OPTI 380B Lab #5 *Op-Amps II, 555, and the Linear Power Supply*
advertisement
OPTI 380B
Lab #5
“Op-Amps II, 555, and the Linear Power Supply”
Dr. Mike Nofziger
Instructor
College of Optical Sciences
University of Arizona
Dr. Mike Nofziger 2010
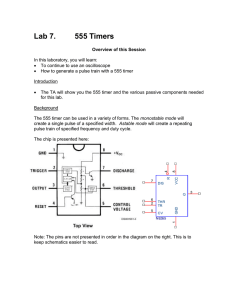
The “555” Timer IC:
• Designed in 1970
• > 1B sold (2003 data), still in wide use
• 8-pin DIP, contains over 20 transistors, 2 diodes, and 15 resistors
• Single voltage power supply (4.5 – 16 V)
• Frequency stability ≈ 1%
• 3 Modes of operation:
- Monostable Mode
- “one shot” pulse generator
- Bistable Mode
- basic flip-flop
- Astable Mode
- oscillator (continuous stream of rectangular pulses, specified frequency)
Dr. Mike Nofziger 2010
The “555” Timer IC:
DIP Layout:
Pin
Name
Purpose
1
GND
Ground, low level (0 V)
2
TRIG
OUT rises, and interval starts, when this input falls
below 1/3 VCC.
3
OUT
This output is driven to +VCC or GND.
4
RESET
A timing interval may be interrupted by driving this
input to GND.
5
CTRL
"Control" access to the internal voltage divider (by
default, 2/3 VCC).
6
THR
The interval ends when the voltage at THR is greater
than at CTRL.
7
DIS
Open collector output; may discharge a capacitor
between intervals.
8
V+, VCC
Positive supply voltage is usually between 3 and 15 V.
Dr. Mike Nofziger 2010
The “555” Timer IC:
• Monostable Mode
- “one shot” pulse generator
- pulse begins with the trigger input < Vcc/3
- pulse width determined by the RC time constant
- pulse ends when the voltage across the capacitor (pins 6&7) = 2/3 Vcc
- t ≈ 1.1RC
Dr. Mike Nofziger 2010
The “555” Timer IC:
• Astable Mode
- oscillator, rectangular pulses
- pulse frequency determined by the RC time constant:
- T = (0.693)(RA + 2RB)C
- Duty Cycle ≡ tH/(tH+tL) = (R1+R2)/(R1+2R2) {≥50%}
= (R1)/(R1+R2) {<50%, with a diode ‘clamp’}
Dr. Mike Nofziger 2010