summer?” Eventually Freedom Summer and the Selma Campaign lead to the Voting Rights Act of 1965. What does this law do? – Eliminated the “literacy” tests that disqualified many voters and stated that fed examiners could enroll voters who had been denied suffrage by local officials. Read about Johnson’s Great Society before we discuss THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT CHANGES • WHAT IS DE FACTO SEGREGATION? Segregation that exists by practice or custom • WHAT IS DE JURE SEGREGATION? Segregation that exists by law • LIST AN EXAMPLE OF EACH TYPE OF SEGREGATION? De Facto – not selling homes to African Americans De Jure – segregated schools • WHY IS DE FACTO SEGREGATION OFTEN MORE DIFFICULT TO ERADICATE THAN DE JURE SEGREGATION? To end De Facto segregation you have to change attitudes, not just eradicate laws. Urban Riots “White Flight” to suburbs African American migration North African Americans lived in decaying slums Landlords didn’t comply with housing and health ordinances Unemployment rates twice as high for blacks than whites De facto segregation African American Schools deteriorating Riots spread like wildfire from 1964-1968 Malcolm X • Born Malcolm Little • Studied under Elijah Muhammad, the head of the Nation of Islam • Black Muslims – – Black superiority and separatism – Advocated armed self-defense • Advocated armed self-defense • Changed his tune by the end of his life “Ballots or Bullets” • Killed giving a speech in Harlem February 21, 1965 • SNCC and CORE became more militant than MLK’s SCLC. – “We Shall Overcome” turned into “We Shall Overrun” – “Black Power” coined by Stokely Carmichael BLACK PANTHERS – created by Huey Newton and Bobby Seale to fight police brutality in the ghetto – Advocated self-sufficiency for African American communities, as well as full employment and decent housing. – Established daycares, free breakfasts, medical clinics, homeless services (won support of people in the ghettos) WHY WAS 1968 A TURNING POINT IN CIVIL RIGHTS? • KERNER COMMISSION: – FORMED BY LBJ – STUDY CAUSES OF URBAN VIOLENCE • FINDINGS: – "OUR NATION IS MOVING TOWARD TWO SOCIETIES; ONE BLACK, ONE WHITE, SEPARATE AND UNEQUAL.“ • LED TO CIVIL RIGHTS ACT OF 1968: – BANNED DISCRIMINATION IN HOUSING Welcome to Contemporary U.S. and World History Pg Assignment Date Date: 1/21/15 85 Social Changes Vocab 1/9 Activity: Women’s Rights 86 Culture and Counterculture 1/13 87 Counterculture & Music 88 Civil Rights Timeline 1/16 89 Civil Rights Movement Changes 1/20 90 Women’s Rights 1/21 Warm Up: Answer the last question on “Civil Rights 1/14 Movement Changes” Homework: *Women’s Rights due Friday 1/23 *End of MP Friday 1/23 *Quarterly Exam next Thursday 1/29 • WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THE RESULTS OF THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT AS SUCCESSFUL, A FAILURE, OR MIXED? EXPLAIN. WHAT DO YOU THINK WERE THE MOST IMPORTANT GAINS OF THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT? The Great Society What was the purpose of LBJ’s Great Society? – To help poverty and civil rights* What does the Great Society do in regards to fight poverty (page 688)? - Economic Opportunity Act (EOA); $1bil in youth programs, antipoverty measures, small-business loans, and job training. What does the Great Society do in regards to healthcare (page 690)? – Medicare:provided hospital insurance and low cost medical insurance for almost every American 65 + – Medicade:extended health insurance to welfare recipients. The Great Society What does the Great Society do in regards to housing (page 690)? – App. $ to build 240,000 units of low-rent housing, est. Department of Housing & Urban Development (HUD), appointed first Af Amer cabinet member as Secretary of HUD What does the Great Society do regards to immigration (page 691)? – Immigration Act of 1965: opened the door to many nonEuropean immigrants to settle in U.S. by ending quotas based on nationality. (reversed quotas from Natl Origins Act of 1924) The Great Society • Good intentions to help poverty but ultimately failed because the money needed to fund the program was redirected to the Vietnam War. Unfinished work/challenges • More tax $ spent inner cities and forced busing of school children angered some whites. • Affirmative Action programs involved making special efforts to hire or enroll groups that have suffered discrimination. – Criticized for “reverse discrimination” What two major problems did President Johnson’s Great Society focus on? •-poverty and civil rights How did the U.S. Supreme Court rule in the 1973 case Roe v. Wade? - legalized abortion in many cases Feminists argued that women should do what? • - be more assertive - be able to choose a career other than homemaker - receive equal pay for equal work • What did the Civil Rights Act of 1964 do? - it prohibited discrimination because of race, gender, religion & national origin What goals of the Civil Rights Movement were achieved by 1970? - The passage of the Civil Rights Act - Elimination of poll taxes and literacy tests - Adoption of affirmative action