Chemistry Of Life, Water, Macro. TEST Review
advertisement

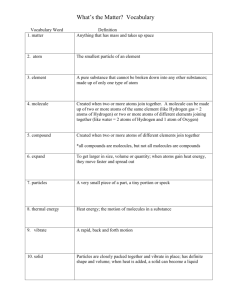
Chemistry of Life, Water, Macromolecule Review In order to prepare for your exam, be able to know what the following terms mean. Drawing pictures/diagrams will help you understand! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. atom - is the simple building block of life. nucleus- is center of an atom. electron- negatively charged particle; located outside the atomic nucleus element- a element is substance consisting entirely of 1 type of atom isotope- Atoms of an element that has a number of Neutrons different from that of the other atoms of the same element 6. compound- substance formed by chemical combination of 2 or more elements in definite 7. ionic bond- a chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron to form a positive ion- and the other atom gains an electron to form a negative ion 8. ion- an atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons 9. covalent bond- the bond formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms 10. molecule- smallest unit of most compounds a slight attraction that develops between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. 11. Van der Waals forces- 12. cohesion- attraction between particles of the same substances 13. adhesion- attraction between two molecules of different substrates 14. pH scale- measurement system to indicate the concentration H ions in a solution 15. acid- a thing that eats away stuff 16. base compound: that produces hydroxide ions in solution 17. monomer-a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer 18. polymer- a substance that has a molecular structure consisting chiefly or entirely of a large number of similar units bonded together, e.g., many synthetic organic materials used as plastics and resins st 19. carbohydrate- compound made up of carbon and hydrogen and oxygen 20. polysaccharide- large molecule made from monosaccharides 21. lipid- macromolecule made mainly from carbon and hydrogen atoms; includes fats,oils, and waxes 22. nucleic acid- macromolecule containing hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, and phosphorus. 23. nucleotides- monomer of nucleic acids made up of five carbon sugar a phosphate and nitrogenous 24. RNA- a molecule that only has one job and that is protein synthesis 25. DNA- building blocks for life Deoxyribonucleic acid 26. protein 27. amino acid - is the building block of proteins. 28. chemical reaction - a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. 29. Reactant- The element and compounds that enter a chemical reactio 30. Product- The elements and compounds that are produced by a chemical reaction 31. Activation Energy- The energy used to start a chemical reaction. 32. Catalyst- Speeds up the chemical reaction. 33. Enzyme- Proteins that act as biological catalysts 34. Substrate- The reaction of an enzyme These are major concepts from our class that you should be able to describe Key Concepts: 1. What three subatomic particles make up atoms? proton, neutron, electron 2. What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Ionic bonds & Covalent bonds 3. What are the bonds involved in water? Between water molecules? Hydrogen Bond 4. Why are water molecules polar? savages because there is a uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. 5. What are acidic solutions?contain higher concentrations of H+ ions than pure water have ph levels above seven 6. What are basic solutions?A solution that has a higher concentration of hydroxide ions that hydrogen ions; a pH between 7 and 14. 7. Draw two water molecules and label the bonds within water and between the molecules. 8. What is the structure and function of carbohydrates? made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 9. What is the structure and function of lipids? chain of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms. 10. What is the structure and function of nucleic acids? Made up of sugar phosphate group and nitrogen molecule. 11. What is the structure and function of proteins? Made up of Carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen and oxygen. 12. What happens to chemical bonds during a chemical reaction? it changes or transforms one set of chemicals to another. 13. How do energy changes affect whether a chemical reaction will occur? 14. Why are enzymes important to living things? they are required for the body to function properly 15. Describe factors that may influence enzyme activity. Temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration and inhabits./