File - Mr. Chan's Science Class
advertisement

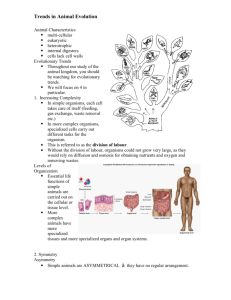
Trends through Animal Kingdom Simple Porifera Cnidaria Fungi Platyhelmithes Algae Nematoda Moss Molluska Ferns Anelida Gymnosperms Arthrpoda Angiosperms Chordata Complex Animal Characteristics Animals can be defined as ___________________________________________________________. There are two main categories: _____________________ and _____________________. Things Every Animal Must Do to Survive It’s good to keep these in mind throughout the animals unit and think about how each animal achieve each of these items Feeding Herbivores eat _____________________________________________________________. ____________________ are organisms that feed on parts of other animals. _____________________ live either inside or attached on the outside of other organisms. Filter feeders _________________________________________________________________. _____________________ feed on decaying plants and animals. Respiration Living cells need to _________________________________ and ___________________________________. Therefore, animals have to breathe. ___________________ can have these gasses diffuse through their skin but larger animals require ________________________________________ to have gas exchange. Internal Transport Small animals may not need specialized transport systems but larger animals need to move nutrients and waste products in and out of the body. ________________________ is usually something larger animals have evolved to solve the problem. Excretion Small aquatic animals can use ___________________ to get rid of harmful metabolism products. Larger animals need a specialized _____________________________ to store and dispose of wastes. Response With more complex evolution, more competition occurs. Complex animals need to ______________________, _________________________, and ________________________________. They develop __________________________ to gather information from the environment. Movement ______________________ animals live their entire lives in one spot. ____________________ animals move around. Reproduction Animals can reproduce sexually and asexually but ___________________________________________. Some __________________________ and some ___________________. Baby animals can either look like miniature versions of adults or ______________________ which have to undergo _______________________________ to change shape dramatically. Review Questions 1. What is an animal? Why is it important to study animals? 2. List the seven essential functions in animals. Define these in your own words. 3. Compare two different kinds of symmetry found in the animal kingdom. Trends in Animal Evolution Levels of Organization Higher animals become more complex in form. In ___________________ animals, functions are carried out on the _________________________ level. In more complex animals, we observe more _______________________________________. Symmetry Simpler animals usually have _______________________ while complex animals have _________________________________. Radial symmetric animal have an imaginary line drawn through the center of their body and ______________________________ repeat around it. They are usually sessile. Bilateral symmetric animals have an imaginary line drawn through the center of the body and one side of the body is the ______________________________ of the other. This creates animals with front ends, back ends, upper and lower sides. __________________ is the front end, ______________________ is the back end, ________________________ is the upper side, and ______________________ is the lower side. Cephalization Complex animals have a concentration of _____________________________ and _______________________________ in their anterior end. The gathering of these things is called cephalization. Nerve cells gather into clusters called _________________. Eventually, they gather in greater numbers to form ___________________. Review Questions 1. Describe the three basic trends in animal evolution. 2. Compare two different kinds of symmetry found in the animal kingdom. 3. Why are specialized cells necessary in multicellular animals?