An Intro to the MOLE
advertisement

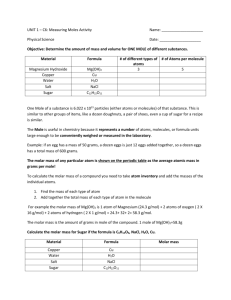
Introduction to the MOLE The chemist’s quantitative system for keeping track of representative particles What is a MOLE? • A mole is _____________ items. • Specifically, a mole is defined as the number of __________ present in _____ grams of ____________________. • And there are ______________________ atoms in _____ grams of _________________. Ranking Moles • List the following substances in order of increasing mass of one mole of the substance. In other words put a 1 under the substance with the smallest mass for one mole and an 8 under the substance which would have the greatest mass for one mole. Carbon Table Salt Baking Soda Water Sucrose Aluminum Hydrogen Gas Copper Metal Just How Big is a MOLE? • Just How Big is a Mole? • * If we were able to count atoms at the rate of 10 million per second, it would take about ______________________ to count the atoms in one mole. • * One mole of soft drink cans is enough to cover the surface of the earth to a depth of over _____________________. • * If you had a mole of unpopped popcorn kernels, and spread them across the United States of America, the country would be covered in popcorn to a depth of over ___________________. • * If you were given a mole of pennies and required to spend 1 million $ per second for your entire life at age 100 you would have __________________% of your money left. • * A mole of basketballs would create a new ______________ the size of the _________________. Carbon-12 and Hydrogen-1 Carbon-12 = 12.0 amu So one atom of Carbon-12 has the same mass as 12 atoms of Hydrogen1. Or you could say that one atom of Carbon-12 is 12 times the mass of one atom of Hydrogen-1 Hydrogen-1 = 1.0 amu Carbon-12 and Hydrogen-1 Continued So that must mean that 1 ______________ atoms of _____________ is ______ times the mass of 1_____________ atoms of ______________. So that must mean that _________________ atoms of _____________ is ______ times the mass of _______________ atoms of ______________. So that must mean that 1 ______________ atoms of _____________ is ______ times the mass of 1_____________ atoms of ______________. THE LOGIC OF IT ALL • One Mole of atoms of Carbon-12 has a mass of _______ grams!! • Therefore one mole of atoms of Hydrogen-1 has a mass of _______ gram!! • The LOGIC: • The mass of one mole of any element is simply the atomic mass of that element expressed in ______________ (instead of _______) The Mass of One Mole • The mass of one mole of sulfur atoms is____ grams. • The mass of one mole of helium atoms is____ grams. • The mass of one mole of gold atoms is ____ grams. • The mass of one mole of water molecules is _______ grams. MOLAR MASS • Definition of Molar Mass – The mass of _______ mole of any substance. Or – The mass of an ______________________ of particles of any substance. Now let’s go back to slide #3 and check how you did! MOLAR MASS continued • How do you calculate molar mass? – For Elements – The molar mass is simply the ___________ mass from the __________________ expressed in _________. – For Compounds – The molar mass is simply the sum of all the molar masses of the elements in the compound -- Add ‘em up!! Representative Particles Reminder • What is the representative particle for each of the following types of substances? – ELEMENT – MOLECULAR (COVALENT) COMPOUND – IONIC COMPOUND