How to Lead Change
advertisement

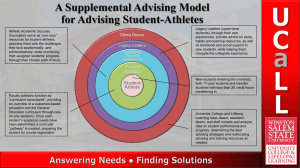
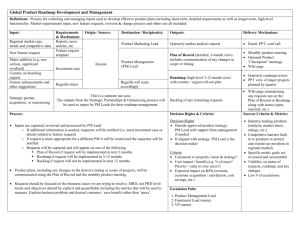
Leading Change THE ROLE OF POLICY IN CHANGE Leading Change – The Role of Policy Drift to Quantitative Compliance- Behavior will focus on whatever is measured in the most precise manner as evaluations not only reflect but influence practice. Incorporate Vision and Change Principles into Outcomes Assessment activities Leading Change – The Role of Policy Administrative support and a reward system are key to implementing practices that promote change. Align personnel and professional evaluation policies (i.e. hiring,tenure,promotion,compensation, teaching load) for faculty and other instructional staff to enhance the student learning experience. Leading Change – The Role of Policy • Professional Societies Recognize science education scholarship at professional meetings and in discipline based journals- Incorporate V&C principles in program certification (ACS, ASBMB) • Funding Agencies Recognize education research needs (released time, funding emphases etc.) in funded initiatives. INCENTIVIZING CHANGE Leading Change: Incentivizing change in institutions. Key Findings 1. Innovation in undergraduate education must be recognized, valued and rewarded at all levels of evaluation and advancement. 2. Innovation requires a clear vision supported by appropriate resources. Key Finding 1: Recognition and reward for evaluation and advancement. RECOMMENDATION Institutions should review and modify their evaluation criteria to reward innovative and transformational teaching practices. ROADMAP 1. Figure out, on a national scale, what it will take to get institutions to take up this issue. 2. Identify at what level and by whom policies are made at one’s institutions regarding evaluation and advancement. 3. Develop new evaluation criteria, reflecting both one's own institutional setting and national trends, that incorporate rewards for innovative and transformational, evidence-based teaching practices. Key Finding 2: A clear vision supported by appropriate resources. RECOMMENDATION: Institutions and funding agencies should develop programs and policies to provide resources such as expertise, money, time, facilities that support innovative and transformational teaching. ROADMAP 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify programmatic aspirations and needs. Develop shared vision and identify champions on campus. Communicate goals clearly. Incentivize pilots/experiments. Be intentional and creative about developing and deploying resources such as time, money, expertise and facilities. ALTERNATIVE PRACTICES Leading Change: Alternative practices for access and retention KEY FINDINGS • Good advising is critical for access and retention of all students • Peer interactions promote community that fosters retention • Interdisciplinary education is critical for student success and core to our liberal education mission Recommendations and Roadmap • Advising should be a far more important part of the student experience – Implement and assess advising systems that use best practices – Leadership must value advising by provide incentives, rewards, resources, and supporting data collection on effectiveness • Provide multiple opportunities for peer interactions to foster community (bridge programs/boot camps, learning communities, peer mentors, etc.) – Leadership must commit to institutionalize programs – Use desire for better student outcomes to motivate resource allocation Recommendations and Roadmap • Explore, study and implement mechanisms that engage students in interdisciplinary thinking – Leadership must overcome barriers to cooperation among departments CREATING MOVEMENTS FOR CHANGE What success looks like. We need everyone with a hand on the elephant to be at the table. Vision & Change Conferences to Promote Student Success • Competitive selection • Institutional team: depth & breadth • Focus on contextual problem • Facilitated – Regional: make plan – National: celebrate start CULTIVATING LEADERSHIP Leading Change: Cultivating Leaders Key Findings 1. Identify 2. Develop and 3. Empower Faculty Talent, Potential, and Experience Importance of identifying potential leaders who are enthusiastic for V&C, showing ability to communicate with broad range of colleagues Leading Change: Cultivating Leaders Key Recommendations 1. Leadership is an expectation embedded in the culture of the Academy 2. Identification, Development, and Empowerment of leaders is a collaborative responsibility. Cultivating Leaders: Roadmap Identify: Graduate Training Hiring Decisions “Stepping up” on committees Develop: Raise awareness Formalize leadership Annual Evaluation Professional Society leadership development Peer Identification Articulate the Expectations …in collaboration with the NSF, AAAS and the HHMI Empower: Explicit “Succession Plan” Faculty Fellow = Explore the Practice Change the language No “Dark Side” Reward leadership