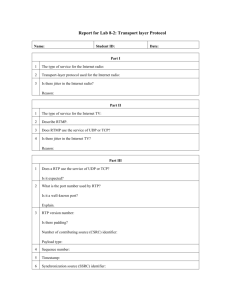
Voice Over IP

Voice Over IP
CS158B Project
By
Shing Chau
Jerry Ko
Ying Li
Agenda
Introduction
Economics of VoIP
VoIP and OSI model comparison
H.323 vs. SIP
RSVP & RTP
Demonstration
Introduction
VoIP
Transmission of voice traffic in packets
Internet as the transmission medium
IP rather than by traditional circuit transmission
-
IP originally for data
-
adaptation to voice network protocols (SIP, H.323, RSVP, RTCP, RTP)
Economics of VoIP
Traditional TDM
Dedicated Circuit switched networks
Dedicated voice-only bandwidth
IP
Uses packet switched networks
Many Services, one network (voice, data)
Leverages existing data infrastructure
Flat monthly rate both long distance and local
Various configurations
VoIP and OSI model Comparison
Session Initiation
Three things takes place in a VoIP session:
Signaling
Encoding
Transmission
Two common protocols used:
H.323 – International Standard
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
H.323
H.323 vs. SIP
Origin
Transport
Emphasis
H.323
ITU
SIP
IETF
Mostly TCP Mostly UDP
Telephony Multimedia
RTP (Real-Time Protocol)
How to send voice over RTP?
Application collects the encoded data in chunks
The audio chunk along with the RTP header form the RTP packet
RTP header contains:
Payload type (7 bits)
Sequence number (16 bits)
Timestamp field (32 bits)
Synchronization source identifier field (32 bits)
RSVP
(Resource Reservation Protocol)
Why a guaranteed QoS is needed?
Voice and Video applications traffic can be transmitted continuously
It requires a guaranteed QoS, in terms of minimum available bandwidth or maximum delay, over the entire path of traffic
How to make the resource reservations?
Path messages contain:
Previous hop address
A session identifier
A sender template (the sender ’ s IP address and port number )
A sender T Spec (maximum data rate, maximum delay, etc)
Reservation messages contain:
Reservation Style
Flow Spec
Filter Spec
Summary
Rsession Initiation
SIP (SNMP): simple
H.323 (CMIP): complex
QoS
RSVP
Voice Transmission
RTP
SIP Call Flow
Invite
100 Trying
180 Ringing
200 OK
ACK
RTP
H.323 Call Flow
TCP connection
H.225 Messages (Setup)
H.225 (CallProceeding, Alerting)
H.225 (Connect)
TCP connection
Terminal Capability Set
MasterSlaveDetermination
OpenLogicalChanel
OpenLogicalChanelAck
RTP stream
RTP stream
RTCP stream
Reference
Voice Over IP by Uyless Black, a guide to Internet voice communications, covers many protocols
Computer Networking -chapter 7 Multimedia
Networking
Course offering
-EE284 Convergent Voice and Data Networks, multimedia in data networks, QoS, Coding,
Signaling, and Inter-working