Student Resource 3.2
Reading: Regulatory Agencies/GAAP
This presentation examines regulatory agencies in the accounting industry and the need for and purpose
of regulation.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
Standardization helps investors make informed decisions about different companies. If financial
information were not standardized, it would be very difficult to compare across different investments.
Regulations promote honest behavior and help industry workers better understand what is expected of
them. It also creates confidence in the system, which encourages investment and allows companies to
grow.
Because so many different stakeholders rely on financial information for important decisions, there is a
need for accounting rules and regulations that are enforced by impartial third parties.
A good regulation is clear, concise, and enforceable. A bad one is difficult to follow and open to
interpretation.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
Governments tax their citizens to pay for certain services. In the United States, an income tax was first
imposed in the 1860s to pay for the Civil War. Then the income tax was deemed unconstitutional and
repealed. In 1913, the 16th amendment to the Constitution instituted a national income tax, which is still in
force.
The IRS is the agency that collects taxes and is one of the most powerful departments in the US
government. The IRS has powers of enforcement to collect taxes, levy fines, and confiscate property.
One big difference between the governmental regulatory agencies and other agencies discussed in this
lesson is that the relationship between the government and individuals or businesses is mandatory. All of
the other entities discussed in this lesson maintain voluntary relationships with individuals and
businesses.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
The SEC is responsible for protecting all investors and making sure the markets run smoothly. It works
closely with Congress to enact and enforce laws to achieve these ends. One way it protects the public is
by setting standards of disclosure for public companies (companies that trade securities on the stock
exchanges). By making all companies disclose the same financial information, the SEC makes it possible
for investors to become informed about whether they should buy, sell, or hold securities. The SEC relies
mostly on the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) to generate accounting rules.
It’s one of two agencies of the ones we’re studying with powers of enforcement (the Internal Revenue
Service is the other one). Every year the SEC catches people guilty of insider trading, accounting fraud,
lying or misleading others about securities and issuing companies, manipulating stock prices, and
stealing customers’ assets, among other infractions.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
Although the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has the legal authority to establish financial
accounting and reporting standards for publicly held companies, it has allowed the accounting profession
to develop its own accounting standards and guidelines. In 1973, the SEC gave the responsibility for
setting accounting standards for public companies to the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
The FASB isn’t part of the government, but it is a private nonprofit organization whose primary purpose is
to develop generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) in the public’s interest. The rules FASB
makes affect how accountants record transactions, and these rules provide guidelines that allow investors
to compare companies with each other in a way that’s meaningful.
GAAP is a set of guidelines established for accountants to follow when recording transactions and
preparing financial statements of companies. One essential part of GAAP is that the guidelines are
general and broad. GAAP allows for different companies to present information differently, as long as the
presentation follows GAAP guidelines.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
The AICPA is a professional organization that tries to help its members succeed in the field of accounting
and to make government and the public in general have confidence in the accounting industry. The
AICPA creates and administers the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) exam to ensure that the industry is
represented by professionals with a high degree of competence and knowledge. In addition, the AICPA
creates standards for audits of private companies as well as ethical standards for CPAs to follow.
Created in 2002 by Congress, the PCAOB is a nonprofit corporation that oversees the audits of public
companies in order to protect investors and the general public. The PCAOB promotes informative,
accurate, and independent audit reports. The five members of the PCAOB are appointed by the SEC.
The difference between the AICPA, PCAOB, and the FASB is that the FASB creates generally accepted
accounting principles (GAAP) guidelines that focus on the information reported on financial statements.
Both the AICPA and PCAOB create wide ranges of behavioral (ethical and professional) guidelines,
which focus on how CPAs and auditors actually do their jobs. The AICPA and the PCAOB both support
the FASB by providing technical support for how to follow the principles made by the FASB and the rules
made by the IRS.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
Financial reports must be prepared objectively, without bias or inconsistency. The following are the seven
principles that guide all other rules that accountants follow:
Principle of regularity or principle of consistency: The same accounting principles must be followed at
all times.
Principle of sincerity: Statements must be presented honestly and accurately.
Principle of the permanence of methods: The same accounting methods and format of statements
should be used over time so they can be compared.
Principle of noncompensation: Companies should completely disclose the truth, and not add fake
positive items to balance out negative items on the financial statements.
Principle of prudence: Accountants should not make the statements look better than they are and they
must use caution when recording transactions.
Principle of continuity: Accountants should record transactions assuming the business will be in
business for a long time and won’t be stopped or interrupted in the short run.
Principle of periodicity: Accounting should be split into periods of the same time length. Each
transaction should be accounted for in a given period and split across many periods if necessary.
By following these principles, accountants create an environment in which managers and investors can
trust the numbers they are given and make intelligent, informed decisions.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
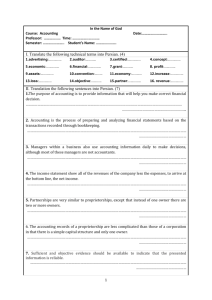
Student Resource 3.3
Vignettes: Regulatory Agencies/GAAP
Student Name:_______________________________________________ Date:___________
Directions: Identify which agency, agencies, or GAAP is presented in each vignette. Write your answers
and your rationale in the space below each description.
Vignette 1
This agency is responsible for protecting all investors and making sure the markets run smoothly. It works
closely with Congress to enact and enforce laws to achieve these ends. One way it protects the public is
by setting standards of disclosure for public companies, or companies that trade shares on the market
exchanges. By making all public companies disclose the same financial information, investors can inform
themselves as to whether they should buy, sell, or hold securities.
This agency relies mostly on another to generate the ideas that become law. So, essentially, the
accounting profession gets to police itself to some extent.
Name the agency that protects investors and the agency it relies on to generate ideas that become laws.
Defend your answers.
Vignette 2
This agency isn’t part of the government. It’s a private nonprofit organization whose primary purpose is to
develop general accounting guidelines within the United States. The rules this agency make affect how
accountants record transactions, and these rules provide guidelines that allow many different
stakeholders such as investors and financial institutions to compare companies with each other in a way
that’s meaningful.
Name the agency and the guidelines it develops.
Defend your answer.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.
AOF Principles of Accounting
Lesson 3 The Regulatory Environment
Vignette 3
This agency creates and administers the CPA exam to set the standard for what you need to know if you
are going to practice as a certified public accountant. Also, it creates audit standards for private
companies and ethical standards for CPAs to follow in an attempt to provide the public with a sense of
confidence when they deal with CPAs. On the other hand, this corporation creates audit standards for
public companies.
Name these two entities.
Defend your answer.
Vignette 4
This agency is one of the most powerful departments in the US government with responsibility for
collecting taxes, levying fines, and confiscating property. The relationship between this agency and
individuals or businesses is mandatory.
Name this agency.
Defend your answer.
Copyright © 2008–2013 National Academy Foundation. All rights reserved.