555 Timer - FCS Wiki
advertisement

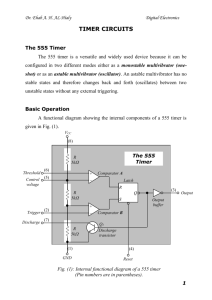
555 Timer ©Paul Godin Updated February 2008 Oscillators ◊ We have looked at simple oscillator designs using an inverter, and had a brief look at crystal oscillators. ◊ In this presentation, we introduce the 555 timer; a versatile device that is easier to calculate, design and configure in a variety of ways. 555.2 A Versatile Device ◊ The 555 Timer is one of the best known IC’s. ◊ The 555 is part of every experimenter's tool kit ◊ Capable of creating a wide variety of circuits, including: ◊ Oscillators with adjustable frequency and Duty Cycle ◊ Monostable Multivibrators ◊ Analog to digital Converters ◊ Frequency Meters ◊ Many other applications…. ◊ The clock on the Vulcan Board is generated by a 555 timer. 555.3 555 Timer Configurations ◊ In this course we will use the 555 timer in 2 modes: ◊ Astable ◊ With some calculations, we can determine the values of the capacitor and the 2 resistors (Ra and Rb) for astable operations. ◊ Monostable ◊ We can determine the value of the resistor and the capacitor with a simple formula for one-shot operations. ◊ There are many other configurations and applications for this device. 555.4 555 Layout Ground Trigger Output Reset Vcc 8 7 6 5 1 2 3 4 Discharge Threshold Control Also available: •556 (two-555’s in one DIP package) •555 in a “metal can” configuration Vcc Ground 1 8 Trigger 2 Output 3 7 Discharge 6 Threshold 4 5 Control Reset 555.5 555.6 Astable Multivibrator Oscillator Configuration ◊ Externally, the 555 requires an RC circuit to create the time delays required for the time high and the time low. ◊ Standard configuration requires ◊ common capacitor ◊ a resistor for the charge cycle ◊ a resistor for the discharge cycle 555.7 General Configuration ◊ Basic connections: ◊ Ground ◊ Vcc ◊ Note: some 555 timers may function at voltages other than 5 volts. ◊ Reset (active low) ◊ Output Ground Trigger Output Reset 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 Vcc Discharge Threshold Control 555.8 General Configuration ◊ Specialized connections: ◊ Trigger ◊ monitors low voltage ◊ Threshold ◊ monitors high voltage ◊ Discharge ◊ path to ground, to discharge the capacitor ◊ Control ◊ specialized input ◊ filtering ◊ special applications Ground Trigger Output Reset 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 Vcc Discharge Threshold Control 555.9 Astable Configuration #1 (“Standard” Configuration) Vcc Vcc Vcc Ground Output Reset Ra 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 Control Discharge Rb Threshold Trigger C 555.10 Astable Calculated Values Note: Duty Cycle must be > 50% Filter Cap 0.01μF 555.11 Astable Configuration #1 (“Standard” Configuration) t1 .693(Ra Rb )C t 2 .693 Rb C f 1 1 t1 t 2 .693(Ra 2Rb )C t1 Ra Rb DC t1 t 2 Ra 2Rb Minimum duty cycle > 50% 555.12 Calculations: Astable Time High, Time Low Set TL 0.693 R B C TH 0.693(R A R B )C TH TL Notes: •The value 0.693 is a factor associated with the charge/discharge cycle of the 555 timer. •Duty Cycle must be > 50% 555.13 Sample Calculation Time High, Time Low Set ◊ Design an oscillator with a frequency of 200Hz with a duty cycle of 78%. 1. Determine Period (T): 1 1 T 0.005 s F 200Hz 2. Determine TH and TL: TH 78 % 0.005 s 0.0039 s 3.9ms TL 22 % 0.005 s 0.0011 s 1.1ms 555.14 Sample Calculation Time High, Time Low Set 3. Since there are 2 variables in the TL equation, select C: C=10μF 4. Determine RB by using the TL equation: TL 0.693R BC 1.1ms 0.693 R B 10F R B 158 .7 555.15 Sample Calculation Time High, Time Low Set 5. Determine the value for RA: TH 0.693(R A R B )C 3.9ms 0.693(R A 158 .7)10F 562 .8 R A 158 .7 R A 404 .1 555.16 Calculations: Astable Frequency, Duty Cycle Set (R A R B ) DC (R A 2R B ) F 1 0.693 (R A 2R B ) C Notes: •The value 0.693 is a factor associated with the charge/discharge cycle of the 555 timer. •Duty Cycle must be > 50% 555.17 Sample Design Frequency, Duty Cycle Set ◊ Build an oscillator using a 555 timer with a frequency of 72kHz at 75% D.C. Use a 100F capacitor. 555.18 Design Solution Frequency, Duty Cycle Set 1- Determine the ratio of the resistors Ra and Rb: Ra Rb 0.75 Ra 2Rb Ra Rb 0.75(Ra 2Rb ) 0.75Ra 1.5Rb Ra 0.75Ra 1.5Rb Rb Ra 2Rb DC 2- Use the ratio in the frequency equation (substitution): f 1.44 1.44 1.44 (Ra 2Rb )C (2Rb 2Rb )C 4RbC 555.19 Design Solution Frequency, Duty Cycle Set 3- Solve for Rb: 72kHz 1.44 1.44 50k 4RbC 4 72k 100 4-Solve for Ra: Ra 2Rb 100k 5-Use standard values (optional step): Ra=100k Rb=47k 555.20 Design Solution Frequency, Duty Cycle Set 6- Calculate actual frequency and DC: 1.44 74 .2kHz (100k (2 47k)) 100 F Error 3.1% (100k 47k) DC 0.757 (100k (2 47k)) Error 1% f 555.21 Design Solution Frequency, Duty Cycle Set 7- Create the circuit diagram using EWB: 555 Timer, 74.2kHz @ 75.7% D.C. 555.22 Minimum Value for Ra ◊ The discharge transistor causes the capacitor to discharge to ground. ◊ Ra must have a minimum value of 25 to prevent a short circuit of the power supply through the discharge transistor. Minimum Value 555.23 In-Class Practice Problem ◊ Design an oscillator with a frequency of 500Hz and a duty cycle of 80%. Use a 10μF Capacitor. Calculate using each of the equation sets. 555.24 OTHER ASTABLE CONFIGURATIONS 555.25 Astable Configuration#2 Rb must be < .5 Ra 555.26 Astable Configuration #3 555.27 555 Timer Operation 555.28 Internal Operation of the 555 Timer ◊ Understanding the internal operation of the 555 timer is important ◊ The device combines various circuit theories. ◊ Various aspects provide a preview of other circuits, such as the Analog to Digital decoders. ◊ Understanding its internal function makes it easier to create new designs with the device. 555.29 Comparator ◊ The comparator is an operational amplifier (opamp) configuration. ◊ The comparator compares 2 analog voltages and provides a digital output. + - If V+ > V-, the output is a digital 1 If V- > V+, the output is a digital 0 555.30 Reference and Comparators A 3-resistor voltage divider provides reference voltages The Comparators provide digital logic to an SR Latch Comparators compare voltage levels. •If “+” is higher, output = 1 •If “-” is higher, output = 0 555.31 Reference and Comparators Pin 8: Vcc connection Pin 6: “Threshold” connection (high Comparator) Pin 5: “Control” connection, used with filter cap. Pin 1: Gnd connection Pin 2: “Trigger” connection (low Comparator) 555.32 Latch and Output The SR Latch holds its output states The Q’ output controls the transistor (“on” or “off”). The reset input can be used to enable or disable the timer. The transistor acts like a switch. The buffer has important electrical functions. 555.33 Latch and Output Pin 7: “Discharge” connection Pin 4: Reset connection (active low reset) Pin 3: Digital Output 555.34 Charge Animation Discharge Animation 555.35 Specification sheet ◊ From the specification sheet for the LM555, determine the following: ◊ Operational voltage range ◊ Maximum current output for each state ◊ Frequency Range ◊ Output rise and fall time What is a disadvantage of the 555 as a timing device? 555.36 Function of the Control Input (Pin5) ◊ Pin 5 is the control voltage connection, and is used to access the 2/3 Vcc point of the voltage divider. ◊ Normally, a 0.01F capacitor is connected to ground to provide output voltage stability. ◊ Used as an input for some applications. ◊ AC to pulse modulation ◊ voltage controlled oscillator 555.37 Design Exercises 555.38 Design Exercises 1. Using a 555 timer, design an oscillator with an output of 6Hz with a duty cycle of 60%. Use a 100μF capacitor. Build in EWB. 2. Using a 555 timer, design an oscillator with an output of 10KHz with a duty cycle of 50%. Use a 3.3μF Capacitor. Build in EWB. 555.39 Animated Slides The following slides contain animations to demonstrate the operations of: 555 as an astable: charge cycle 555 as an astable: discharge cycle 555.40 + <> 01 10 01 - <> + 10 Vc Capacitor Charges viastate Ra and Rb Latch inQ aoutput set Q’ is low; is high Capacitor continues to charge Lower comparator provides logic Upper comparator + input is Latch receives a reset state Q’ is high; Q output is low Transistor is “on” and a connection Capacitor to state. discharge low. Latch in hold greater thanbegins 2/3 Vcc reference to ground is made. Animated charge cycle 555.41 - >< + 01 01 10 + <> - 10 Vc Capacitor is discharging. Q output Upper comparator + voltage less Latch in a hold state. Lower comparator + voltage is Latch is set. Q’ is low. is low. Q output is high. than reference Transistor is “off”. Capacitor greater than – voltage. voltage. begins to charge. Animated discharge cycle 555.42 END ©Paul R. Godin prgodin°@ gmail.com 555.43