Myoclonus - UMMS Wiki

MYOCLONUS
PRESENTED BY MATTHEW EBRIGHT PGY-2
MYOCLONUS - OUTLINE
Definition
Pathophysiology
Classification
Etiologies
Specific Examples
Evaluation
Treatment
Videos
DEFINE MYOCLONUS
What is it?
• Rapid
• Brief
• Involuntary
• Contraction
• One or multiple muscles, around a joint
• Symmetry?
• Synchrony?
Differential Diagnosis?
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Not entirely clear!
• Reduced intracortical inhibition
• Hyper-excitable sensorimotor cortex
• Cerebellar degeneration
• Striatal lesions
HOW TO CLASSIFY
MYOCLONUS
1.
Anatomic localization
2.
Time course
3.
Triggers
4.
Other general clinical features
HOW TO CLASSIFY
MYOCLONUS
1.
Anatomic localization
2.
Time course
3.
Triggers
4.
Other general clinical features
LOCALIZATION
Is it…
• Focal
• Segmental
• Multi-focal
• Diffuse/generalized
LOCALIZATION
Cortical
• Diffuse vs focal
• Sensorimotor cortex
Subcortical
• Cortical-subcortical and subcortical-nonsegmental
Segmental
• Brainstem
• Spine
HOW TO CLASSIFY
MYOCLONUS
1.
Anatomic localization
2.
Time course
3.
Triggers
4.
Other general clinical features
TIME COURSE
Non-progressive
• Spinal, benign rolandic epilepsy, JME, post-hypoxic, iatrogenic, metabolic
Progressive
• Neurodegenerative, epilepsia partialis continua
Rapid onset or progression
• CJD, SSPE, post-infectious, anti-NMDA, metabolic, psychogenic
HOW TO CLASSIFY
MYOCLONUS
1.
Anatomic localization
2.
Time course
3.
Triggers
4.
Other general clinical features
TRIGGERS
1.
Spontaneous
2.
Action-induced
3.
Sensory-induced
HOW TO CLASSIFY
MYOCLONUS
1.
Anatomic localization
2.
Time course
3.
Triggers
4.
Other general clinical features
CLINICAL GROUPING
Primary Secondary
PRIMARY MYOCLONUS
• Physiologic
• Essential/hereditary
• Myoclonus-dystonia syndrome
• Hyperekplexia
• Epileptic
• EPC, benign rolandic epilepsy, juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, familial cortical tremor with epilepsy
• Primary progressive myoclonus of aging
SECONDARY MYOCLONUS
• Progressive myoclonic encephalopathies and storage diseases
•
Lafora body
• MERRF
• Lipofuscinosis
•
Unverricht disease
• Ramsay Hunt
• Krabbe
• Tay Sachs
• Sandhoff
•
Sialidosis (cherry-red spot myoclonus)
• Gaucher type III
• Dentatorubrual-pallidoluysian atrophy
SECONDARY MYOCLONUS
• Neurodegenerative diseases
• Alzheimer dementia
• Parkinson disease
• Dementia with Lewy bodies
• Corticobasal degeneration
• Multiple system atrophy
• Frontotemporal dementia
SECONDARY MYOCLONUS
• Infectious/Inflammatory
• Encephalitis (NMDA encephalitis)
• Post-infectious
• SSPE
• Opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome
SECONDARY MYOCLONUS
• Metabolic
• Liver, renal, dialysis, sodium, glucose, Celiac, Whipples
• Drugs/Toxins
• Anti-convulsants, anti-psychotics, anesthetics, morphine, levodopa, contrast, heavy metals
• Nervous System Damage
• Post-hypoxic, traumatic, stroke, spinal cord lesions, demyelinating disease
• Psychogenic
SPECIFIC EXAMPLES
• Myoclonus-dystonia
• Syndrome of essential myoclonus
• Action-induced multifocal myoclonus
• Cervical dystonia or writer’s cramp
• Autosomal dominant
• Alcohol-responsive
SPECIFIC EXAMPLES
• Post-Hypoxic Myoclonus (Lance-Adams Syndrome)
• Subcortical, multifocal
• Action-induced, exquisitely
• Days to weeks after recovery
SPECIFIC EXAMPLES
• Neurodegenerative Diseases
• PD – levodopa, amantadine, severe late disease
• Corticobasal degeneration – action induced and stimulus sensitive
• MSA – low-amplitude, irregular, arrhythmic, hands and fingers, face
• LBD
• CJD – aggressive, progressively multifocal
SPECIFIC EXAMPLES
• Opsoclonus-myoclonus ataxia syndrome
• Chaotic myoclonic eye movements
• Oscillopsia
• Multifocal, action-related myoclonus
• Paraneoplastic or post-infectious
SPECIFIC EXAMPLES
• Hyperekplexia
• Autosomal dominant
• Stiff babies
• Episodic tonic spasms
• Nocturnal myoclonus
• Exaggerated startle responses
• Brainstem localization
• Non-habituating
• Overly-sensitive to stimuli
• May persist through life
SPECIFIC EXAMPLES
• Canine myoclonus
• Distemper - RNA virus
• Multi-system disease
• Encephalomyelitis
• Myoclonus, seizures, rapid neurodegeneration
EVALUATION
• Localize!
• Labs, CSF?
• Imaging
• EMG
• EEG-EMG
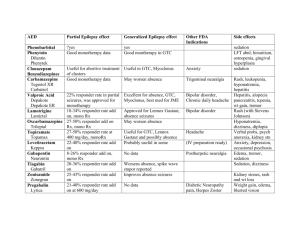
TREATMENT
EXAMPLE VIDEOS
Opsoclonus-Myoclonus https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zX4j0IsFbAk
Propriospinal Myoclonus https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W15D8N0wlyY
Generalized Myoclonus in SSPE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pfCQP7IL2XY
Myoclonic Dystonia http://wolterskluwer.http.internapcdn.net/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/MP4s/ permalink/cont/a/cont_19_5_2013_08_08_zadikoff_190510_sdc3.mp4
Post-hypoxic Myoclonus (Lance-Adams) http://wolterskluwer.http.internapcdn.net/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/MP4s/ permalink/cont/a/cont_19_5_2013_08_08_espay_190510_sdc4.mp4
Amantadine-induced http://wolterskluwer.http.internapcdn.net/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/MP4s/ permalink/cont/a/cont_19_5_2013_08_08_espay_190510_sdc6.mp4
and http://wolterskluwer.http.internapcdn.net/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/MP4s/ permalink/cont/a/cont_19_5_2013_08_08_espay_190510_sdc7.mp4
VIDEOS
Corticobasal Degeneration http://wolterskluwer.http.internapcdn.net/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/MP4 s/permalink/cont/a/cont_19_5_2013_08_08_duker_190510_sdc11.mp4
Unverricht-Lundborg http://wolterskluwer.http.internapcdn.net/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/MP4 s/permalink/cont/a/cont_19_5_2013_08_08_morgante_190510_sdc12.mp4
Hyperekplexia http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-2767882/The-fathers-literally-scared-STIFF-time-s-startled-sudden-noise-taken-surprise.html
Focal Cortical Myoclonus https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHeCok19jWo
Palatal Myoclonus – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GlnxI93PrMM
Canine Myoclonus – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MHQhoH5gYWo
IN SUMMARY
Myoclonus:
History
Exam
Localize
Time course
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treat
Neurology all in one special!