Enzymes
advertisement

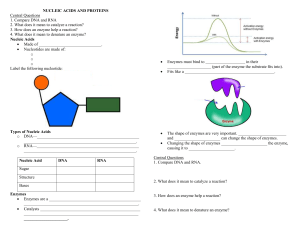
HAPPY TUESDAY BELLWORK: 1. On your Bellwork Sheet write “Complete Lab Procedures”. 2. Get together with your lab group and complete your lab write up. A. Group Names B. Question: How can I decrease the dissolving rate of a lifesaver? C. Hypothesis D. Procedures (Must have 5 steps) DNA & ENZYME NOTECARDS PERIOD 4 & 5 DUE TUESDAY (10/14/14) Protein DNA Nucleotide Nucleic Acid Deoxyribose Nitrogenous Base Hydrogen Bond Adenine Cytosine Guanine Thymine Double Helix Antiparallel Catalyst Substrate Enzyme (“-ase” must be in your definition) Active Site Enzyme-Substrate Complex ESSENTIAL QUESTION: HOW DOES A BIOLOGICAL CATALYST WORK? DESIGN AN EXPERIMENT: HOW CAN YOU DECREASE THE DISSOLVING RATE OF A LIFE SAVER? Due at the end of class: Lab Report including… Name Question: How can I decrease the dissolving rate of a lifesaver? Hypothesis: “If we _________, then the dissolving rate of the lifesaver will decrease.” Procedure: (must include at least 5 steps) Data: (table, graph, etc) Available Materials: Ziploc bags Hammer Water Soda Oil Hot plate (warm up liquids) Cups Stirrers Ice NOTE! Your experiment tomorrow cannot take longer than 15 minutes total. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How long did it take for the original lifesaver to dissolve? How long did it take for the new lifesaver to dissolve? Why do you think there was a difference in time? What is a catalyst? What is an enzyme? How does this lab relate to enzymes and catalyst? ENZYMES… Enzymes are special proteins that work in the body to help speed up reactions Enzymes are biological catalysts. Catalyst: a substance that helps to speed up a chemical reaction but is not used up in the reaction Enzymes can be used over and over again. amylase - in saliva pepsin - in stomach Lactase - breaks down lactose DNA Polymerase I (DNA replication) DNA Polymerase III (DNA replication) RNA Polymerase (mRNA synthesis) Helicase (DNA replication) Ligase (DNA replication) ENZYME FUNCTION Enzymes work best under certain internal conditions. Enzymes help maintain homeostasis in living organisms. Enzymes reduce the activation energy needed in a reaction and speed up the rate at which the reaction is completed. •Enzymes are VERY specific and perform very specialized tasks •Substrates are chemicals that bind to the enzyme and become altered (bonds formed and/or broken), producing a product •Enzymes have specific shapes that match or react with specific substrates (like a lock and key) Draw this in your notes complex