The Beginnings of the Cold War
advertisement

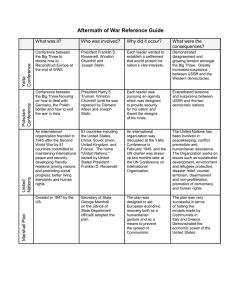
The Beginnings of the Cold War 1945 - 1953 Lividia Palace, Yalta, Crimea Yalta Conference (Feb. 4 – 11, 1945) Poland moved west & govt. broadened Germany & Berlin divided into 4 occupation zones USSR to declare war on Japan 2-3 months after V-E Day & recognize Nationalist China Would regain what it lost in RussoJapanese War Korea divided at 38th parallel Declaration of Liberated Europe promised to est. democracies & rebuild economies of liberated nations Winston Churchill, Franklin D. Roosevelt & Josef Stalin at Yalta (copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s) Post-WWII Eastern Europe The United Nations Charter devised at Dunbarton Oaks (1944) & San Francisco (1945) General Assembly – all nations have a vote Security Council – 5 permanent members (US, USSR, Britain, France & China) each have veto power Other members serve limited terms Other arms: UNESCO, UNICEF, WHO, etc. Potsdam Conference (July 17 – Aug. 2, 1945) Clement Attlee, Harry Truman & Josef Stalin at Potsdam, Aug. 1, 1945 (from the Truman Pres. Library & Museum collection) Germany disarmed & industry dismantled Occupiers take reparations out of zones Council of Foreign Ministers to settle Italy, Finland, Hungary, Bulgaria & Romania (treaties in 1947) Nuremberg Trials (Nov. 1945 Oct. 1946) result in execution of top Nazis for “crimes against humanity” Nazis on Trial at Nuremburg Atomic Diplomacy Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s Decision to use A-bombs at end of WWII partly influenced by desire to impress Soviet Union Henry Wallace warned of dangerous arms race leading to nuclear war Truman saw nuclear weapons as effective deterrent to Soviet aggression Soviets tested their own A-bomb in Sept. 1949 U.S. began building H-bomb in 1950 (tested in 1954) Atomic Culture: Bikini The Bomb and Containment Policy MAD = mutually assured destruction George F. Kennan Long Telegram (1946) warned Soviets couldn’t be trusted, but should be met with patient resolve “X Article” (1947) called for containing Soviet expansion & proving superiority of U.S. ideals NSC-68 (1950) codified containment policy By all means short of war, block Soviet expansion, expose lies, induce retraction, & sow “seeds of destruction” within USSR The Beginnings of the Cold War in Europe 1945: Soviets est. puppet regimes in Poland & Romania 1946: Soviets reject Baruch Plan to share atomic secrets Truman blasts Molotov for violating Yalta agreements Churchill gives “Iron Curtain” speech 1947: Communist coup in Hungary U.S. announces Truman Doctrine & Marshall Plan National Security Act: Dept. of Defense unified old War & Navy Dept.s Joint Chiefs of Staff coordinates military plans between the 4 service branches National Security Council: President,Vice President, Sec. of State, Sec. of Defense, CIA & FBI Directors, National Security Advisor Central Intelligence Agency conducts spying & covert operations The Division of Germany 1948: Soviets est. puppet regime in Czechoslovakia Soviets blockade W. Berlin U.S. stages Berlin Airlift (1948-49) British, French & U.S. occupation zones merged into “Trizonia” – becomes West Germany in 1949 Soviets est. puppet regime in East Germany Divided Europe, 1949-1989 Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) = 1st permanent alliance for U.S. Soviets created Warsaw Pact & COMECON to counter NATO & Marshall Plan The Beginnings of the Cold War in Asia Japan occupied & rebuilt solely by U.S. Mao Zedong’s Communists took over China in 1949 Caroline, Marshall & Mariana islands put under U.S. trusteeship Gen. Douglas MacArthur wrote new Japanese constitution Permanent treaty signed in 1951 Mao Zedong Jiang Jieshi’s Kuomintang fled to Taiwan Korea divided at 38th parallel by Yalta agreement UN held elections in South in 1948 North more industrialized, but fewer people Jiang Jieshi The Korean War (1950-1953) Kim Il-Sung got reluctant approval from Stalin Truman got immediate UN action – saw it as 1930s all over again Invasion of North brought Chinese into war Armistice signed July 27, 1953 Cost to the U.S.: Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s British, Canadian, Turkish & other troops, too Est. defensive line around Pusan, then staged Inchon landing War prolonged due to Synghman Rhee’s desire for reunification Mao wanted Soviet aid to take Taiwan 80% of Chinese industry in Manchuria 54,000 dead; 103,000 injured; $69.5 billion 1.5 million Chinese & N. Korean casualties The Home Front Executive Branch Loyalty Program (1947) Soviet Spy Cases: McCarran Internal Security Act (1950) Alger Hiss convicted of perjury (1950) Julius & Ethel Rosenberg convicted of espionage (1951) & executed (1953) Unlawful to contribute to the est. of a totalitarian gov’t “Communist front” org. members had to register; denied travel visas & gov’t jobs Sen. Joseph McCarthy led Senate Permanent Investigation Committee (195354) Copyright 2000, Bedford/St. Martin’s Spies Like Us Alger Hiss Julius & Ethel Rosenberg Postwar Conservatives Classic liberals – feared expansion of government power Many were former Communists disillusioned with Stalin & USSR. Argued that liberal Democrats were either dangerously naïve or else traitors James Burnham argued containment wasn’t enough – too defensive, and not spiritually inspiring Whittaker Chambers said that the transcendent issue was religious – both Communism & secular humanism were atheistic James Burnham Whittaker Chambers