Wright Presentation - Personal Web Pages
advertisement

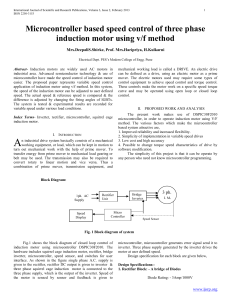
Variable Speed Drive of Single Phase Induction Motor Using Frequency Control Method Mr. Aung Zaw Latt Dr. Ni Ni Win Department of Electrical Power Engineering Technological University (Myitkyina) Myitkyina, Myanmar azlatt@gmail.com Department of Electrical Power Engineering Mandalay Technological university Mandalay, Myanmar Phone: 095-02-88712, Fax: 095-02-88702 Presented by Jason Wright ECGR 6185, Adv. Embedded Systems March 20, 2013 1 Agenda Motivation Induction Machine Operation: Speed Control Traditional Variable Frequency Drives A Simpler Approach for Single Phase Motors Functional Block Diagram Frequency Control H-Bridge Inverter Timing Output Waveforms Performance Conclusion References 2 Motivation: Induction Machine Operation: Speed Control • By far most popular type of motor used by industry • Governed by the following Equation: 3 Motivation: Traditional Variable Frequency Drives • • • • • Costly (VFD > Motor) Complex Can be large More common for three phase motors DC inverters require high switching frequencies and more switching elements • Can have smoother output 4 Simple Inverter Circuit Three Phase Voltage Source Inverter (VSI): 5 Motivation: A Simpler Approach for Single Phase Motors Mr. Latt proposes using an H-bridge and a simple digital (ON or OFF) output signal to simulate AC with a DC source. The output voltage is a modified square wave, but given the motor windings’ inherent low-pass filtering, the current waveform approximates a sinusoid. This approach offers several advantages: 6 Functional Block Diagram Block Diagram for the Speed Control of Single-Phase Induction Motor Using Inverter 7 Frequency Control SG3525A PWM Controller • • • • Built-in oscillator Adjust PWM frequency with a potentiometer or other variable resistance Has two outputs to drive two transistors The two transistors then drive the HBridge Inverter IRF 840 Power MOSFET: 8 H-Bridge Inverter There are 4 valid operative modes: 1. 2. 3. 4. T1-T4 ON: Applies positive voltage (Vs) to the load. T2-T3 ON: Applies negative voltage (-Vs) across the load. T1-T3 ON: Applies zero volts across the load. T2-T4 ON: Applies zero volts across the load. 9 Timing Diagram 10 Waveform Comparison Sinusoidal PWM (SPWM) with carrier signal: Six-Step Drive Waveform: Trapezoidal Waveform from Latt’s Variable Speed Drive: 11 Performance No load: Table of Results: Under Load: 12 Conclusion AC asynchronous motor speed could be controlled by varying the pulse width frequency with a variable resistor. The crude waveform does a decent job at providing a sinusoidal current with the help of the lowpass filtering provided by the motor windings. Using a simple inverter consisting of only 4 power MOSFETs reduced drive cost: Part Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost SG3525A, PWM Chip 1 0.483 0.483 IRF 840, Power MOSFET 4 0.79223 3.16892 GBPC3508-E4/51, 800V rectifier 1 2.84 2.84 PDB12-F4151-104BF, Pot. 1 0.48 0.48 C 124 Transistor 1 0.02124 0.02124 MJE 12002 Transistor 1 0.47 0.47 7812, 12V DC Regulator 1 0.19375 0.19375 OVERALL COST: $7.66 13 References Latt, Aung Zaw, and Ni Ni Win, Ph.D. "Variable Speed Drive of Single Phase Induction Motor Using Frequency Control Method." IEEE Xplore. N.p., 20 Apr. 2009. Web. 10 Mar. 2013. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Induction_motor http://ecee.colorado.edu/copec/book/slides/Ch4slide.pdf http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/SG3525A-D.PDF (datasheet for SG3525A) http://www.digikey.com/ Photos: – – – – – – – Latt, Aung Zaw, and Ni Ni Win, Ph.D. "Variable Speed Drive of Single Phase Induction Motor Using Frequency Control Method." IEEE Xplore. N.p., 20 Apr. 2009. Web. 10 Mar. 2013. http://www.mindconnection.com/library/electrical/motorslip.htm http://ecee.colorado.edu/copec/book/slides/Ch4slide.pdf http://www.iccfl.com/product_info.php?products_id=8191 http://www.onsemi.com/pub_link/Collateral/SG3525A-D.PDF (datasheet for SG3525A) http://www.iccfl.com/product_info.php?products_id=8191 http://www.aliexpress.com/compare/compare-irf840-mosfet.html 14