Social_Studies_Review[1][1]
![Social_Studies_Review[1][1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009867160_1-625f26dc0a9feba95527f3406ca3b987-768x994.png)
A Review of
Adapted from: North Carolina Geographic Alliance
PowerPoint Presentations
2007
Where is It?
Why is It There?
Two Types of
Location
•Absolute
•Relative
A specific place on the Earth’s surface
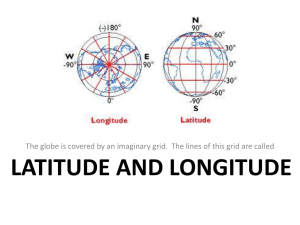
Uses a grid system
Latitude and longitude
A global address
Absolute Location
North Carolina
36° N Latitude
79° W longitude
Chapel Hill
35° 55' N Latitude
79° 05' W Longitude
Where a place is in relation to another place
Uses directional words to describe
Cardinal and intermediate directions
North Carolina is bordered by
Virginia on the north, South Carolina and Georgia on the south, and
Tennessee on the west.
The Atlantic Ocean forms North
Carolina's east coast.
North Carolina is one of the
Southeastern States
Land Features
Mountains, plains, and plateaus
Climate
Bodies of Water
http://www.wetmaap.org/Cape_Hatteras/ch_tm_2.html
Photos above: Steve Pierce
People
Culture
Language
Religion
Buildings and
Landmarks
Cities
How People Interact With Their
Environment
People . . .
Adapt
to Their Environment
Modify
Their Environment
Depend
on Their Environment http://www.fotosearch.com/comp/corbis/DGT119/BAG0017.jpg
The Mobility of
People
Goods
Ideas
How Places are linked to one another and the world
What Places Have in Common
Political Regions
Landform Regions
Agricultural Regions
Cultural Regions
http://www.authorstream.com/Presentation/
Durante-59780-5-Themes-Geog-6th-Grade-
World-Geography-continued-five-Location-
Place-Regions-Region-Mov-of-geo-
Education-ppt-powerpoint/
absolute location
The location of a point on the Earth's surface that can be expressed by a grid reference such as latitude and longitude. altitude
Height of an object in the atmosphere above sea level. atlas
A bound collection of maps. boundary
A line indicating the limit of a country, state, or other political jurisdiction. cartographer
A person who draws or makes maps or charts. continent
One of the large, continuous areas of the Earth into which the land surface is divided.
degree
A unit of angular measure: A circle is divided into 360 degrees, represented by the symbol o . Degrees are used to divide the roughly spherical shape of the Earth for geographic and cartographic purposes. elevation
The height of a point on the Earth's surface above sea level.
Equator
An imaginary circle around the Earth halfway between the
North Pole and the South Pole; the largest circumference of the Earth. globe
A true-to-scale map of the Earth that duplicates its round shape and correctly represents areas, relative size and shape of physical features, distances, and directions.
grid
A pattern of lines on a chart or map, such as those representing latitude and longitude, which helps determine absolute location. hemisphere
Half of the Earth, usually conceived as resulting from the division of the globe into two equal parts, north and south or east and west. international date line
A line of longitude generally 180 degrees east and west of the prime meridian. The date is one day earlier to the east of the line. latitude
Imaginary lines that cross the surface of the Earth parallel to the
Equator, measuring how far north or south of the Equator a place is located.
legend A key to what the symbols or pictures in a map mean.
longitude
Imaginary lines that cross the surface of the Earth, running from north to south, measuring how far east or west of the prime meridian a place is located. map
A picture of a place that is usually drawn to scale on a flat surface. ocean
The salt water surrounding the great land masses, and divided by the land masses into several distinct portions, each of which is called an ocean. prime meridian
An imaginary line running from north to south through Greenwich, England, used as the reference point for longitude. scale
The proportional relationship between a linear measurement on a map and the distance it represents on the Earth's surface. sea level
The ocean surface. topography
The physical features of a place; or the study and depiction of physical features, including terrain relief.
From Human Prehistory to Early Civilizations
Hunting and gathering (H&G) economies dominated until 9000 BCE. H&G groups were small and roles were separated between men and women, but no social inequalities yet existed.
Population growth was slow, partly because fertility rates among women were limited due to longer years of breast-feeding.
During the Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age) which ran up until about 10,000 BCE, humans first learned to use only simple tools of wood and stone.
The development of cave paintings, rituals, goddesses, speech, and languages increased communication and gave way to various cultures.
The human species, homo sapiens sapiens , was thought to have originated in Africa. Gradual migration, facilitated by innovations like fire and clothing, pushed humans out of Africa about
750,000 years ago and to China, Britain, and
Australia.
Most scholars believe that humans crossed the
Bering Strait, the ice bridge from Siberia to
Alaska, about 30,000 years ago.
During the “Middle Stone” Age from 10,000 to 7,000 BCE humans improved their ability to sharpen tools to make better weapons and cutting tools. Mesolithic peoples domesticated animals like cows, which led to increased food supply and population growth. This acceleration in population, though, led to more conflicts and wars.
The “New Stone Age” was a result of better tool use, more elaborate social organization and population pressure. The Neolithic
Revolution saw the development of agriculture, which had its roots in the Middle
East as early as 10,000 BCE.
Farming led to the domestication of more animals and the ability to support more people. Agriculture methods were initially difficult to learn and were often mixed with older and more reliable H&G techniques.
Agriculture spread to almost all geographic areas with more concentrated zones of farming in the Andes, Mesoamerica, West
Africa, the Middle East, India,
North China, and Southeast Asia.
Societies became mostly agricultural, in which most people were farmers and the production of food was the main economic activity.
Farming led to increased curiosities about scientific matters like weather patterns.
The discovery of metal tools dating back to
4000 BCE marks the beginning of this next age of human existence. Copper was the first metal to be used and in the Middle East stone tools were no longer used. Metalworking greatly aided agriculture as farmers were able to work the land more efficiently.
Because farming took less work and time specialization of jobs came about with
“occupations” for artisans, toolmakers, and woodworkers.
The earliest civilizations formed in
Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus River Basin and China. A society can only be called a civilization if it has developed a writing system. Cuneiform was the first type of writing. H&G peoples did not develop civilizations due to lack of stability and not all agricultural societies were civilizations.
Nomads were often considered barbaric for their lack of civilization.
Civilizations often have stronger class divisions and greater separations between the rulers and the ruled. Male superiority was very evident and women were subject to subordinate roles.
Located between the two rivers in an area called Mesopotamia, it was the very first civilization. The Sumerians, who invaded and then inhabited the area around 3500 BCE, developed the first cuneiform alphabet.
Ziggurats, massive towers, were the first architectural monuments. City- states were the primary form of govt., in which slavery did exist.
After the Sumerians the Akkadians and then the Babylonians invaded Mesopotamia. The
Babylonian king, Hammurabi, devised
Hammurabi’s Law Code. After the Babylonians came the Semitic peoples, the Assyrians and then the Persians.
This 2 nd center of civilization, formed around
3000 BCE, was located along the Nile River.
The pharaoh was the king and had a great deal of power. Pyramids served as tombs for pharaohs. The economy was much focused on irrigation along the Nile. Egypt was later invaded by the kingdom of Kush. The
Egyptians made great achievements in mathematics (creating the concept of a 24 hour day) art (hieroglyphics and tomb art) and architecture.
Emerging around 2500 BCE along the river.
This civilization supported the large cities of
Harappa and Mohenjo Daro. The Indus River peoples created their won alpahbet, writing system and artistic forms.
Developed along the Huanghe (Yellow River) in
China, it flourished in considerable isolation.
Their govt. was compromised of a well organized state and they produced advanced technology. Chinese River Valley peoples were the first to devise a ideographic writing system, and made great accomplishments in astronomy, art, and music. Massive structures were not a part of their culture. A line of kings called the Shang ruled around 1500 BCE
(Shang Dynasty).
Be able to describe each of the ages of human existence. (Paleolithic, Mesolithic…)
Compare and contrast the development of two of the four early civilizations.
Be able to describe each of the four civilizations in terms of geographic locations and other relevant terms.
study of government: the study of political organizations and institutions, especially governments
http://www.congressforkids.net/Constitution
_index.htm
Work through all the links on this site!
Beginnings of European Exploration
Leif Eriksson
A Norse seamen, who sailed within sight of continent in the eleventh century.
Ruler Portugal, sponsored voyages aimed at adding territory and gaining control of trading routes to increase the power and wealth of Portugal. He also wanted to spread
Christianity and prevent the further expansion of Islam and Africa.
Pole Star: from the horizon south of the equator, one cannot see the Pole star
Until 1460, captain had no way to determine their position if they sailed too far south.
As the Portuguese began to trade and explore along the coast of Africa, they brought back slaves, ivory, gold, and knowledge of the
African coast. It looked as though the
Portuguese might find a route to the Indian ocean, and it was clear that the voyages sponsored by Prince Henry were benefiting
Portugal in many ways.
Amerigo Vespucci not Columbus. Vespucci took part in several voyages to the New World and wrote a series of descriptions that not only gave
Europeans an image of this “New World”but also spread the idea that the discovered lands were not part of Asia and India.
Vasco da Gama, crossed the Isthmus of Panama and came to another ocean, which separates the
American continents from China.
Discovered at the southern end of South
America a strait that provided access to the ocean west of Americas.
Cortez led a small military expedition against the Aztecs and Mexico. Cortez and his men failed in their first attack on the Aztecs capital city, Tenochtitlan, but were ultimately successful.
Pizarro’s expedition enabled the Spanish to begin to explore and settle South America.
However, the sole purpose of the conquistadors, explorations was defeating the native to gain access to gold, silver, and other wealth.
The first permanent settlement established by the Spanish was predominantly military fort of St. Augustine, located in present-day
Florida. In 1598, Juan de Onate led a group of
500 settlers north from Mexico and established a colony and what is now New
Mexico.
1497 John Cabot discovers Newfoundland while he searches for the Northwest Passage.
1502 Amerigo Vespucci returns from his explorations of the New World. American continents named after him by German mapmaker. 1513 Vasco Nunez de
Balboa discovers the eastern shore of the Pacific
Ocean.
Juan Ponce de Leon searches for the
Fountain of Youth in Florida. 1519 - 1522 Ferdinand
Magellan and his crew sail around the world. 1521
Hernando Cortez defeats the Aztec Empire.
Francisco Pizarro defeats the Inca Empire. 1534
Jacques Cartier discovers the St. Lawrence River and the Great Lakes. 1539 - 1542 Hernando De Soto explores the southeastern United States. 1540
Francisco Vasquez de Coronado explores the southwestern United States and discovers the Grand
Canyon. 1577 Sir Francis Drake becomes the first
Englishman to sail around the world. 1673 Father
Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet explore the
Mississippi River. 1682 Rene-Robert de La Salle explores the Mississippi River from the Great Lakes to the
Gulf of Mexico.
Colonization of Jamestown http://www.preservationvirginia.org/rediscov ery/page.php?page_id=6
Slave Trade http://abolition.nypl.org/home/
Trials held in Salem , Massachusetts , in 1692 that led to the execution of twenty people for allegedly practicing witchcraft . The trials are noted for the hysterical atmosphere in which they were conducted; many townspeople were widely suspected of witchcraft on flimsy evidence.
Religion and the great awakening http://nationalhumanitiescenter.org/tserve/ eighteen/ekeyinfo/grawaken.htm
American Revolution http://www.theamericanrevolution.org/
Sugar Act
Stamp Act
Declaratory Act
Tea Act
Thomas Hutchinson
Boston Tea Party
Coercive Acts
First Continental Congress
Paul Revere
William Dawes
Minutemen
“shot heard ‘round the world”
George Washington
King George III
Declaration of Independence
July 4, 1776
Crossing of the Delaware (Trenton, NJ &Princeton,
NJ)
Treaty of Paris (know terms of the agreement)
The stock market crash happened on Black
Thursday, October 24, 1929.
Almost 13 million shares were traded and prices fell.
Investment banks tried to boost the market by buying.
On Black Tuesday, October 29, 1929, the market fell 40 points.
Herbert Hoover was elected in 1928.
In 1929, Congress passed the Agricultural
Marketing Act, which created the Federal
Farm Fund. The board was to lend $500 million to agricultural cooperatives to buy commodities to sell at higher prices.
The Federal Home Loan Bank Act, passed in
July 1932, created home loan banks. Its purpose was to help avoid foreclosures on homes.
Franklin D. Roosevelt elected in 1932.
Civilian Conservation Corps enrolled 250,000 young men aged 18 to 24 from families on relief to go to camps where they worked on flood control, soil conservation, and forest projects.
The Public Works Administration distributed money to state and local governments for building schools, highways, and hospitals.
The National Industrial Recovery Act was passed in June 1933.
Under this Act, Roosevelt established the
National Recovery Administration (NRA). The goal was the self-regulation of business and the development of fair prices, wages, hours, and working conditions.
Slogan: “We do our part”
The economy improved but did not recover.
The Works Progress Administration (WPA) began in May 1935, and employed people from the relief roles for 30 hours a week for double pay.
Social Security Act was passed in 1935. It established a retirement plan for people over the age of 65. The plan was funded by a tax on wages, paid equally by employees and employers.
The Wagner Act (1935) resulted in growth of union membership, but sparked conflict within the labor movement.
In November 1935, John L. Lewis formed the
Committee for Industrial Organization (CIO) to unionize basic industries, presumably within the
American Federation of Labor (AFL) formed in
1886.
The CIO was ordered to disband in 1936. Rebels refused and were expelled. This caused labor strikes which marked the end of the 1930s.
Roosevelt officially proclaimed neutrality of the
United States on September 5, 1939.
At 7:55 a.m. on Sunday, December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the American fleet in Pearl Harbor. This was declared as “a date which will live in infamy”.
On December 8, 1941, Congress declared war on
Japan.
On December 11, 1941, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States.
On January 1, 1942, representatives of 26 nations came together to sign the Declaration of the United
Nations which promised not to make a separate peace with their common enemies.
Roosevelt died on April 12, 1945, and Vice
President Harry S. Truman took office.
On July 16, 1945, the Manhattan Project exploded the first atomic bomb at Alamogordo,
New Mexico.
On August 6, 1945, the U.S. dropped to atomic bomb, Enola Gay on Hiroshima, Japan.
On August 9 th the U.S. dropped a second bomb on Nagasaki, Japan.
Japan surrender on August 14, 1945.
To aid in The Cold War, President Truman asked
Congress for $400 million in military and economic aid for Greece and Turkey. In his
Truman Doctrine, he argued that the U.S. must support free peoples who were resisting
Communist domination.
On July 25, 1950 North Korea invaded South
Korea. President Truman committed U.S. forces to the United Nations military effort. General
Douglas MacArthur would command the troops.
Dwight D. Eisenhower was elected president in 1952.
January 1959, Fidel Castro overthrew the dictator of Cuba. Castro criticized the U.S. and aligned Cuba closely with the Soviet
Union. The U.S. broke off diplomatic relations in January 1961.
In 1958, Congress established the National
Aeronautics and Space Administration
(NASA) to coordinate research and development.
This was to ensure that the U.S. would not fall behind technologically.
• Democratic Senator John F. Kennedy (1917 –
1963) – won the presidential election of 1960.
•
•
Robert F. Kenney – pushed for civil rights, including desegregation of interstate transportation in the South, integration of schools, and supervision of elections.
President Kennedy presented a comprehensive civil rights bill to Congress in 1963.
•
•
200,000 people marched and demonstrated on behalf of the bill which was held up in Congress.
Martin Luther King Jr., gave his “I Have a Dream” speech.
• Attacking Big Government- Republican
Ronald Reagan (1911-2004) defeated Carter by a large electoral majority in 1980. Reagan placed priority on cutting taxes. He based his approach on supply-side economics, the idea that if government left more money in the hands of people, they would invest rather than spend the excess on consumer goods.
•
•
•
Central Intelligence Agency – Began training some
2,000 men to invade Cuba and to overthrow Fidel
Castro.
Bay of Pigs – On April 19, 1961, this force invaded at the Bay of Pigs; opposing forces pinned them down, demanded their surrender, and captured some 1,200 men.
Nikita Khrushchev (1894 – 1971) – called on by
Kennedy to dismantle the missile bases and remove all weapons capable of attacking the
United States from Cuba.
•
•
• Lee Harvey Oswald – On November 22, 1963,
Oswald assassinated President Kennedy in
Dallas, TX.
Jack Ruby killed Oswald two days later.
Lyndon B. Johnson (1908 – 1973) – succeeded
John Kennedy as President of the United
States.
•
•
•
•
The Civil Rights Act of 1964
Outlawed racial discrimination by employers and unions
Created the Equal Employment Opportunity
Commission (EEOC) to enforce the law
Eliminated the remaining restrictions on black voting
•
•
•
•
In 1965, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. announced a voter registration drive.
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 authorized the attorney general to appoint officials to register voters.
In 1966, New York and Chicago experienced riots and in 1967 Newark and Detroit experienced riots.
The Kerner Commission investigated the riots and concluded that the riots were due to a
•
•
•
•
The Kerner Commission…s ocial system that prevented African Americans from getting good jobs and crowded them into ghettos.
On April 4, 1968, James Earl Ray assassinated
Martin Luther King Jr. in Memphis, TN.
Ray was an escaped convict and plead guilty to the murder.
He was sentenced to 99 years in Prison
More than 100 cities experienced riots after his sentencing.
• Ngo Dinh Diem – The United States sent military advisors to South Vietnam to aid
Diem government after the defeat of the
French in Vietnam in 1954.
•
•
•
Republican Richard M. Nixon (1913 – 1994) – defeated Democratic nominee Hubert
Humphrey by a margin of 1% point by emphasizing stability and order.
Conservative Warren E. Burger – appointed by
Nixon in 1969 as chief justice.
Henry Kissinger , president’s national security advisor, announced that “peace was at hand” a few days before 1972.
•
•
•
•
Senator George McGovern – Democratic nominee who lost to Nixon by a landslide.
Gerald Ford (1913 – 2006) – became president after Nixon.
Carter’s Moderate Liberalism – In 1976, the
Democrats nominated James Earl Carter (1924 - ), governor of Georgia, who narrowly defeated Ford in the election.
Ran on the basis of his integrity and lack of
Washington connections.
•
•
• Offered amnesty to Americans who had fled the draft and gone to other countries during the Vietnam War.
Carter’s Foreign Policy – Carter negotiated a treaty with Panama, that provided for the transfer or ownership of the canal to Panama in 1999 and guaranteed its neutrality.
The Iranian Crisis – In 1978, a revolution forced the shah of Iran to flee the country and replaced him with a religious leader, Ayatollah Ruhollah
Khomeini (ca. 1900 – 1989).
•
•
Iran Contra- In 1985 and 1986, several Reagan officials sold arms to the Iranians in hopes of encouraging them to use their influence in obtaining the release of American hostages being held in Lebanon.
The Election of 1988- Vice President George
H.W. Bush (1924-) won the Republican nomination. Bush defeated Democrat Michael
Dukakis, but the Republicans were unable to make any inroads in Congress.
•
•
Operation Just Causes- Manuel Noriega provided an important link in the drug traffic between South American and the United
States. After economic sanctions, diplomatic efforts, and an October 1989 coup failed to out
Noriega, Bush ordered 12,000 troops into
Panama on December 20 for what became known as Operation Just Cause.
Persian Gulf Crisis- On August, Iraq invaded
Kuwait.
•
•
An act that Bush denounced as “naked aggression.” The United States quickly banned most trade with Iraq, froze Iraq’s and Kuwait’s assets in the United States, and sent aircraft carriers to the Persian Gulf.
On February 23, the allied air assault begin. Four days later, Bush announced the liberation of
Kuwait and ordered offensive operations to cease.
The UN established the terms for the ceasefire, which Iraq accepted on April 6 th .
•
•
•
In 1999, the Serbian government attacked ethnic Albanians in Kosovo, a province of
Serbia.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), led by the United States, responded by bombing Serbia.
Serbia forces withdrew from Kosovo after several weeks of bombing.
•
•
•
The election polls were close and few ventured to predict the outcome.
Clinton’s Vice President, Al Gore (1948 - ) won the popular vote but the electoral college was very close. Florida (the state governed by George W.
Bush’s brother) was pivotal in deciding the election.
George W. Bush (1946 - ), son of former President
George H. W. Bush, appeared to win Florida by a very small margin forcing a recount.
•
•
The Election of 1992- William Jefferson Clinton
(1946-) won 43 percent of the popular vote and 370 electoral votes, while President Bush won 37 percent of the popular vote and 168 electoral votes.
Domestic Affairs. The North American Free Trade
Agreement (NAFTA), negotiated by Bush administration, eliminated most tariffs and other trade barriers among the United States, Canada, and
Mexico. Passed by Congress and signed by Clinton in 1993, NAFTA became law in January 1994.
•
•
Impeachment and Acquittal.- Clinton received criticism for alleged wrongdoing in connection with a real estate development called Whitewater.
While governor of Arkansas, Clinton had invested in Whitewater, along with James B. and Susan
McDougal, owners of a failed savings and loan institution.
After Congress renewed the independent counsel law, a three judge panel appointed Kenneth W.
Starr to the new role of independent prosecutor.
• The Starr Investigation yielded massive findings in the late 1998, roughly midway into
Clinton’s second term, including information on an adulterous affair that Clinton had had with Monica Lewinsky while she was an intern in the White House. The Senate acquitted him of all charges in February 1999.
•
•
• The morning of September 11, 2001, hijackers deliberately crashed two US commercial jetliners into the World Trade Center in New
York City.
The 110-story twin tower toppled.
Another plane crashed into the Pentagon just outside Washington, D.C.
•
•
•
Passengers on another hijacked airplane took over the plan crashing it in Pennsylvania.
Some 2,750 people died in the destruction of the World Trade Center, 184 people died at the
Pentagon, and 40 died in the Pennsylvania crash.
Bush cast prime suspicion on the Saudi exile
Osama bin Laden.
Check out US Presidents http://www.whitehouse.gov/about/presidents
To
http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp
?id=3750579
Kids Economic Terms