electricity
advertisement

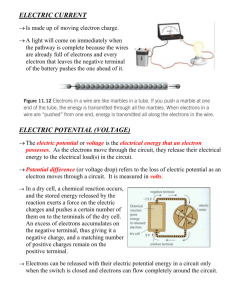
ELECTRICITY Electric Fence Experiment. Can you guess what will happen? What would life be like without electricity? List 4 things that you would miss the most: 1) ______________________________ 2) ______________________________ 3) ______________________________ 4) ______________________________ Atomic Structure Electrons negative Protons positive Neutrons neutral Positive and Negative Charge when objects have excess electrons, they become negatively charged Opposites ATTRACT Objects with the same charge REPEL Static electricity occurs when electrons transfer to your clothes or hair and give them a charge. When you touch something, the charge is released, causing a "jolt" Each hair is negatively charged and repels other hairs. Or balloons stick to the cat Electric fields surround every charge and can act upon other objects (even without touching them) The force created by this field can either attract or repel Conductor - material in which electrons can flow freely Ex. Metals, such as copper Insulator - electrons do not move easily through Ex. plastic, rubber What is Grounding? Buildings often install lightning rods, which provide a path for electrons to take to the earth, bypassing the building and sensitive electronic equipment What Is Electric Current? - movement of electrons in a single direction - measured in amperes (AMPS) This diagram shows a simple LED driver circuit. When the battery is connected the positive end of the battery pulls electrons from the negative end of the battery and through the circuit. This circuit has three basic properties: 1. voltage 2. current 3. resistance Circuit = a closed path that electric current follows This flow of electrons can power things like light bulbs Resistance = tendency for material to oppose the flow of electrons -- electric current loses energy as it flows -- resistance is measured in OHMS * Copper has a low resistance, hence it is used for household wiring and other electronics STOP AND THINK 1. A positively charged subatomic particle is ____ negatively charged subatomic particle is ____ 2. Amperes are used to measure _________ 3. A closed path that electrons (current) can flow through is a: 4. Materials that current can flow through easily are called: 5. OHMS are used to measure the __________ of a circuit. As the length of a wire increases, so does its resistance As the wire becomes thinner, its resistance increases the thin wire in a tungsten light bulb glows due to this resistance Ohm's Law -- the current (I) in a circuit equals the voltage difference (V) divided by resistance (R) Quick Calculations: 1. What is the current (I) of a circuit with a voltage difference of 20 volts and a resistance of 10 ohms. 2. What is the Voltage difference in a circuit with a resistance of 11 ohms, and a current of 2 amperes. Circuits How many electrical devices can you see in this room? Name 2. Circuits have: 1) source of voltage difference (battery or outlet) 2) device that uses the energy (light) 3) conductors (wires) form a closed path to device Series Circuit Example: A string of christmas lights, when one light burns out, no lights will work. Why? Because that burned-out bulb breaks the circuit to all the bulbs. Each bulb along the path shares the voltage, so the bulbs may appear dim. Parallel Circuits Series circuits aren't a good way to wire a house. If you turned off one light, then all the lights would go out. Parallel circuits contain two or more branches Disadvantage: Even when you turn a light off, current continues to flow through the system. This is why you shouldn't stick a fork in an electric socket! Circuit Diagrams = = A switch can break a circuit And turn a device on or off Does it matter where you place the switch? Identify the type of circuit: ______________________ ______________________ What is a fuse? Fuses contain a tiny piece of metal that melts if the current gets too high - this breaks the circuit. Too many appliances on in one room can overload the circuit and blow a fuse. Where does electricity come from? Most electricity comes from converting heat energy into electrical energy - burning fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas. Some electricity is generated from dams, and nuclear reactors How do dams generate electricity? As water flows through the dam it spins turbines, which will create electricity. These are referred to as: HYDROELECTRIC DAMS How are dams built? How do they hold all that water back? What happens when dams fail? Cost of Electricity 1) Most companies charge by the amount of energy used 2) This is measured in kilowatt hours (kWh) 3) Each light bulb in your house costs money to leave on! 4) Meters outside your house measure how much energy is used Check out: http://www.energyeducation.tx.gov/ What is the difference between alternating current and direct current? Check out http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/edison/ sfeature/acdc.htmlhttp://www.pbs.org/w gbh/amex/edison/sfeature/acdc.html AC = alternating current DC = direct current Direct Current is found in simple circuits like a battery powered flashlight. AC current are used to power large grids, like the electricity that comes to your home AC vs DC Current What is the problem with AC current? Why is it used for most household electricity? What is a microgrid? Video: https://youtu.be/g17f9J1-r-k QUIZ TIME: Electricity 1. What happens when an object has an excess number of electrons? a) object is positive b) object is negative 2. Name something that is a conductor: 3. What unit is electric current measured in? 4. What unit is electric energy measured in (think power bill)? 5. The force that causes electrons to flow is the ____________ difference. 6. Is the image showing a parallel or series circuit? 7. Where does the electricity come from that powers your house? 8. What causes a fuse to be blown? 9. _________ Law can be used to calculate voltage. 10. Resistance is the tendency for ____________ to oppose the flow of ____________.